Cardiac Pharmacology
... – Results in a rush of sodium ions intracellularly and in very rapid depolarization • Slow channel selectively permeable to calcium and to a lesser extent to sodium ...
... – Results in a rush of sodium ions intracellularly and in very rapid depolarization • Slow channel selectively permeable to calcium and to a lesser extent to sodium ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... different sleep stages. The functions of these activity patterns are not fully understood, but they might contribute to memory consolidation. Indeed, different types of memory appear to be consolidated during different sleep stages. Evidence suggests, for example, that slow-wave sleep (SWS) is parti ...
... different sleep stages. The functions of these activity patterns are not fully understood, but they might contribute to memory consolidation. Indeed, different types of memory appear to be consolidated during different sleep stages. Evidence suggests, for example, that slow-wave sleep (SWS) is parti ...
Quiz Answers
... cell from depolarizing and block the cell from generating an action potential. Since the action potential is the signal that neurons use in cell-to-cell communication, the ability of a neuron to communicate would be inhibited. 14. Now that you have addressed some of the basic biology of this case, e ...
... cell from depolarizing and block the cell from generating an action potential. Since the action potential is the signal that neurons use in cell-to-cell communication, the ability of a neuron to communicate would be inhibited. 14. Now that you have addressed some of the basic biology of this case, e ...
Neurons and Glial Cells
... neurons, continues into adulthood. Neurogenesis was rst discovered in songbirds that produce new neurons while learning songs. For mammals, new neurons also play an important role in learning: about 1000 new neurons develop in the hippocampus (a brain structure involved in learning and memory) each ...
... neurons, continues into adulthood. Neurogenesis was rst discovered in songbirds that produce new neurons while learning songs. For mammals, new neurons also play an important role in learning: about 1000 new neurons develop in the hippocampus (a brain structure involved in learning and memory) each ...
Neurons eat glutamate to stay alive
... too much of it causes toxicity by overactivating postsynaptic receptors. When postsynaptic receptors are activated, the postsynaptic cytoplasmic calcium concentration rises, activating proteases, lipases, and endonucleases, causing cellular damage and cell death. Given the broad implications of this ...
... too much of it causes toxicity by overactivating postsynaptic receptors. When postsynaptic receptors are activated, the postsynaptic cytoplasmic calcium concentration rises, activating proteases, lipases, and endonucleases, causing cellular damage and cell death. Given the broad implications of this ...
Fast Rhythmic Bursting Cells: The Horizontal
... Quantifications from the NeuroExploper software indicated that RS3 has the largest total volume while the FRB cell has the largest total surface area and dendritic length (Fig 5A). All 5 cells displayed similar cell body length with the FRB cell having the longest. the interneuron has the biggest ce ...
... Quantifications from the NeuroExploper software indicated that RS3 has the largest total volume while the FRB cell has the largest total surface area and dendritic length (Fig 5A). All 5 cells displayed similar cell body length with the FRB cell having the longest. the interneuron has the biggest ce ...
Anatomy Nervous System Learning Objectives
... o Describe the structure and function of the limbic system and reticular formation o Briefly explain how an EEG is produced and its uses o Differentiate between lower motor neurons and higher motor neurons o Describe the neural pathways involved in the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts o Compare t ...
... o Describe the structure and function of the limbic system and reticular formation o Briefly explain how an EEG is produced and its uses o Differentiate between lower motor neurons and higher motor neurons o Describe the neural pathways involved in the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts o Compare t ...
34. Organ of balance and hearing
... Otoliths are located within the matrix of the macula Changing head position produces a change of pressure on the otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and ...
... Otoliths are located within the matrix of the macula Changing head position produces a change of pressure on the otolith-weighted matrix, stimulating the hair cells that stimulate the receptors of the vestibular nerve Vestibular nerve fibers conduct impulses to the brain and sense head position and ...
The Role of Selective Transport in Neuronal Protein
... targeting of all polarized neuronal proteins. NgCAM is concentrated in the axonal plasma membrane despite its abundant transport into dendrites. Thus, our results demonstrate that at least two distinct mechanisms underlie the selective targeting of polarized proteins in nerve cells: one mechanism, f ...
... targeting of all polarized neuronal proteins. NgCAM is concentrated in the axonal plasma membrane despite its abundant transport into dendrites. Thus, our results demonstrate that at least two distinct mechanisms underlie the selective targeting of polarized proteins in nerve cells: one mechanism, f ...
P-GAP-43 Is Enriched in Horizontal Cell
... thickness were cut with a freezing microtome. For immunostaining with 2G12 or 7B10, sections or cultures were incubated 30 min in 0.01% digitonin (Gasser and Laemmli 1987), followed by overnight incubation at 4 °C in 2G12 (hybridoma supernatant) (Meiri and others 1991; Brittis and others 1995) or 7B ...
... thickness were cut with a freezing microtome. For immunostaining with 2G12 or 7B10, sections or cultures were incubated 30 min in 0.01% digitonin (Gasser and Laemmli 1987), followed by overnight incubation at 4 °C in 2G12 (hybridoma supernatant) (Meiri and others 1991; Brittis and others 1995) or 7B ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... Neurons have specialised functions and vary in shape and size depending on where they are located and on their specific function. Some neurons specialise in transmitting (sending) information from sensory receptors, sensory organs, tendons or muscles to the CNS. Other neurons specialise in sending i ...
... Neurons have specialised functions and vary in shape and size depending on where they are located and on their specific function. Some neurons specialise in transmitting (sending) information from sensory receptors, sensory organs, tendons or muscles to the CNS. Other neurons specialise in sending i ...
Information processes in neurons
... be later called the neuronal doctrine, Cajal proposed unidirectional transmission of nerve impulses from dendrites through soma to axon and called it the law of dynamic polarization. In the same way as Cajal postulated the neuron as a basic anatomical unit, McCulloch and Pitts postulated the neuron ...
... be later called the neuronal doctrine, Cajal proposed unidirectional transmission of nerve impulses from dendrites through soma to axon and called it the law of dynamic polarization. In the same way as Cajal postulated the neuron as a basic anatomical unit, McCulloch and Pitts postulated the neuron ...
Optogenetics Review1 - Department Of Biological Sciences
... has high temporal resolution, the electrical field is generally non-uniform and many untargeted neurons are stimulated simultaneously. It is thus difficult to identify which neurons are stimulated. On the other hand, a single, identified neuron can be selectively stimulated with an intracellular or ...
... has high temporal resolution, the electrical field is generally non-uniform and many untargeted neurons are stimulated simultaneously. It is thus difficult to identify which neurons are stimulated. On the other hand, a single, identified neuron can be selectively stimulated with an intracellular or ...
FINE STRUCTURE OF NERVE FIBERS AND GROWTH CONES OF
... portion a p p e a r e d similar. Parts of area c (Fig. 4) were seen in four sections. This spread-out region resembled t h a t in a in t h a t in the most distal portion (c') a n d in the filopodia, only vacuoles a n d the dense m a t r i x were seen; m i d w a y (d) these were found along with long ...
... portion a p p e a r e d similar. Parts of area c (Fig. 4) were seen in four sections. This spread-out region resembled t h a t in a in t h a t in the most distal portion (c') a n d in the filopodia, only vacuoles a n d the dense m a t r i x were seen; m i d w a y (d) these were found along with long ...
Structure and Function of Neurons - Assets
... locations within the neuron’s specialized structure; therefore some functions occur in one part of the neuron but not another. For example, all the nuclear DNA is transcribed in the soma but all protein synthesis does not occur there, because the synthetic machinery of polysomes and endoplasmic reti ...
... locations within the neuron’s specialized structure; therefore some functions occur in one part of the neuron but not another. For example, all the nuclear DNA is transcribed in the soma but all protein synthesis does not occur there, because the synthetic machinery of polysomes and endoplasmic reti ...
Bio 103 Nervous System
... Sodium-Potassium exchange pump - exchange of 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ [ moves 3 Na+ out of the cell; moves 2 K+ into the cell; uses ATP as energy source to move these ions] - used to maintain the resting potential (______) ...
... Sodium-Potassium exchange pump - exchange of 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ [ moves 3 Na+ out of the cell; moves 2 K+ into the cell; uses ATP as energy source to move these ions] - used to maintain the resting potential (______) ...
– Necrosis Brain, Neuron 1
... Figure Legend: Figure 1 Neuronal necrosis in a male F344 rat from an acute inhalation study. The black arrow identifies acute eosinophilic necrosis. By contrast, the red arrow identifies a relatively normal neuron, and the arrowhead identifies a pyknotic nucleus amid associated vacuolation of the ne ...
... Figure Legend: Figure 1 Neuronal necrosis in a male F344 rat from an acute inhalation study. The black arrow identifies acute eosinophilic necrosis. By contrast, the red arrow identifies a relatively normal neuron, and the arrowhead identifies a pyknotic nucleus amid associated vacuolation of the ne ...
1) - Blackwell Publishing
... However, losses of cortical regions have relatively less debilitating consequences than loss of the same amount of subcortical regions. Remember, the subcortical regions control most of our autonomic functions, like breathing and heart rate. 35) Answer: (c). Brain studies have been conducted using e ...
... However, losses of cortical regions have relatively less debilitating consequences than loss of the same amount of subcortical regions. Remember, the subcortical regions control most of our autonomic functions, like breathing and heart rate. 35) Answer: (c). Brain studies have been conducted using e ...
pdf 2.5M
... serve, and which of those might be relevant for biologically inspired computational devices. In this vein, actual computational models were proposed [6–10]. These particular models adopt a continuous-time setting and feature nonlinear network properties. The investigation of the neurons’ dynamics is ...
... serve, and which of those might be relevant for biologically inspired computational devices. In this vein, actual computational models were proposed [6–10]. These particular models adopt a continuous-time setting and feature nonlinear network properties. The investigation of the neurons’ dynamics is ...
Slide 1
... neurons shifts the function to the right toward higher tone burst levels (arrow). This shift adjusts the dynamic range of the fiber so that it can signal changes in tone burst level for higher sound levels; this is likely to be an important function of OC neurons. (B) Level function from the same fi ...
... neurons shifts the function to the right toward higher tone burst levels (arrow). This shift adjusts the dynamic range of the fiber so that it can signal changes in tone burst level for higher sound levels; this is likely to be an important function of OC neurons. (B) Level function from the same fi ...
Radial migration: Retinal neurons hold on for the ride
... now know a lot more about the roles of the apical and basal processes, and the significance of their attachment, in promoting movement. This work also demonstrates that radial migration is a robust phenomenon that cells can accomplish in multiple ways, likely because of the severe consequences for t ...
... now know a lot more about the roles of the apical and basal processes, and the significance of their attachment, in promoting movement. This work also demonstrates that radial migration is a robust phenomenon that cells can accomplish in multiple ways, likely because of the severe consequences for t ...
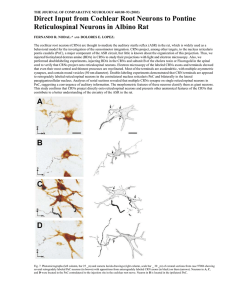
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... FERNANDO R. NODAL1* AND DOLORES E. LOPEZ2 The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticula ...
... FERNANDO R. NODAL1* AND DOLORES E. LOPEZ2 The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticula ...
CHAPTER 2 THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
... -70 to 30 millivolts and then rapidly returning to its original value. This rapid change of membrane potential which may last about a millisecond is called an ...
... -70 to 30 millivolts and then rapidly returning to its original value. This rapid change of membrane potential which may last about a millisecond is called an ...
peripheral nervous system
... The axon: It is a slender process. It may transfer the nerve impulses from the beginning part (axon hillock) to the end (axon terminal). Because the axoplasm does not contain RNA and ribosome, proteins synthesis cannot take place in the axon. All axonal proteins, therefore, must come from the cell b ...
... The axon: It is a slender process. It may transfer the nerve impulses from the beginning part (axon hillock) to the end (axon terminal). Because the axoplasm does not contain RNA and ribosome, proteins synthesis cannot take place in the axon. All axonal proteins, therefore, must come from the cell b ...
Nervous system
... • A change in charge that travels as a wave along the membrane of a neuron • Called an action potential • Depends on the movement of sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+) between the interstitial fluid and the inside of the neuron. ...
... • A change in charge that travels as a wave along the membrane of a neuron • Called an action potential • Depends on the movement of sodium ions (Na+) and potassium ions (K+) between the interstitial fluid and the inside of the neuron. ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.