Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... their cell bodies; only one fiber is an axon and the rest are dendrites; neurons which lie within the brain or spinal ...
... their cell bodies; only one fiber is an axon and the rest are dendrites; neurons which lie within the brain or spinal ...
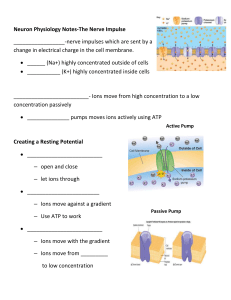
Neuron Physiology Notes
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
Electrophysiology - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Separation of charge is defined as potential energy (the potential to do work), thus this separation of charge is termed “membrane potential” or Voltage and in cells is measured in millivolts (mV). If the charge is allowed to move across the membrane then the potential energy is turned into work, th ...
... Separation of charge is defined as potential energy (the potential to do work), thus this separation of charge is termed “membrane potential” or Voltage and in cells is measured in millivolts (mV). If the charge is allowed to move across the membrane then the potential energy is turned into work, th ...
Structure of the Cell Membrane
... Example: Fast - O2, CO2, H2O Slow - C6H12O6 Can’t – polypetides (proteins) polysaccarides (starches) B. Non-Polar enough Example: O2, CO2, Steroids, Lipids Note: Ions do not move through membranes very well (Na+, Cl-, H+, ) due hydration shell ...
... Example: Fast - O2, CO2, H2O Slow - C6H12O6 Can’t – polypetides (proteins) polysaccarides (starches) B. Non-Polar enough Example: O2, CO2, Steroids, Lipids Note: Ions do not move through membranes very well (Na+, Cl-, H+, ) due hydration shell ...
The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions
... A brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV Action potentials are only generated by muscle cells and neurons They do not decrease in strength over distance They are the principal means of neural communication An action potential in the axon of a neuron is a nerve ...
... A brief reversal of membrane potential with a total amplitude of 100 mV Action potentials are only generated by muscle cells and neurons They do not decrease in strength over distance They are the principal means of neural communication An action potential in the axon of a neuron is a nerve ...
Nervous Tissue
... – K+ flows out more readily than Na+ flows in – Na+/K+ pump maintains concentrations of Na + (3 out) and K + (2 in) ...
... – K+ flows out more readily than Na+ flows in – Na+/K+ pump maintains concentrations of Na + (3 out) and K + (2 in) ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
The Nervous System
... What is the name of the small spaces that exist between the neurons? Can you give an example of a chemical that can be found in this space? How does the cell membrane become polarized in a neuron? What are the major ions associated with generating a membrane potential? Which ions are present in larg ...
... What is the name of the small spaces that exist between the neurons? Can you give an example of a chemical that can be found in this space? How does the cell membrane become polarized in a neuron? What are the major ions associated with generating a membrane potential? Which ions are present in larg ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
... • Seratonin is the brain chemical that is associated with moods, concentration and attention Thinking about the information in the last slides, explain what happens in the brain with people who are depressed ...
intro anat 1 - mshsRebeccaMazoff
... • Both plants and animals must maintain stable fluid environments for all of their cells – Each cell must get nutrients from and dump waste into the fluid bathing them – Concentrations must be kept compatible for / with metabolism ...
... • Both plants and animals must maintain stable fluid environments for all of their cells – Each cell must get nutrients from and dump waste into the fluid bathing them – Concentrations must be kept compatible for / with metabolism ...
Neurotox I
... Carrier-mediated transport systems exist for entry of certain required molecules (e.g., hexoses, carboxylic acids, amino acids (separate ones for neutral, basic, and acidic amino acids), amines, and inorganic ions ...
... Carrier-mediated transport systems exist for entry of certain required molecules (e.g., hexoses, carboxylic acids, amino acids (separate ones for neutral, basic, and acidic amino acids), amines, and inorganic ions ...
Nervous Tissue
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
File
... 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membrane to become negative, thus initiating an action potential. 3. Repolarization – Na+ channels close, K+ moves back into th ...
... 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membrane to become negative, thus initiating an action potential. 3. Repolarization – Na+ channels close, K+ moves back into th ...
Cell Structure and Function
... together to perform a specific function. Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, ner ...
... together to perform a specific function. Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, ner ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
Neural Tissue – Chapter 12
... from its outer surface. These ions move toward the open channels, replacing ions that have already entered the cell. This is called local current. (As sodium ions move into the cell, other sodium ions fill in the gaps.) This causes adjacent portions of the cell membrane to become depolarized. The de ...
... from its outer surface. These ions move toward the open channels, replacing ions that have already entered the cell. This is called local current. (As sodium ions move into the cell, other sodium ions fill in the gaps.) This causes adjacent portions of the cell membrane to become depolarized. The de ...
nervoussystemwebquest
... The membrane potential is the difference of charges across the plasma membrane When the membrane is at resting potential, there is no transmitting of signals. The voltage is usually around -70 mV. This membrane potential is due to the concentration of ions on the two sides of the membranes. Sodium ( ...
... The membrane potential is the difference of charges across the plasma membrane When the membrane is at resting potential, there is no transmitting of signals. The voltage is usually around -70 mV. This membrane potential is due to the concentration of ions on the two sides of the membranes. Sodium ( ...
Membrane potential (mV)
... Anions (negatively charged proteins, nucleic acids, and other large molecules) that cannot pass through membrane ...
... Anions (negatively charged proteins, nucleic acids, and other large molecules) that cannot pass through membrane ...
ppt - UK College of Arts & Sciences
... The students will learn how to properly record the potential across a membrane, with glass electrodes, in the DEL1 and DEL2 muscles in a crayfish. The students furthered their investigation of membrane potentials by determining the effects of increased extracellular K+ levels. Using several solution ...
... The students will learn how to properly record the potential across a membrane, with glass electrodes, in the DEL1 and DEL2 muscles in a crayfish. The students furthered their investigation of membrane potentials by determining the effects of increased extracellular K+ levels. Using several solution ...
Nervous System
... The faster the body can send out signals, the faster one can react. But how does the body increase the speed of conduction? The axon of some neurons is covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwan ...
... The faster the body can send out signals, the faster one can react. But how does the body increase the speed of conduction? The axon of some neurons is covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwan ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
nervous system
... • Motor nerves lead to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • Example: increasing of the heart rate after a car crash, stomach releasing HCl when food is present • ______________________ Division (Stressed state of mind: fight/flight) • ______________________ Division (Relaxed state of mind: fe ...
... • Motor nerves lead to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • Example: increasing of the heart rate after a car crash, stomach releasing HCl when food is present • ______________________ Division (Stressed state of mind: fight/flight) • ______________________ Division (Relaxed state of mind: fe ...
Chapter - Heartland Community College
... 10. Which statement is NOT true about the neuron cell membrane? A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of t ...
... 10. Which statement is NOT true about the neuron cell membrane? A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of t ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.