No Slide Title
... • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels are opened or closed by various stimuli – enables cell to turn electrical currents on and off ...
... • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels are opened or closed by various stimuli – enables cell to turn electrical currents on and off ...
Synaptic Transmission and Neurotransmitters
... – Dendrites receive incoming signals – If sufficient, cell goes into firing mode ...
... – Dendrites receive incoming signals – If sufficient, cell goes into firing mode ...
Nervous tissues
... There are three main types of neurons, which are classified according their function: Those that conduct impulses from the sensory organs to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are called sensory (or afferent) neurons; those that conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the ...
... There are three main types of neurons, which are classified according their function: Those that conduct impulses from the sensory organs to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are called sensory (or afferent) neurons; those that conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the ...
Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... interneurons in the brain. 2.Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 3.Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles ...
... interneurons in the brain. 2.Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 3.Muscles in the arm carry out the response and you reach to pick up the phone 4. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the muscles ...
Electrical dimensions in cell science - Journal of Cell Science
... Fig. 1. Naturally occurring EFs in tissues arise from polarised ion transport. The mammalian corneal epithelium model is shown. (A)Tight junctions (purple dots) in the upper layers of the intact epithelium seal neighbouring cells to each other as well as restricting lateral mobility of membrane pro ...
... Fig. 1. Naturally occurring EFs in tissues arise from polarised ion transport. The mammalian corneal epithelium model is shown. (A)Tight junctions (purple dots) in the upper layers of the intact epithelium seal neighbouring cells to each other as well as restricting lateral mobility of membrane pro ...
Slide ()
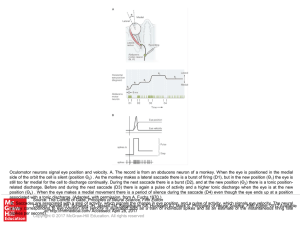
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
Ch. 7: The Nervous System
... 6. At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse (gap between nerves) to signal the adjoining nerves to continue the impulse. 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward ...
... 6. At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse (gap between nerves) to signal the adjoining nerves to continue the impulse. 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward ...
the nervous system - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... The diagram below is a representation of the architecture of the nervous system. If you'll notice at the very top is the central nervous system. It's necessary to understand that the brain and spinal cord receive all sensory information from the outside world and the inside world called visceral. Th ...
... The diagram below is a representation of the architecture of the nervous system. If you'll notice at the very top is the central nervous system. It's necessary to understand that the brain and spinal cord receive all sensory information from the outside world and the inside world called visceral. Th ...
Exam 5 - Spring13 - Take home
... 1. What is the net (total) electrochemical force (its size and direction) acting on Na+ at the resting potential (-70mV)? 2. What is the net (total) electrochemical force (its size and direction) acting on Na+ at the peak of the action potential (+30mV)? 3. What is the net (total) electrochemical fo ...
... 1. What is the net (total) electrochemical force (its size and direction) acting on Na+ at the resting potential (-70mV)? 2. What is the net (total) electrochemical force (its size and direction) acting on Na+ at the peak of the action potential (+30mV)? 3. What is the net (total) electrochemical fo ...
Ear
... sound of aero plane. The he was about to fall but in the next moment he could control himself. In this event two special organs co-ordinated the works. a. What is sense organ? b. What is meant by binocular vision? c. Describe the process of function of the mentioned organ which function with light. ...
... sound of aero plane. The he was about to fall but in the next moment he could control himself. In this event two special organs co-ordinated the works. a. What is sense organ? b. What is meant by binocular vision? c. Describe the process of function of the mentioned organ which function with light. ...
Chapter 2 The Neural Impulse
... A) Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. B) Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. C) The nerve impulse involves the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane. D) Within a neuron, information ...
... A) Neurons in the central nervous system have myelin sheaths, while those in the peripheral nervous system do not. B) Some neurons have axons that are several feet long. C) The nerve impulse involves the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane. D) Within a neuron, information ...
File
... The sodium-potassium pump in the nerve cell membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. More K+ ions leak across the membrane than N ...
... The sodium-potassium pump in the nerve cell membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. More K+ ions leak across the membrane than N ...
Section 35-2: The Nervous System The nervous system controls and
... The sodium-potassium pump in the nerve cell membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. More K+ ions leak across the membrane than N ...
... The sodium-potassium pump in the nerve cell membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. More K+ ions leak across the membrane than N ...
Lab #6: Neurophysiology Simulation
... negative, and the membrane potential moves back towards the resting potential. Once the membrane potential is repolarized below threshold, the voltage-gated K+ channels close. Although the resting potential has been restored, the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+ are now different from resting ...
... negative, and the membrane potential moves back towards the resting potential. Once the membrane potential is repolarized below threshold, the voltage-gated K+ channels close. Although the resting potential has been restored, the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+ are now different from resting ...
Electrical Properties of Hypothalamic Neuroendocrine Cells
... zations manifest themselves in the neurons' electrical behavior. In particular, this investigation will focus on whether the electrical functioning of the neuroendocrine cell resembles that of non-endocrine neurons or of nonnervous glandular cells (12, 21, 28). 1 The preoptic nucleus of lower verteb ...
... zations manifest themselves in the neurons' electrical behavior. In particular, this investigation will focus on whether the electrical functioning of the neuroendocrine cell resembles that of non-endocrine neurons or of nonnervous glandular cells (12, 21, 28). 1 The preoptic nucleus of lower verteb ...
Brain_s Building Blocks-Student
... – located at extreme ends of the axon’s branches – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) • Synapse – infinitely small space (20-30 billionths of a meter) – exists between and end bulb and its adjacent body organ, heart, muscle ...
... – located at extreme ends of the axon’s branches – miniature container that stores chemicals called neurotransmitters (used to communicate with neighboring cells) • Synapse – infinitely small space (20-30 billionths of a meter) – exists between and end bulb and its adjacent body organ, heart, muscle ...
AP Stuff to go over with 4th and 5th periods
... • Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type. Evidence of your learning is a demonstrated understanding of the following: • 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel l ...
... • Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell type. Evidence of your learning is a demonstrated understanding of the following: • 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel l ...
A temporal trace and SOM-based model of complex cell development
... instantaneous activation for the winning neuron. This SOM part of the learning rule is intended to model the eMects of lateral connections on activity-dependent development. For examples of SOM’s used in modelling lateral connections, see the excellent review by Erwin et al. [5]. Also, it has shown ...
... instantaneous activation for the winning neuron. This SOM part of the learning rule is intended to model the eMects of lateral connections on activity-dependent development. For examples of SOM’s used in modelling lateral connections, see the excellent review by Erwin et al. [5]. Also, it has shown ...
Neuron Stations
... 1) Cell body: take one long pipe cleaner and roll it into a ball. Inside the cell body is the nucleus, which is the control center of the cell. Q2: Do you know what DNA is, where is it? 2) Axon: take another long pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so the ...
... 1) Cell body: take one long pipe cleaner and roll it into a ball. Inside the cell body is the nucleus, which is the control center of the cell. Q2: Do you know what DNA is, where is it? 2) Axon: take another long pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so the ...
Neurons and Nervous Systems
... In a chemical synapse neurotransmitters from a presynaptic cell bind to receptors in a postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft—about 25 nanometers wide—separates the cells. ...
... In a chemical synapse neurotransmitters from a presynaptic cell bind to receptors in a postsynaptic cell. The synaptic cleft—about 25 nanometers wide—separates the cells. ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE EAR
... Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, is channeled into the ear canal by the pinna. Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate like a drum, and changing it into mechanical energy. The malleus, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, starts the ossicles into motion. (T ...
... Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, is channeled into the ear canal by the pinna. Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate like a drum, and changing it into mechanical energy. The malleus, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, starts the ossicles into motion. (T ...
Optogenetics - FSU Program in Neuroscience
... • Expression of GFP-ArchT allows for optical inhibition • In vitro: illumination decreases membrane potential and ...
... • Expression of GFP-ArchT allows for optical inhibition • In vitro: illumination decreases membrane potential and ...
Topic 11: Human health and physiology (17 hours)
... penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
... penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
19.11 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE
... outside to inside, 10 distinct layers are usually seen in histologic sections. 1) The RPE consists of one layer of melanin-rich cuboidal cells. Separated from the choroid by Bruch basement membrane, they are between the choroid and outer tips of photoreceptors. 2) A layer of rods and cones, arranged ...
... outside to inside, 10 distinct layers are usually seen in histologic sections. 1) The RPE consists of one layer of melanin-rich cuboidal cells. Separated from the choroid by Bruch basement membrane, they are between the choroid and outer tips of photoreceptors. 2) A layer of rods and cones, arranged ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.