Science 10 Unit 1: Sustainability of Ecosystems
... plant life. Yet, nitrogen in its gaseous form is almost entirely unusable to organisms. It must first be converted or “fixed” into a more usable form. The process of converting nitrogen is called fixation. • There are specialized bacteria whose function it is to fix nitrogen, converting it, so that ...
... plant life. Yet, nitrogen in its gaseous form is almost entirely unusable to organisms. It must first be converted or “fixed” into a more usable form. The process of converting nitrogen is called fixation. • There are specialized bacteria whose function it is to fix nitrogen, converting it, so that ...
Ch5 Guided Notes
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
PROTEIN TURNOVER AND NITROGEN ECONOMY - U
... 2. excess glutamate formed undergoes amination to glutamine and then to alphaketoglutaramic acid, a neurotoxic compound 3. high ammonia increase blood levels of some amino acids; these compete with other amino acids for transport across blood-brain barrier; thus, predominant transport of one or a ...
... 2. excess glutamate formed undergoes amination to glutamine and then to alphaketoglutaramic acid, a neurotoxic compound 3. high ammonia increase blood levels of some amino acids; these compete with other amino acids for transport across blood-brain barrier; thus, predominant transport of one or a ...
ECOLOGY
... in a population reproduce at a constant rate. (in natural populations this does not occur for very long) • Carrying Capacity of the Environment:The maximum population that a particular environment can support • Limiting Factors : those environmental factors that keep a population at the carrying cap ...
... in a population reproduce at a constant rate. (in natural populations this does not occur for very long) • Carrying Capacity of the Environment:The maximum population that a particular environment can support • Limiting Factors : those environmental factors that keep a population at the carrying cap ...
Ecology PowerPoint
... nutrients are recycled § Three basic nutrient cycles are present in all ecosystems allowing organisms to obtain needed nutrients to function effectively ...
... nutrients are recycled § Three basic nutrient cycles are present in all ecosystems allowing organisms to obtain needed nutrients to function effectively ...
1 The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle of Forest Ecosystems
... store of nutrients, including N, which can be exchanged against equivalent charges of other ions. However, under certain conditions, for example following a change in species composition in the flora, the humus itself can also be remobilised if the edaphic conditions or the decomposing organisms cha ...
... store of nutrients, including N, which can be exchanged against equivalent charges of other ions. However, under certain conditions, for example following a change in species composition in the flora, the humus itself can also be remobilised if the edaphic conditions or the decomposing organisms cha ...
1 The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle of Forest Ecosystems
... store of nutrients, including N, which can be exchanged against equivalent charges of other ions. However, under certain conditions, for example following a change in species composition in the flora, the humus itself can also be remobilised if the edaphic conditions or the decomposing organisms cha ...
... store of nutrients, including N, which can be exchanged against equivalent charges of other ions. However, under certain conditions, for example following a change in species composition in the flora, the humus itself can also be remobilised if the edaphic conditions or the decomposing organisms cha ...
Earth`s Resources, Interactions, and Cycles
... air by breathing and during decay of their bodies and waste. – The remains of some plants and animals become part of the Earth’s crust by turning into coal, oil, or ...
... air by breathing and during decay of their bodies and waste. – The remains of some plants and animals become part of the Earth’s crust by turning into coal, oil, or ...
Keystone Ecology Quia Quiz
... 6. 6. Agricultural runoff can carry fertilizers into lakes and streams. This runoff can cause algae populations to greatly increase. Which effect does this change in the algae population sizes most likely have on affected lakes and streams? (1 point) a decrease in water level an increase in water c ...
... 6. 6. Agricultural runoff can carry fertilizers into lakes and streams. This runoff can cause algae populations to greatly increase. Which effect does this change in the algae population sizes most likely have on affected lakes and streams? (1 point) a decrease in water level an increase in water c ...
Name - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... _____ 33. A tapeworm living in the intestines of a cow _____ 34. The honey guide bird leads the honey badger to the bees hive; both eat the honey. 35. Name the step in a biogeochemical cycle: Options are nitrogen fixation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, percolation, decomposition, transpiratio ...
... _____ 33. A tapeworm living in the intestines of a cow _____ 34. The honey guide bird leads the honey badger to the bees hive; both eat the honey. 35. Name the step in a biogeochemical cycle: Options are nitrogen fixation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, percolation, decomposition, transpiratio ...
Ecology, Biomes, Food Webs Unit Review
... • What is Ecology? • What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? • Be able to identify the following parts of a food chain/food web: o Producer o Secondary Consumer o Consumer o Tertiary Consumer o Carnivore o Decomposer o Herbivore • Biomes o Be able to differentiate between factors ...
... • What is Ecology? • What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? • Be able to identify the following parts of a food chain/food web: o Producer o Secondary Consumer o Consumer o Tertiary Consumer o Carnivore o Decomposer o Herbivore • Biomes o Be able to differentiate between factors ...
Assn5
... 5. Describe a biochemical procedure that selectively inhibits DNA synthesis, but has no affect on RNA synthesis. Answer this question by identifying a compound that inhibits one of the enzymes you showed in question 4. 5 Point Bonus 1. Beginning with NaNO2, trace the path of nitrogen into the struct ...
... 5. Describe a biochemical procedure that selectively inhibits DNA synthesis, but has no affect on RNA synthesis. Answer this question by identifying a compound that inhibits one of the enzymes you showed in question 4. 5 Point Bonus 1. Beginning with NaNO2, trace the path of nitrogen into the struct ...
Ecology Clicker Challenge (Final Review)
... most other species, while the sea urchin population destroys coral reefs. For this reason, sea stars are considered a. primary consumers. c. apex predators. b. a keystone species. d. a pioneer species. 11. Decomposers are essential in every ecosystem because a. they are able to create their own ener ...
... most other species, while the sea urchin population destroys coral reefs. For this reason, sea stars are considered a. primary consumers. c. apex predators. b. a keystone species. d. a pioneer species. 11. Decomposers are essential in every ecosystem because a. they are able to create their own ener ...
Ecology - Cloudfront.net
... Carbon cycle•Photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon and oxygen through the environment. ...
... Carbon cycle•Photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon and oxygen through the environment. ...
APES Ch 3 Ecosytems What are they and how do
... • The phosphorous cycle does not include the atmosphere. • The major reservoir is phosphate salts containing phosphate ions in terrestrial rock formations and ocean bottom sediments. • The phosphorous cycle is slow compared to water, carbon and nitrogen cycles ...
... • The phosphorous cycle does not include the atmosphere. • The major reservoir is phosphate salts containing phosphate ions in terrestrial rock formations and ocean bottom sediments. • The phosphorous cycle is slow compared to water, carbon and nitrogen cycles ...
Document
... - once the nitrogen has been fixed into the soil in the form of nitrates it is then available to be used by plants (natural fertilizer). - Plants convert the nitrates into proteins - Animals eat the nitrogen rich plants making more proteins - Animal either dies and decays or poops releasing ammonia ...
... - once the nitrogen has been fixed into the soil in the form of nitrates it is then available to be used by plants (natural fertilizer). - Plants convert the nitrates into proteins - Animals eat the nitrogen rich plants making more proteins - Animal either dies and decays or poops releasing ammonia ...
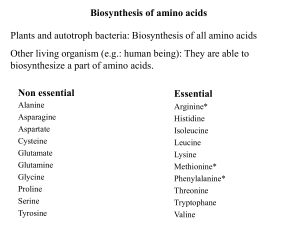
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
Name Date Period ______ STUDY GUIDE: ECOLOGY Matching: a
... 14. Sum total of all the different forms of genetic information carried by all organisms living on Earth today ...
... 14. Sum total of all the different forms of genetic information carried by all organisms living on Earth today ...
Nitrogen cycle

The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is nitrogen, making it the largest pool of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitrogen cycle.