sci 10 exam review b.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 49. Draw an electron dot diagram for Mg. 50. What ion will K form? 51. What ion will Mg form? 52. What ion will Br form? 53. What ion will Al form? 54. What ion will S form? 55. Will He form an ion? Why or why not? 56. Will Xe form an ion? Why or why not? 57. Will Ca form a cation or anion? 58. Will ...
... 49. Draw an electron dot diagram for Mg. 50. What ion will K form? 51. What ion will Mg form? 52. What ion will Br form? 53. What ion will Al form? 54. What ion will S form? 55. Will He form an ion? Why or why not? 56. Will Xe form an ion? Why or why not? 57. Will Ca form a cation or anion? 58. Will ...
Biology 1407 Notes Exam 5 - Ecology Ch 34, 37, 38 Ecology
... Define and give an example of the competitive exclusion princip le and resource partitioning. Define the term predation and describe its effect on the predator and prey species and on the community. What are keystone species and how do they affect the community? What is herbivory? Describe some of t ...
... Define and give an example of the competitive exclusion princip le and resource partitioning. Define the term predation and describe its effect on the predator and prey species and on the community. What are keystone species and how do they affect the community? What is herbivory? Describe some of t ...
Ecology Test
... Nitrogen in nitrogen gas is “fixed” by nitrogen fixing bacteria into the soil as ammonium. Nitrifying bacteria convert it to nitrates which are then absorbed by plants. Denitrifying bacteria can release nitrates back into the atmosphere as nitrogen gas. ...
... Nitrogen in nitrogen gas is “fixed” by nitrogen fixing bacteria into the soil as ammonium. Nitrifying bacteria convert it to nitrates which are then absorbed by plants. Denitrifying bacteria can release nitrates back into the atmosphere as nitrogen gas. ...
Role of the Master regulator HetR in the cellular differentiation
... of cellular differentiation. The questions that we address is which kinase phosphorylates HetR? Is HetR phosphorylation needed for the establishment of the pattern? What are the mechanism underlying the temporal dynamic of HetR transcriptional control through the differentiation process? To answer t ...
... of cellular differentiation. The questions that we address is which kinase phosphorylates HetR? Is HetR phosphorylation needed for the establishment of the pattern? What are the mechanism underlying the temporal dynamic of HetR transcriptional control through the differentiation process? To answer t ...
chapter 3 Biology - e
... The highest percentage of air (78%) is nitrogen, but the plants cannot use this nitrogen. The circulation of nitrogen can be shown by the diagram shown below. Atmospheric N2 Lightning ...
... The highest percentage of air (78%) is nitrogen, but the plants cannot use this nitrogen. The circulation of nitrogen can be shown by the diagram shown below. Atmospheric N2 Lightning ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Carbon cycles within living organisms via photosynthesis and respiration, as well as, via the decomposition of organic matter by bacteria and fungi. The atmosphere and ocean are important reservoirs of carbon dioxide. Limestone, peat, coal, oil and natural gas are also reservoirs of carbon. Prokaryo ...
... Carbon cycles within living organisms via photosynthesis and respiration, as well as, via the decomposition of organic matter by bacteria and fungi. The atmosphere and ocean are important reservoirs of carbon dioxide. Limestone, peat, coal, oil and natural gas are also reservoirs of carbon. Prokaryo ...
Document
... Suggested sessions for Inorganic Nitrogen Morning: • Uptake and retention of inorganic nutrients • Transport and transformation of inorganic nutrients across ecosystems • Coupled biogeochemical processes and stoichiometry - N, P, and organic C dynamics • Role of nutrients and stoichiometry in contr ...
... Suggested sessions for Inorganic Nitrogen Morning: • Uptake and retention of inorganic nutrients • Transport and transformation of inorganic nutrients across ecosystems • Coupled biogeochemical processes and stoichiometry - N, P, and organic C dynamics • Role of nutrients and stoichiometry in contr ...
NO 3
... • Decomposers gradually break down the protein in dead plants and animals into amino acids – decomposition. • Decomposers include bacteria and fungi which produce protease enzymes. • They use some of the amino acids for their own growth. • The rest is broken down into ammonia. • Ammonia is also prod ...
... • Decomposers gradually break down the protein in dead plants and animals into amino acids – decomposition. • Decomposers include bacteria and fungi which produce protease enzymes. • They use some of the amino acids for their own growth. • The rest is broken down into ammonia. • Ammonia is also prod ...
Effects of Increased Temperature and Nitrogen on Non-N
... So, What’s New then???????? None to our knowledge have shown the relationship of the increase Temperature and Nitrogen level to toxin production and then its effect on the zooplankton (herbivory) and the competition between the N-fixers and non- N-fixing cyanobacteria. Nitrogen Fixation: Conversi ...
... So, What’s New then???????? None to our knowledge have shown the relationship of the increase Temperature and Nitrogen level to toxin production and then its effect on the zooplankton (herbivory) and the competition between the N-fixers and non- N-fixing cyanobacteria. Nitrogen Fixation: Conversi ...
Chapter 2 - Holden R
... Organism-this is the actual plant or animal by itself For example: a rabbit Populations- a group of organisms, all the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time For example: the rabbits in Holden Communities- composed of multiple populations in an area at the same ...
... Organism-this is the actual plant or animal by itself For example: a rabbit Populations- a group of organisms, all the same species, which interbreed and live in the same area at the same time For example: the rabbits in Holden Communities- composed of multiple populations in an area at the same ...
Describing Matter
... Once nitrogen enters a plant, it becomes part of the food chain. The fixed nitrogen absorbed by the plant is used to make proteins, amino acids and DNA (nitrogen-containing organic macromolecules). If the plant gets eaten by an herbivore (or other primary consumer), the herbivore will digest the nit ...
... Once nitrogen enters a plant, it becomes part of the food chain. The fixed nitrogen absorbed by the plant is used to make proteins, amino acids and DNA (nitrogen-containing organic macromolecules). If the plant gets eaten by an herbivore (or other primary consumer), the herbivore will digest the nit ...
Ecology
... A. Ecological Organization Organism ________ Community Biome (Ecosystem) ________ Successful Ecosystems must have: 1. A constant flow of ________ (________ is the primary source of energy for _________ ecosystem) 2. __________ of resources. *________ (__________ and limiting factors): pH, soil, te ...
... A. Ecological Organization Organism ________ Community Biome (Ecosystem) ________ Successful Ecosystems must have: 1. A constant flow of ________ (________ is the primary source of energy for _________ ecosystem) 2. __________ of resources. *________ (__________ and limiting factors): pH, soil, te ...
What four areas does population size depend on?
... • -Evaporation- From areas of concentration of water (Ponds, lakes etc.) • -Transpiration- H20 lost from plants ...
... • -Evaporation- From areas of concentration of water (Ponds, lakes etc.) • -Transpiration- H20 lost from plants ...
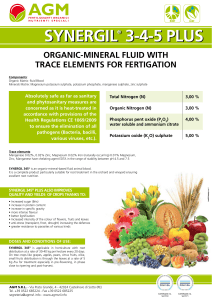
synergil® 3-4-5 plus synergil® 3-4-5 plus
... Absolutely safe as far as sanitary and phytosanitary measures are concerned as it is heat-treated in accordance with provisions of the Health Regulations CE 1069/2009 to ensure the elimination of all pathogens (Bacteria, bacilli, various viruses, etc.). ...
... Absolutely safe as far as sanitary and phytosanitary measures are concerned as it is heat-treated in accordance with provisions of the Health Regulations CE 1069/2009 to ensure the elimination of all pathogens (Bacteria, bacilli, various viruses, etc.). ...
metabolism of lipids
... urea, dextrose, phenol-red indicator Urease +. urease releases ammonia from the urea, ammonia increases the pH, color of the indicator changes into purple Urease -. dextrose utilized, producing acid, decreasing the pH, coloring the medium yellow Originally the color of the medium is dark yellow/oran ...
... urea, dextrose, phenol-red indicator Urease +. urease releases ammonia from the urea, ammonia increases the pH, color of the indicator changes into purple Urease -. dextrose utilized, producing acid, decreasing the pH, coloring the medium yellow Originally the color of the medium is dark yellow/oran ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... A pyramid of BIOMASS shows that the producer at the base has the greatest biomass and that this DECREASES, level by level, to the final consumer, which has the smallest biomass. ...
... A pyramid of BIOMASS shows that the producer at the base has the greatest biomass and that this DECREASES, level by level, to the final consumer, which has the smallest biomass. ...
No Slide Title
... The Nitrogen Cycle • Nitrogen cycle - the process in which nitrogen circulates among the air, soil, water, plants, and animals in an ecosystem. – Nitrogen makes up 78 percent of the gases in the atmosphere. • All organisms need nitrogen to build proteins and DNA, which are used to build new cells. ...
... The Nitrogen Cycle • Nitrogen cycle - the process in which nitrogen circulates among the air, soil, water, plants, and animals in an ecosystem. – Nitrogen makes up 78 percent of the gases in the atmosphere. • All organisms need nitrogen to build proteins and DNA, which are used to build new cells. ...
plant
... Ammonification: dead organisms & waste (through urine/dung) contain Nitrogen ammonia & ammonium ions (by decomposer bacteria) for plants Denitrification: N2 released back into atmosphere (by bacteria) Plants use nitrates to form AA, animals get nitrogen by eating plants ...
... Ammonification: dead organisms & waste (through urine/dung) contain Nitrogen ammonia & ammonium ions (by decomposer bacteria) for plants Denitrification: N2 released back into atmosphere (by bacteria) Plants use nitrates to form AA, animals get nitrogen by eating plants ...
Vocabulary Review
... organisms and the other living and nonliving components of their environment ...
... organisms and the other living and nonliving components of their environment ...
Science Chapter 7 Notes
... dioxide when they breakdown wastes in the environment. 3. Oxygen Cycle: a. Producers release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. b. Most organisms need oxygen to carry out their own life processes. ...
... dioxide when they breakdown wastes in the environment. 3. Oxygen Cycle: a. Producers release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. b. Most organisms need oxygen to carry out their own life processes. ...
Document
... found in DNA, RNA, proteins and ATP. Nitrogen atoms must be used over and over again so that new molecules can be made and used by all living things. In the atmosphere, nitrogen gas is the most abundant gas. Plants and animals cannot use nitrogen gas, but certain bacteria can change it into a usable ...
... found in DNA, RNA, proteins and ATP. Nitrogen atoms must be used over and over again so that new molecules can be made and used by all living things. In the atmosphere, nitrogen gas is the most abundant gas. Plants and animals cannot use nitrogen gas, but certain bacteria can change it into a usable ...
Reading Guide
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
... 27. Aromatic amino acids are both keto- and glucogenic because they are broken down into ___________________ and either ______________ or _______________. 28. Why is excess nitrogen from metabolic processes not simply excreted as ammonia? 29. What is glutamate’s particular role in nitrogen eliminat ...
Science Chapter 7 Notes - msgreenshomepage
... dioxide when they breakdown wastes in the environment. 3. Oxygen Cycle: a. Producers release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. ...
... dioxide when they breakdown wastes in the environment. 3. Oxygen Cycle: a. Producers release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. ...
Nitrogen cycle

The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is nitrogen, making it the largest pool of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitrogen cycle.