On the nature and ecological functions of soil soluble organic
... 2003, Zhu & Carreiro 2004, Chen et al. 2005a, b). In temperate forest ecosystems, concentrations of SON extracted by various methods from surface soils (0–15 cm) generally ranged from 6.5 to 16.3 mg kg–1 (Hannam & Prescott 2003, Zhong & Makeschin 2003, Zhu & Carreiro 2004). Our recent studies have a ...
... 2003, Zhu & Carreiro 2004, Chen et al. 2005a, b). In temperate forest ecosystems, concentrations of SON extracted by various methods from surface soils (0–15 cm) generally ranged from 6.5 to 16.3 mg kg–1 (Hannam & Prescott 2003, Zhong & Makeschin 2003, Zhu & Carreiro 2004). Our recent studies have a ...
The Biochemical Sequence
... Obviously without robust transport, nowhere near as much nutrient reaches the leaves or is stored in the fruits. Chemical agriculture gets around this to some extent, since-even with a weak transport system-anything that is highly soluble, such as potassium nitrate, is simply taken up along with wat ...
... Obviously without robust transport, nowhere near as much nutrient reaches the leaves or is stored in the fruits. Chemical agriculture gets around this to some extent, since-even with a weak transport system-anything that is highly soluble, such as potassium nitrate, is simply taken up along with wat ...
2 H
... Oxygen Requirements • Aerobic: – Absolute need of oxygen to survive – Used as a final electron acceptor – Used by bacteria that carry out an oxidative or aerobic respiratory metabolism ...
... Oxygen Requirements • Aerobic: – Absolute need of oxygen to survive – Used as a final electron acceptor – Used by bacteria that carry out an oxidative or aerobic respiratory metabolism ...
Read the complete press article
... The first paddock was 42 ha, and since then, the area has grown to the current size of 264 ha of rainfed permanent pastures and 80 ha of fodder crops partially under irrigation. He has been able to increase his herd from the original 300 merino ewes to the current 2200 Assaf milking ewes by transfor ...
... The first paddock was 42 ha, and since then, the area has grown to the current size of 264 ha of rainfed permanent pastures and 80 ha of fodder crops partially under irrigation. He has been able to increase his herd from the original 300 merino ewes to the current 2200 Assaf milking ewes by transfor ...
The benefits of Multi-K - Potassium Nitrate - Haifa
... Increases the concentration of electrolytes inside the cell Thus protecting the cell from frost damages The potassium in Multi-K Encourages establishment and branching of roots Improves water uptake from the soil Thus enhancing the plant’s ability to withstand drought ...
... Increases the concentration of electrolytes inside the cell Thus protecting the cell from frost damages The potassium in Multi-K Encourages establishment and branching of roots Improves water uptake from the soil Thus enhancing the plant’s ability to withstand drought ...
Document
... When chloride (Cl-) concentration in the soil solution increases, plants take it up on the account of essential anionic nutrients, especially nitrate. High concentrations of chloride may cause toxic effects and even death of plants Multi-K is free of detrimental chloride, so it is a safe for use in ...
... When chloride (Cl-) concentration in the soil solution increases, plants take it up on the account of essential anionic nutrients, especially nitrate. High concentrations of chloride may cause toxic effects and even death of plants Multi-K is free of detrimental chloride, so it is a safe for use in ...
Fertilizers & Nutrients
... • Includes granular & slow release fertilizers applied to the growing media. ...
... • Includes granular & slow release fertilizers applied to the growing media. ...
Exam Two: Ecology Part 1
... IDENTIFY polar, temperate and tropical zones on earth IDENTIFY the different zones in aquatic ecosystems IDENTIFY the process that builds most of the organic molecules found on earth IDENTIFY an example of primary or secondary succession OUTLINE primary and secondary production OUTLINE community OUT ...
... IDENTIFY polar, temperate and tropical zones on earth IDENTIFY the different zones in aquatic ecosystems IDENTIFY the process that builds most of the organic molecules found on earth IDENTIFY an example of primary or secondary succession OUTLINE primary and secondary production OUTLINE community OUT ...
Vocabulary
... pyramid of numbers pyramid of energy pyramid of biomass first law of thermodynamics monoculture biological amplification second law of thermodynamics Questions 1. Describe the difference of how matter and energy are used in an ecosystem. Be specific! 2. List the order of the zones of the atmosphere, ...
... pyramid of numbers pyramid of energy pyramid of biomass first law of thermodynamics monoculture biological amplification second law of thermodynamics Questions 1. Describe the difference of how matter and energy are used in an ecosystem. Be specific! 2. List the order of the zones of the atmosphere, ...
Good Bacteria - Effingham County Schools
... In the soil and in the plants roots bacteria help turn atmospheric nitrogen into protein. Example: rhizobia bacteria live in the roots of peanuts. The rhizobia bacteria change the nitrogen gas into compounds of nitrogen that the plants then convert into proteins. Food Processing Plant The cocci bact ...
... In the soil and in the plants roots bacteria help turn atmospheric nitrogen into protein. Example: rhizobia bacteria live in the roots of peanuts. The rhizobia bacteria change the nitrogen gas into compounds of nitrogen that the plants then convert into proteins. Food Processing Plant The cocci bact ...
10 kcal/m 2 /year
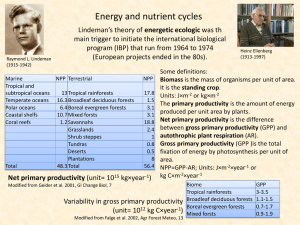
... There is only a limited amount of resources (water, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon) on the earth In order to keep these resources available to organisms, they must be recycled after they are used Cycle: a process that recycles a resource so that you end up with what you started with Nitrogen Cycle 1. Nitr ...
... There is only a limited amount of resources (water, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon) on the earth In order to keep these resources available to organisms, they must be recycled after they are used Cycle: a process that recycles a resource so that you end up with what you started with Nitrogen Cycle 1. Nitr ...
Non-Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixers
... Biological nitrogen fixation takes many forms in nature from the 1) symbiotic forms including blue-green algae (nostoc), 2) lichens, actinomycetes, non legume 3) associative symbiosis and the 4) and free-living soil bacteria. These types of N2 fixation contribute significant quantities of NH3 to nat ...
... Biological nitrogen fixation takes many forms in nature from the 1) symbiotic forms including blue-green algae (nostoc), 2) lichens, actinomycetes, non legume 3) associative symbiosis and the 4) and free-living soil bacteria. These types of N2 fixation contribute significant quantities of NH3 to nat ...
Isotope Fractionation: Why Aren`t We What We Eat?
... Nitrogen abundance analysis has been applied to the analysis of trophic level in ecosystems based on the observation that nitrogen abundances increase by about 2‰ with each step up the food chain (Minagawa & Wada, 1984). The discrimination processes that lead to this phenomenon, however, are not wel ...
... Nitrogen abundance analysis has been applied to the analysis of trophic level in ecosystems based on the observation that nitrogen abundances increase by about 2‰ with each step up the food chain (Minagawa & Wada, 1984). The discrimination processes that lead to this phenomenon, however, are not wel ...
NeponsetPresentation - BIOEEOS660-f12
... There are many sources of excess nutrients in the Neponset watershed. Fertilizer, animal waste, runoff from impervious surfaces, direct input of grass clippings from lawns and golf courses, leaky sewers, bad septic systems, and dams all contribute excess nutrients to the system (Neponset.org). ammon ...
... There are many sources of excess nutrients in the Neponset watershed. Fertilizer, animal waste, runoff from impervious surfaces, direct input of grass clippings from lawns and golf courses, leaky sewers, bad septic systems, and dams all contribute excess nutrients to the system (Neponset.org). ammon ...
Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions
... 78% of nitrogen in our biosphere is atmospheric, which is not usable by most living organisms. Luckily, there are nitrogen fixing bacteria that take atmospheric nitrogen gas and convert it to ammonia. These bacteria live on the roots of certain plants called legumes. (peanuts, beans, peas). The nitr ...
... 78% of nitrogen in our biosphere is atmospheric, which is not usable by most living organisms. Luckily, there are nitrogen fixing bacteria that take atmospheric nitrogen gas and convert it to ammonia. These bacteria live on the roots of certain plants called legumes. (peanuts, beans, peas). The nitr ...
APES Review #2
... RESULTS Phytoplankton abundance parallels the abundance of phosphorus in the water (a). Nitrogen, however, is immediately taken up by algae, and no free nitrogen is measured in the coastal waters. The addition of ammonium (NH4) caused heavy phytoplankton growth in bay water, but the addition of pho ...
... RESULTS Phytoplankton abundance parallels the abundance of phosphorus in the water (a). Nitrogen, however, is immediately taken up by algae, and no free nitrogen is measured in the coastal waters. The addition of ammonium (NH4) caused heavy phytoplankton growth in bay water, but the addition of pho ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... essential component of all living material. From microscopic bacteria to plants and animals, nitrogen is a required component of all biological material. Nitrogen makes up over 70% of the earth’s atmosphere and is found mostly in the elemental N2 gaseous form. For cells and living organisms to be ab ...
... essential component of all living material. From microscopic bacteria to plants and animals, nitrogen is a required component of all biological material. Nitrogen makes up over 70% of the earth’s atmosphere and is found mostly in the elemental N2 gaseous form. For cells and living organisms to be ab ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... is the fate of most of NH3 channeled there. Urea → bloodstream → kidneys → urine ...
... is the fate of most of NH3 channeled there. Urea → bloodstream → kidneys → urine ...
Document
... in location of the phenyl group. Isoflavones are produced via a branch of the general phenylpropanoid pathway that produces flavonoid compounds in higher plants. Soybeans are the most common source of isoflavones in human food; the major isoflavones in soybean are genistein and daidzein. The phenylp ...
... in location of the phenyl group. Isoflavones are produced via a branch of the general phenylpropanoid pathway that produces flavonoid compounds in higher plants. Soybeans are the most common source of isoflavones in human food; the major isoflavones in soybean are genistein and daidzein. The phenylp ...
Engineering Nitrogen Use Efficient Crop Plants
... tissues can return N to the amino acid pool15. The carbon skeletons utilized by these reactions are obtained from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Once N has been taken up and assimilated, it is transported throughout the plant predominantly as glutamine, asparagine, glutamate, and aspartate for ...
... tissues can return N to the amino acid pool15. The carbon skeletons utilized by these reactions are obtained from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Once N has been taken up and assimilated, it is transported throughout the plant predominantly as glutamine, asparagine, glutamate, and aspartate for ...
Biotic interactions
... Uniqueness of soil as an habitat/ecosystem Eating in the soil Detritivores are often obliged to eat both organic matter and mineral material : eat the soil altogether Eating organic matter transforms the organic matter ...
... Uniqueness of soil as an habitat/ecosystem Eating in the soil Detritivores are often obliged to eat both organic matter and mineral material : eat the soil altogether Eating organic matter transforms the organic matter ...
this lecture as PDF here - Development of e
... inexhaustible reservoir of this essential element. The N 2 molecule is very stable so that breaking it down to atoms that can be incorporated in inorganic and organic chemical forms of nitrogen is the limiting step in the nitrogen cycle. This does occur by highly energetic processes in lightning dis ...
... inexhaustible reservoir of this essential element. The N 2 molecule is very stable so that breaking it down to atoms that can be incorporated in inorganic and organic chemical forms of nitrogen is the limiting step in the nitrogen cycle. This does occur by highly energetic processes in lightning dis ...
Nitrogen cycle

The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is nitrogen, making it the largest pool of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitrogen cycle.