YSP_POSTER_10_v02 - Department of Biological Science
... The transfer of energy and nutrients through consumption (i.e. predation and herbivory) links together species in natural communities. Communities are structured by what ecologists call topdown effects (changes in the lower trophic levels as a result of top predators) and bottom-up effects (changes ...
... The transfer of energy and nutrients through consumption (i.e. predation and herbivory) links together species in natural communities. Communities are structured by what ecologists call topdown effects (changes in the lower trophic levels as a result of top predators) and bottom-up effects (changes ...
ppt
... not yet encountered significant environmental deterioration. Question: Do we want to?? Do we want to reach KHuman? ...
... not yet encountered significant environmental deterioration. Question: Do we want to?? Do we want to reach KHuman? ...
Definitions
... relative frequency. For biological diversity these items are organized at many levels …. Thus the term biodiversity encompasses different ecosystems, species, genes and their relative abundance. (US Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, 1987). ...
... relative frequency. For biological diversity these items are organized at many levels …. Thus the term biodiversity encompasses different ecosystems, species, genes and their relative abundance. (US Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, 1987). ...
A) changed directly into proteins B) transported out of the leaves
... B) They are producers that rely indirectly on other producers. C) They are not limited by natural predators. D) They are not dependent on other species. 46. Abiotic factors that affect the growth of grass in a lawn include A) B) C) D) ...
... B) They are producers that rely indirectly on other producers. C) They are not limited by natural predators. D) They are not dependent on other species. 46. Abiotic factors that affect the growth of grass in a lawn include A) B) C) D) ...
ap biology summer assignment 2014
... trophic level. Another way of defining net primary production is as the amount of new biomass added in a given period of time. Why is net primary production, or the amount of new biomass/unit of time, the key measurement to ecologists? ...
... trophic level. Another way of defining net primary production is as the amount of new biomass added in a given period of time. Why is net primary production, or the amount of new biomass/unit of time, the key measurement to ecologists? ...
AP BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2015 The AP curriculum is
... trophic level. Another way of defining net primary production is as the amount of new biomass added in a given period of time. Why is net primary production, or the amount of new biomass/unit of time, the key measurement to ecologists? ...
... trophic level. Another way of defining net primary production is as the amount of new biomass added in a given period of time. Why is net primary production, or the amount of new biomass/unit of time, the key measurement to ecologists? ...
Some Questions to Ponder
... temperature and precipitation along the west continental coasts What limits primary productivity in open oceanic waters? How are these limiting factors mediated by the physical properties of the habitat? Graph the spectrum of solar radiation outside the atmosphere and at Earth’s surface. Describe ho ...
... temperature and precipitation along the west continental coasts What limits primary productivity in open oceanic waters? How are these limiting factors mediated by the physical properties of the habitat? Graph the spectrum of solar radiation outside the atmosphere and at Earth’s surface. Describe ho ...
A cross-system meta-analysis reveals coupled predation effects on
... meta-analysis of prey diversity and biomass responses to local manipulation of predator presence. We found 291 predator removal experiments from 87 studies assessing both diversity and biomass responses. Across ecosystem types, predator presence significantly decreased both biomass and diversity of ...
... meta-analysis of prey diversity and biomass responses to local manipulation of predator presence. We found 291 predator removal experiments from 87 studies assessing both diversity and biomass responses. Across ecosystem types, predator presence significantly decreased both biomass and diversity of ...
Measuring progress_SC_EEA_5-OCT - Eionet Projects
... • Accessible resource: the surplus (actual stocks and flows) which can be used considering 1) physical constraints (timeliness and location, cyclical risks, biochemical quality) & 2) the amount to be left to nature for ecosystem reproduction. N.B.: When returned to the ecosystem (leftovers in agricu ...
... • Accessible resource: the surplus (actual stocks and flows) which can be used considering 1) physical constraints (timeliness and location, cyclical risks, biochemical quality) & 2) the amount to be left to nature for ecosystem reproduction. N.B.: When returned to the ecosystem (leftovers in agricu ...
Future directions of fisheries management
... thresholds to trigger management actions allows for a focused, efficient regulation of a single fishery. However, with the singlespecies approach, habitat characteristics, interactions between species, and natural variability are not incorporated, contributing to scientific uncertainty and potentially m ...
... thresholds to trigger management actions allows for a focused, efficient regulation of a single fishery. However, with the singlespecies approach, habitat characteristics, interactions between species, and natural variability are not incorporated, contributing to scientific uncertainty and potentially m ...
Symbiotic ~ commensalisms
... organization called a community. • Communities are groups of interacting populations of different species. ...
... organization called a community. • Communities are groups of interacting populations of different species. ...
Ecology of Populations Student study guide
... B. Be able to explain how organisms react to changes either abiotic or biotic in their habitat and how these changes must fall within a range of tolerance before they can survive. (363365) C. Be able to explain the concept “niche” and contrast generalists and specialists. (365) D. Be able to explain ...
... B. Be able to explain how organisms react to changes either abiotic or biotic in their habitat and how these changes must fall within a range of tolerance before they can survive. (363365) C. Be able to explain the concept “niche” and contrast generalists and specialists. (365) D. Be able to explain ...
Ecosystems - mrhodges.net
... A food chain is a way of showing the relationships that exist between animals, plants and micro organisms. Each step along the way is called a trophic level. One thing to keep in mind is that only 10% of the energy from gets transferred from one trophic level to the next. The other 90% is used by th ...
... A food chain is a way of showing the relationships that exist between animals, plants and micro organisms. Each step along the way is called a trophic level. One thing to keep in mind is that only 10% of the energy from gets transferred from one trophic level to the next. The other 90% is used by th ...
SOIL MICRO AND MACROORGANISMS The free living components
... wholly parasitic. Free living protozoa in soil feed on dissolved organic substances and other organism. Many feed by grazing and predation, the soil ciliates depend primarily on bacteria for food, some feed additionally on yeasts and other protozoa and even on small metazoan such as rotifers. The so ...
... wholly parasitic. Free living protozoa in soil feed on dissolved organic substances and other organism. Many feed by grazing and predation, the soil ciliates depend primarily on bacteria for food, some feed additionally on yeasts and other protozoa and even on small metazoan such as rotifers. The so ...
Ninth Grade Biology
... Section 13.2: Biotic and Abiotic Factors Key concept: Every ecosystem includes both living and nonliving factors. Main ideas: An ecosystem includes both biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors. Changing once factor in an ecosystem can affect many other factors. Section 13.3: Energy in ecosys ...
... Section 13.2: Biotic and Abiotic Factors Key concept: Every ecosystem includes both living and nonliving factors. Main ideas: An ecosystem includes both biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors. Changing once factor in an ecosystem can affect many other factors. Section 13.3: Energy in ecosys ...
Effects of acid rain
... 1. Methods used to reduce sulfur dioxide from smokestacks are an attempt by humans to (1) lessen the amount of insecticides in the environment (2) eliminate diversity in wildlife (3) lessen the environmental impact of acid rain (4) use nonchemical controls on pest species 2. What are some of the ca ...
... 1. Methods used to reduce sulfur dioxide from smokestacks are an attempt by humans to (1) lessen the amount of insecticides in the environment (2) eliminate diversity in wildlife (3) lessen the environmental impact of acid rain (4) use nonchemical controls on pest species 2. What are some of the ca ...
Science Grade 6 – Grade Level Expectations
... Show how fossil and other evidence can be used to document past life and conditions on Earth. Explain how fossil or other evidence can be used to document environmental changes (extinction, evolution, major climatic changes, and relative age of rock layers). ...
... Show how fossil and other evidence can be used to document past life and conditions on Earth. Explain how fossil or other evidence can be used to document environmental changes (extinction, evolution, major climatic changes, and relative age of rock layers). ...
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Note
... stable ecosystem to exist: 1. There must be a constant supply of energy (sunlight for photosynthesis). 2. There must be living organisms that can incorporate the energy into organic compounds (food). 3. There must be a recycling of materials between organisms and the environment. ...
... stable ecosystem to exist: 1. There must be a constant supply of energy (sunlight for photosynthesis). 2. There must be living organisms that can incorporate the energy into organic compounds (food). 3. There must be a recycling of materials between organisms and the environment. ...
Document
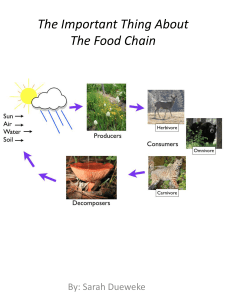
... The important thing about a food chain is that all the organisms in that food chain are affected by the changes in the ecosystem in which they live. • A food chain shows the link between animals and what they eat. • When scientists draw a food chain, they use arrows. • The arrow means “is eaten by. ...
... The important thing about a food chain is that all the organisms in that food chain are affected by the changes in the ecosystem in which they live. • A food chain shows the link between animals and what they eat. • When scientists draw a food chain, they use arrows. • The arrow means “is eaten by. ...
Allocation in High-Sea Fisheries
... Reality though forced me to the Keplerian epiphany that fisheries management science has, because of various uncertainties, to instead be primarily an exercise in robust statistical estimation Though, as an Applied Mathematician, I considered (like Kepler) that this “smelt like a cartload of dung” ...
... Reality though forced me to the Keplerian epiphany that fisheries management science has, because of various uncertainties, to instead be primarily an exercise in robust statistical estimation Though, as an Applied Mathematician, I considered (like Kepler) that this “smelt like a cartload of dung” ...
Understanding ecosystem dynamics for conservation of
... 1. Ecosystems have higher-order emerging properties that can affect the conservation of species. We identify some of these properties in order to facilitate a better understanding of them. 2. Nonlinear, indirect effects of food web interactions among species can produce counterintuitive changes in p ...
... 1. Ecosystems have higher-order emerging properties that can affect the conservation of species. We identify some of these properties in order to facilitate a better understanding of them. 2. Nonlinear, indirect effects of food web interactions among species can produce counterintuitive changes in p ...
Chapter 2 Large marine ecosystems assessment methodology
... affecting the delivery (and value) of ecosystem services (Box 5), with potential consequences for people (Box 6). While this conceptual framework identifies the protection of ecosystem services as the main pathway for mitigating consequences for people, under some other internationally recognized va ...
... affecting the delivery (and value) of ecosystem services (Box 5), with potential consequences for people (Box 6). While this conceptual framework identifies the protection of ecosystem services as the main pathway for mitigating consequences for people, under some other internationally recognized va ...
1 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... C) when the organism chooses the nutrition that it needs D) when an organism selects a specific environment in which to live from the range of options it encounters. E) is demonstrated when population growth rises sharply at first, and then begins to level off as the limiting factors become stronger ...
... C) when the organism chooses the nutrition that it needs D) when an organism selects a specific environment in which to live from the range of options it encounters. E) is demonstrated when population growth rises sharply at first, and then begins to level off as the limiting factors become stronger ...
Draft Fisheries Plan Palmerston
... Some areas of Palmerston atoll are still healthy and host good amount of fish. ...
... Some areas of Palmerston atoll are still healthy and host good amount of fish. ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.