BIODIVERSITY-ECOSYSTEM FUNCTION RESEARCH
... any change in species composition (the identity of species present) constitutes a change in biodiversity (Chapin et al. 2000). However, in the BDEF literature, a clear distinction has been made between effects of biodiversity (as defined above) and effects of composition (e.g., Downing & Leibold 200 ...
... any change in species composition (the identity of species present) constitutes a change in biodiversity (Chapin et al. 2000). However, in the BDEF literature, a clear distinction has been made between effects of biodiversity (as defined above) and effects of composition (e.g., Downing & Leibold 200 ...
Ecosystems and Population Change Ecosystems and Population
... oikos, meaning “the place where one lives,” with logos, meaning “study of.” Ecological studies can begin at the level of a single organism. For example, an investigation could be designed to determine how the individual interacts with its environment, and how factors in the environment affect its gr ...
... oikos, meaning “the place where one lives,” with logos, meaning “study of.” Ecological studies can begin at the level of a single organism. For example, an investigation could be designed to determine how the individual interacts with its environment, and how factors in the environment affect its gr ...
Chapter 16(18)-FA.indd
... of demersal trawl surveys using the swept areamethod (see Appendix A). Two different types of demersal survey were conducted in the area, i.e. the coastal and offshore surveys, both conducted in different areas and years. To determine the biomass for the total area, information from the offshore and ...
... of demersal trawl surveys using the swept areamethod (see Appendix A). Two different types of demersal survey were conducted in the area, i.e. the coastal and offshore surveys, both conducted in different areas and years. To determine the biomass for the total area, information from the offshore and ...
Ch. 7 Notes-Aquatic Ecosystems
... • Rocky shores have many more plants and animals than sandy shores do because the rocks provide anchorage for seaweed that animals can live on. • Sandy shores dry out when the tide goes out, and many organisms that live between sand grains eat the plankton left stranded on the sand. • A Barrier isla ...
... • Rocky shores have many more plants and animals than sandy shores do because the rocks provide anchorage for seaweed that animals can live on. • Sandy shores dry out when the tide goes out, and many organisms that live between sand grains eat the plankton left stranded on the sand. • A Barrier isla ...
Terrestrial Habitat, Ecosystem and Plants Technical Report
... areas of the earth’s surface based on surficial geology, landforms, soils, vegetation, climate, wildlife, water and human features. The dominance of any one or more of these factors varies with the given ecological land unit. This holistic approach to land classification can be applied incrementally ...
... areas of the earth’s surface based on surficial geology, landforms, soils, vegetation, climate, wildlife, water and human features. The dominance of any one or more of these factors varies with the given ecological land unit. This holistic approach to land classification can be applied incrementally ...
ESM 201
... Mainly because of human demand for energy, obtained by burning fossil fuels, humans are causing rapid increases in atmospheric CO2. What are the sources and sinks for this CO2? What controls global CO2? What are the impacts of increased CO2 on climate? Evidence for and against global warming. What a ...
... Mainly because of human demand for energy, obtained by burning fossil fuels, humans are causing rapid increases in atmospheric CO2. What are the sources and sinks for this CO2? What controls global CO2? What are the impacts of increased CO2 on climate? Evidence for and against global warming. What a ...
How Communities Evolve - New England Complex Systems Institute
... energy values would be represented as a trajectory. These trajectories, which represent the behavior of the variables of the system, correspond in general to solutions of a system of differential equations. The continuous arrival of radiant energy from the sun, which is transformed into plant resour ...
... energy values would be represented as a trajectory. These trajectories, which represent the behavior of the variables of the system, correspond in general to solutions of a system of differential equations. The continuous arrival of radiant energy from the sun, which is transformed into plant resour ...
BCS312 Module 1
... order to understand the interactions of a vulnerable ecosystem. As tools of analysis, we enlist multiple disciplines and the perspectives of time, size, and complexity of the organism to explain patterns of ecological activity. The biocomplexity of the Arctic is linked to the global ecosystem, and n ...
... order to understand the interactions of a vulnerable ecosystem. As tools of analysis, we enlist multiple disciplines and the perspectives of time, size, and complexity of the organism to explain patterns of ecological activity. The biocomplexity of the Arctic is linked to the global ecosystem, and n ...
Soil Biological Communities
... Why They Are Important Bacteria are important in the carbon cycle. They contribute carbon to the system by fixation (photosynthesis) and decomposition. Bacteria are important decomposers in grassland environments. Actinomycetes are particularly effective at breaking down tough substances like cellul ...
... Why They Are Important Bacteria are important in the carbon cycle. They contribute carbon to the system by fixation (photosynthesis) and decomposition. Bacteria are important decomposers in grassland environments. Actinomycetes are particularly effective at breaking down tough substances like cellul ...
International Capital vs. Local Population: The Environmental Conflict
... Pollution from mining can be controlled by technology. However, the total amount of effluents can be reduced only if material removal diminishes. Instead, most of the time, water or air pollution is reduced by “storing” pollutants in special places. When natural environmental variations or human er ...
... Pollution from mining can be controlled by technology. However, the total amount of effluents can be reduced only if material removal diminishes. Instead, most of the time, water or air pollution is reduced by “storing” pollutants in special places. When natural environmental variations or human er ...
BIOSC 141-S14 96KB Jul 14 2014 05:40:02 PM
... 17. Discuss the various climatic features associated with terrestrial ecosystems, and discuss their distinctive life forms. Discuss aquatic ecosystems and their distinctive life forms. 18. Discuss and interpret the movement of energy and materials through ecosystems. Interpret food webs and pyramids ...
... 17. Discuss the various climatic features associated with terrestrial ecosystems, and discuss their distinctive life forms. Discuss aquatic ecosystems and their distinctive life forms. 18. Discuss and interpret the movement of energy and materials through ecosystems. Interpret food webs and pyramids ...
Climate
... cover is a good insulator that insulates the ground; and melting snow is a heat sink, owing to its latent heat of fusion (Zhang et al., 1997). In spite of the high albedo from spring and early summer snow and cloud cover, net radiation is positive throughout the year (Hare, F. K. 1972). The microcli ...
... cover is a good insulator that insulates the ground; and melting snow is a heat sink, owing to its latent heat of fusion (Zhang et al., 1997). In spite of the high albedo from spring and early summer snow and cloud cover, net radiation is positive throughout the year (Hare, F. K. 1972). The microcli ...
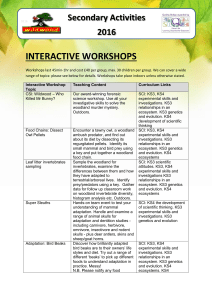
Secondary Activities
... Workshops last 45min-1hr and cost £40 per group, max. 30 children per group. We can cover a wide range of topics: please see below for details. Workshops take place indoors unless otherwise stated. ...
... Workshops last 45min-1hr and cost £40 per group, max. 30 children per group. We can cover a wide range of topics: please see below for details. Workshops take place indoors unless otherwise stated. ...
Integrating Different Organizational Levels in Benthic Biodiversity
... measure of diversity and some measure of ecosystem functioning. Diversity encompasses all levels of biological organization from genes to ecosystems; however, most BEF studies emphasize the consequences of species richness. Ecosystem functioning includes all ecological processes such as element cycl ...
... measure of diversity and some measure of ecosystem functioning. Diversity encompasses all levels of biological organization from genes to ecosystems; however, most BEF studies emphasize the consequences of species richness. Ecosystem functioning includes all ecological processes such as element cycl ...
Homeostasis and the envrionment
... cooperation. They are natural occurrences and cause cells to stick to one another. An example of a biofilm is the layer of dental plaque that forms on teeth overnight. In this example, the biofilm can disrupt homeostasis by cause tooth decay. ...
... cooperation. They are natural occurrences and cause cells to stick to one another. An example of a biofilm is the layer of dental plaque that forms on teeth overnight. In this example, the biofilm can disrupt homeostasis by cause tooth decay. ...
Document
... which there is a significant edge influence (Chen et al. 1992). Distance of edge influence may be considered to represent a zone of edge influence that extends to both sides of the edge, in which structure or composition is different from either of the adjacent communities. This zone may actually be ...
... which there is a significant edge influence (Chen et al. 1992). Distance of edge influence may be considered to represent a zone of edge influence that extends to both sides of the edge, in which structure or composition is different from either of the adjacent communities. This zone may actually be ...
Comparative Cryptogam Ecology: A Review of Bryophyte and
... † Background Recent decades have seen a major surge in the study of interspecific variation in functional traits in comparative plant ecology, as a tool to understanding and predicting ecosystem functions and their responses to environmental change. However, this research has been biased almost excl ...
... † Background Recent decades have seen a major surge in the study of interspecific variation in functional traits in comparative plant ecology, as a tool to understanding and predicting ecosystem functions and their responses to environmental change. However, this research has been biased almost excl ...
biodiversity loss and ecosystem functioning
... Such detrital material is largely derived from macroalgae; on shores that are dominated by microalgae, much of the primary production passes directly into a diverse assemblage of in situ grazers (Mann 1973, Miller and Mann 1973, Raffaelli and Hawkins 1996, Leguerrier et al. 2003). Changes in cover o ...
... Such detrital material is largely derived from macroalgae; on shores that are dominated by microalgae, much of the primary production passes directly into a diverse assemblage of in situ grazers (Mann 1973, Miller and Mann 1973, Raffaelli and Hawkins 1996, Leguerrier et al. 2003). Changes in cover o ...
AGE 301: PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
... In this lesson, the characteristics and global distribution of three fundamental climatic elements, namely temperature, evaporation and precipitation will be discussed. In Physical Geography II, climate was defined as the average conditions of the atmosphere near the earth’s surface over a period of ...
... In this lesson, the characteristics and global distribution of three fundamental climatic elements, namely temperature, evaporation and precipitation will be discussed. In Physical Geography II, climate was defined as the average conditions of the atmosphere near the earth’s surface over a period of ...
How molecular tools can help understanding species
... assessment of these before and after restoration is essential to set up restoration goals and evaluate success. These interactions include pollination, seed dispersal, nitrogen fixation and other microbial symbioses as developed in the examples above, but also top-down control of keystone species o ...
... assessment of these before and after restoration is essential to set up restoration goals and evaluate success. These interactions include pollination, seed dispersal, nitrogen fixation and other microbial symbioses as developed in the examples above, but also top-down control of keystone species o ...
The Bottom Line: Impacts of Alien Plant Invasions in Protected Areas
... nutrient cycling, hydrology and fire regimes (Levine et al. 2003). These authors found that many studies examined the impacts of invasions on plant diversity and composition, but fewer than 5 % test whether these effects arise through competition, allelopathy, alteration of ecosystem variables or ot ...
... nutrient cycling, hydrology and fire regimes (Levine et al. 2003). These authors found that many studies examined the impacts of invasions on plant diversity and composition, but fewer than 5 % test whether these effects arise through competition, allelopathy, alteration of ecosystem variables or ot ...
Genetic variation and community change selection, evolution, and
... extent to which evolutionary forces change genetic variation in one species and affect associated communities, and whether these changes feed back to affect the original species, is less clear. One conceptual model for understanding the extended effects of evolution acting on intraspecific genetic va ...
... extent to which evolutionary forces change genetic variation in one species and affect associated communities, and whether these changes feed back to affect the original species, is less clear. One conceptual model for understanding the extended effects of evolution acting on intraspecific genetic va ...
Genetic variation and community change selection, evolution, and
... extent to which evolutionary forces change genetic variation in one species and affect associated communities, and whether these changes feed back to affect the original species, is less clear. One conceptual model for understanding the extended effects of evolution acting on intraspecific genetic va ...
... extent to which evolutionary forces change genetic variation in one species and affect associated communities, and whether these changes feed back to affect the original species, is less clear. One conceptual model for understanding the extended effects of evolution acting on intraspecific genetic va ...
2013 печ. 521М Ecology
... complexity of ecosystems over longer temporal and broader spatial scales. The International Long Term Ecological Network manages and exchanges scientific information among research sites. The longest experiment in existence is the Park Grass Experiment that was initiated in 1856. Another example inc ...
... complexity of ecosystems over longer temporal and broader spatial scales. The International Long Term Ecological Network manages and exchanges scientific information among research sites. The longest experiment in existence is the Park Grass Experiment that was initiated in 1856. Another example inc ...
Food webs: reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity
... Ecosystem function: the physical, chemical, and biological processes or attributes that contribute to the self-maintenance of the ecosystem; including energy flow, nutrient cycling, filtering, buffering of contaminants, and regulation of populations. Interaction strength: a measure of how much a pre ...
... Ecosystem function: the physical, chemical, and biological processes or attributes that contribute to the self-maintenance of the ecosystem; including energy flow, nutrient cycling, filtering, buffering of contaminants, and regulation of populations. Interaction strength: a measure of how much a pre ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.