Human Involvement in Food Webs
... to plants, inter alia. Food webs are a synthesis of bottom-up energy and nutrient flow from plant producers to consumers and top-down regulation of producers by consumers. The trophic cascade is the simplest topdown interaction and accounts for a great deal of what is known about food webs. In three- ...
... to plants, inter alia. Food webs are a synthesis of bottom-up energy and nutrient flow from plant producers to consumers and top-down regulation of producers by consumers. The trophic cascade is the simplest topdown interaction and accounts for a great deal of what is known about food webs. In three- ...
Organic matter and biological activity
... In general, bacteria decompose the easy-to-use substrates; simple carbon compounds such as root exudates and fresh plant litter. The waste products produced by bacteria become soil organic matter. This waste material is less decomposable than the original plant and animal material, but can be used b ...
... In general, bacteria decompose the easy-to-use substrates; simple carbon compounds such as root exudates and fresh plant litter. The waste products produced by bacteria become soil organic matter. This waste material is less decomposable than the original plant and animal material, but can be used b ...
Locally rare species influence grassland ecosystem multifunctionality
... trophic groups using standard methodology (see electronic supplementary material, table S1 for details). Overall, our sampling included approximately 4300 taxa (the taxonomic unit varied between groups, electronic supplementary material, table S1, but we refer to all as ‘species’, for simplicity). T ...
... trophic groups using standard methodology (see electronic supplementary material, table S1 for details). Overall, our sampling included approximately 4300 taxa (the taxonomic unit varied between groups, electronic supplementary material, table S1, but we refer to all as ‘species’, for simplicity). T ...
Introduction
... Adopt a linear outline by building each new idea on the previous one. As this paper will show, the clear-cutting of the rainforest has already eliminated much of the natural habitat of the red-tailed swallow, thus reducing the population growth rate of a species that plays a vital part in maintainin ...
... Adopt a linear outline by building each new idea on the previous one. As this paper will show, the clear-cutting of the rainforest has already eliminated much of the natural habitat of the red-tailed swallow, thus reducing the population growth rate of a species that plays a vital part in maintainin ...
PDF
... a national or regional sustainability wealth account or can serve as a standalone wealth index to assess the management of ecosystem as a whole. We extend Fenichel and Abbott (2014) and Fenichel et al. (2016), FA, method to approximate realized shadow prices for multiple interacting stocks of natura ...
... a national or regional sustainability wealth account or can serve as a standalone wealth index to assess the management of ecosystem as a whole. We extend Fenichel and Abbott (2014) and Fenichel et al. (2016), FA, method to approximate realized shadow prices for multiple interacting stocks of natura ...
Lesson Overview
... changes that occur in a community over time. • especially after disturbances, as some species die out and new species move in. • the number of different species present typically increases. ...
... changes that occur in a community over time. • especially after disturbances, as some species die out and new species move in. • the number of different species present typically increases. ...
best policy guidance for the integration of biodiversity and
... opportunities to provide benefits to biodiversity and ecosystem services through restoration. • Harvest and resource consumption is highly relevant to operations that cause direct exploitation of species but also relates to all operations that use natural water supplies in their operations. Recomme ...
... opportunities to provide benefits to biodiversity and ecosystem services through restoration. • Harvest and resource consumption is highly relevant to operations that cause direct exploitation of species but also relates to all operations that use natural water supplies in their operations. Recomme ...
Locally rare species influence grassland ecosystem
... trophic groups using standard methodology (see electronic supplementary material, table S1 for details). Overall, our sampling included approximately 4300 taxa (the taxonomic unit varied between groups, electronic supplementary material, table S1, but we refer to all as ‘species’, for simplicity). T ...
... trophic groups using standard methodology (see electronic supplementary material, table S1 for details). Overall, our sampling included approximately 4300 taxa (the taxonomic unit varied between groups, electronic supplementary material, table S1, but we refer to all as ‘species’, for simplicity). T ...
Ecology - Hardin County Schools
... All organisms have the ability to grow and reproduce. To grow and reproduce, organisms must get materials and energy from the environment. Plants obtain their energy from the sun through photosynthesis, whereas animals obtain their energy from other organisms. Either way, these plants and animals, a ...
... All organisms have the ability to grow and reproduce. To grow and reproduce, organisms must get materials and energy from the environment. Plants obtain their energy from the sun through photosynthesis, whereas animals obtain their energy from other organisms. Either way, these plants and animals, a ...
Caught in the food web: complexity made simple?*
... similar the combined species are and what questions we ask about them. Suppose, for example, that in a model of an upwelling system we create a trophic species called dinoflagellates, a lesser condensation than the typical trophic species. Dinoflagellates are important in the diet of newly-hatched a ...
... similar the combined species are and what questions we ask about them. Suppose, for example, that in a model of an upwelling system we create a trophic species called dinoflagellates, a lesser condensation than the typical trophic species. Dinoflagellates are important in the diet of newly-hatched a ...
Undetected Species Losses, Food Webs, and
... to facilitate increased predation on ungulate neonates, at least in localized settings, prey-predator relationships are dynamic across space and time. If the loss of wolves promotes coyote numbers, then a top-down effect on fawn survival may be prominent (Berger, 2007). Still, the role of potentiall ...
... to facilitate increased predation on ungulate neonates, at least in localized settings, prey-predator relationships are dynamic across space and time. If the loss of wolves promotes coyote numbers, then a top-down effect on fawn survival may be prominent (Berger, 2007). Still, the role of potentiall ...
Food webs and energy transfer in a grassland ecosystem
... Explain to students that detritivores and decomposers complete food chains. Detritivores are organisms that eat non-living plant and animal remains. For example, scavengers such as some raptors eat dead animals. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria, turn organic waste, such as decaying plants, into i ...
... Explain to students that detritivores and decomposers complete food chains. Detritivores are organisms that eat non-living plant and animal remains. For example, scavengers such as some raptors eat dead animals. Decomposers like fungi and bacteria, turn organic waste, such as decaying plants, into i ...
ecosystem
... consumers (carnivores) to consumers (carnivores) to tertiary tertiary consumers (carnivores consumers that feed on other carnivores) (carnivores that feed on other carnivores) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... consumers (carnivores) to consumers (carnivores) to tertiary tertiary consumers (carnivores consumers that feed on other carnivores) (carnivores that feed on other carnivores) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Succession Power Point Notes - ESC-2
... How does secondary succession help restore equilibrium to a region destroyed by a flood? F ...
... How does secondary succession help restore equilibrium to a region destroyed by a flood? F ...
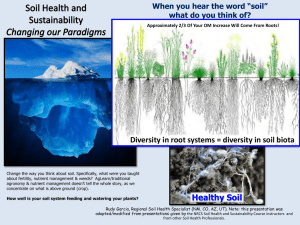
Diversity in root systems = diversity in soil biota Healthy Soil
... In non-mycorrhizal rhizospheres, amino acids, which are the primary components of proteins, must undergo extensive and time-consuming decomposition processes by bacteria and other soil organisms before nitrogen is released in inorganic (NH4), plant-usable forms. Bacteria (Nitrosomonas/Nitrobacter) c ...
... In non-mycorrhizal rhizospheres, amino acids, which are the primary components of proteins, must undergo extensive and time-consuming decomposition processes by bacteria and other soil organisms before nitrogen is released in inorganic (NH4), plant-usable forms. Bacteria (Nitrosomonas/Nitrobacter) c ...
13 Vocabulary Practice
... from accessing its entire home range. 10. A practice in which natural resources are used and ...
... from accessing its entire home range. 10. A practice in which natural resources are used and ...
Animating the Carbon Cycle - University of California, Santa Cruz
... carbon exchange and storage. Although mechanisms accounting for the role of animals in biogeochemical processes in general, and the carbon cycle specifically, are becoming better understood (Vanni 2002; Schmitz and others 2010), the magnitude of their effects remains remain poorly quantified. This i ...
... carbon exchange and storage. Although mechanisms accounting for the role of animals in biogeochemical processes in general, and the carbon cycle specifically, are becoming better understood (Vanni 2002; Schmitz and others 2010), the magnitude of their effects remains remain poorly quantified. This i ...
Using Natural Range of Variation to Set Decision Thresholds: A
... Fig. 8.1 Three potential relationships between natural range of variation (NRV; open circle), desired conditions (filled circle), and current conditions (hatched circle) and ease of path among them (line). a Desired conditions are within NRV; moving current conditions to either will require effort. ...
... Fig. 8.1 Three potential relationships between natural range of variation (NRV; open circle), desired conditions (filled circle), and current conditions (hatched circle) and ease of path among them (line). a Desired conditions are within NRV; moving current conditions to either will require effort. ...
Ecosystems and Energy
... Phosphorus is a major constituent of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP Phosphate (PO43−) is the most important inorganic form of phosphorus The largest reservoirs are sedimentary rocks of marine origin, the soil, oceans, and organisms ...
... Phosphorus is a major constituent of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP Phosphate (PO43−) is the most important inorganic form of phosphorus The largest reservoirs are sedimentary rocks of marine origin, the soil, oceans, and organisms ...
Ch. 42 Text
... Phosphorus is a major constituent of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP Phosphate (PO43−) is the most important inorganic form of phosphorus The largest reservoirs are sedimentary rocks of marine origin, the soil, oceans, and organisms ...
... Phosphorus is a major constituent of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP Phosphate (PO43−) is the most important inorganic form of phosphorus The largest reservoirs are sedimentary rocks of marine origin, the soil, oceans, and organisms ...
Bio 4.3
... glacier exposed barren rock. Over the course of more than 100 years, a series of changes has led to the hemlock and spruce forest currently found in the area. Changes in this community will continue for centuries. ...
... glacier exposed barren rock. Over the course of more than 100 years, a series of changes has led to the hemlock and spruce forest currently found in the area. Changes in this community will continue for centuries. ...
Introduction - Princeton University Press
... iron, and participate in redox reactions (Hartzfeld et al. 2002). Such chemical interactions are important across a broad spectrum of biological processes from nutrient absorption in the gut of mammalian herbivores to the decomposition of terrestrial plant litter. The chemistry of primary producers ...
... iron, and participate in redox reactions (Hartzfeld et al. 2002). Such chemical interactions are important across a broad spectrum of biological processes from nutrient absorption in the gut of mammalian herbivores to the decomposition of terrestrial plant litter. The chemistry of primary producers ...
Animating the Carbon Cycle - University of California, Santa Cruz
... carbon exchange and storage. Although mechanisms accounting for the role of animals in biogeochemical processes in general, and the carbon cycle specifically, are becoming better understood (Vanni 2002; Schmitz and others 2010), the magnitude of their effects remains remain poorly quantified. This i ...
... carbon exchange and storage. Although mechanisms accounting for the role of animals in biogeochemical processes in general, and the carbon cycle specifically, are becoming better understood (Vanni 2002; Schmitz and others 2010), the magnitude of their effects remains remain poorly quantified. This i ...
Plant–soil feedbacks: connecting ecosystem ecology and evolution
... interactions with soil microbes create genetic environments that also impact phenotypes. Such is the case when plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in the soil environment produce phytohormones that direct plant root growth, mycorrhizal development of roots or root nodule formation for symbiotic nit ...
... interactions with soil microbes create genetic environments that also impact phenotypes. Such is the case when plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in the soil environment produce phytohormones that direct plant root growth, mycorrhizal development of roots or root nodule formation for symbiotic nit ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.