Producers are the energy gateway
... If the plants or other producers of an ecosystem were removed, there would be no way for energy to enter the food web, and the ecological community would collapse. That's because energy isn't recycled: instead, it's dissipated as heat as it moves through the ecosystem, and must be ...
... If the plants or other producers of an ecosystem were removed, there would be no way for energy to enter the food web, and the ecological community would collapse. That's because energy isn't recycled: instead, it's dissipated as heat as it moves through the ecosystem, and must be ...
Ecology - One Day Enrichment
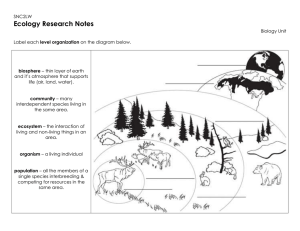
... Levels of Organization • Species – group of organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring • Population – a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area • Community – different populations that live in the same area • Ecosystem – all the organisms plus the ...
... Levels of Organization • Species – group of organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring • Population – a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area • Community – different populations that live in the same area • Ecosystem – all the organisms plus the ...
Community Ecology - Jedi`s Biology Web Page
... A biological community consists of interacting species, usually living within a defined area. A community lies between the spatial scales of a population and a biome. Community Ecology is the study of how a given ecosystem functions. Matter is conserved Matter = all material in the universe that has ...
... A biological community consists of interacting species, usually living within a defined area. A community lies between the spatial scales of a population and a biome. Community Ecology is the study of how a given ecosystem functions. Matter is conserved Matter = all material in the universe that has ...
Ecology Notes Powerpoint
... The population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. ...
... The population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth, at the population’s carrying capacity. ...
Marine Ecology Terms
... • Acid rain is formed when sulfur and nitrogen oxide are emitted into the air from burning of fossil fuels. ...
... • Acid rain is formed when sulfur and nitrogen oxide are emitted into the air from burning of fossil fuels. ...
Foraging/Hunting-Gathering:
... Low-energy budget: It’s the minimum outlay of energy for the extraction of necessary resources Generally, the adaptive strategy used by H-G’s Primary source of energy – human muscle power! ...
... Low-energy budget: It’s the minimum outlay of energy for the extraction of necessary resources Generally, the adaptive strategy used by H-G’s Primary source of energy – human muscle power! ...
Ecology Review Set
... 2. Explain the carbon cycle and how pollution relates to it. 3. What processes are involved in the hydrologic (water) cycle? 4. How does the carbon cycle relate to the oxygen cycle? 5. How is carbon released in to the atmosphere? 6. How is carbon released into the soil? 7. Define the terms biotic an ...
... 2. Explain the carbon cycle and how pollution relates to it. 3. What processes are involved in the hydrologic (water) cycle? 4. How does the carbon cycle relate to the oxygen cycle? 5. How is carbon released in to the atmosphere? 6. How is carbon released into the soil? 7. Define the terms biotic an ...
Notes - Academic Workshop
... An ecosystem consists of both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) things interacting together in a natural environment. Sort the biotic and abiotic limiting factors to population size in a community. Biotic (living) ...
... An ecosystem consists of both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) things interacting together in a natural environment. Sort the biotic and abiotic limiting factors to population size in a community. Biotic (living) ...
Ch 4 Outline
... B. A population consists of a group of interacting individuals of the same species occupying a specific area. Genetic diversity explains why these individuals may not behave nor look exactly alike. The habitat is the place where a population or an individual usually lives. Its distribution or range ...
... B. A population consists of a group of interacting individuals of the same species occupying a specific area. Genetic diversity explains why these individuals may not behave nor look exactly alike. The habitat is the place where a population or an individual usually lives. Its distribution or range ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems: What are They and How Do They Work
... B. A population consists of a group of interacting individuals of the same species occupying a specific area. Genetic diversity explains why these individuals may not behave nor look exactly alike. The habitat is the place where a population or an individual usually lives. Its distribution or range ...
... B. A population consists of a group of interacting individuals of the same species occupying a specific area. Genetic diversity explains why these individuals may not behave nor look exactly alike. The habitat is the place where a population or an individual usually lives. Its distribution or range ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... 2. Some of the biomass must be used for the producers’ own respiration. Net primary productivity (NPP) is the rate which producers use photosynthesis to store biomass minus the rate which they use energy for aerobic respiration. NPP measures how fast producers can provide biomass needed by consumers ...
... 2. Some of the biomass must be used for the producers’ own respiration. Net primary productivity (NPP) is the rate which producers use photosynthesis to store biomass minus the rate which they use energy for aerobic respiration. NPP measures how fast producers can provide biomass needed by consumers ...
unit 6 vocabulary: ecology
... 6. Transpiration- loss of water through a plant’s leaves 7. Precipitation –water falling in any form, such as snow, ice, or rain 8. Evaporation- change of matter from a liquid state to a gaseous state (vapor) at a temperature below its boiling point 9. Ecology- The study of interactions between orga ...
... 6. Transpiration- loss of water through a plant’s leaves 7. Precipitation –water falling in any form, such as snow, ice, or rain 8. Evaporation- change of matter from a liquid state to a gaseous state (vapor) at a temperature below its boiling point 9. Ecology- The study of interactions between orga ...
Keystone Biology Review Guide – Ecology BIO.B.4.1.1 Describe the
... BIO.B.4.2.3 Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle). The Water Cycle Key processes in the water cycle are evaporation, transpiration, and precipitation. The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the two ...
... BIO.B.4.2.3 Describe how matter recycles through an ecosystem (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle). The Water Cycle Key processes in the water cycle are evaporation, transpiration, and precipitation. The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the two ...
Unit 2: Cytology
... Carrying capacity: maximum population size of the species that can be supported indefinitely. Dynamic equilibrium – populations fluctuate around carrying capacity. J-shaped ...
... Carrying capacity: maximum population size of the species that can be supported indefinitely. Dynamic equilibrium – populations fluctuate around carrying capacity. J-shaped ...
Unit 2 * Ecology
... Position that organisms occupy on the food chain or each step in the food chain ...
... Position that organisms occupy on the food chain or each step in the food chain ...
Vocabulary Unit Four The Ecosystem and the Environment # 1-10
... 18. Still Water – water that does not flow; land locked; no outlet or inlet 19. Running Water – water that continuously flows/moves to larger main body of water; inlet and outlet 20. Shallow Seas – oceans and continents meet; sunlight reaches the bottom levels to create diverse life in the water (p ...
... 18. Still Water – water that does not flow; land locked; no outlet or inlet 19. Running Water – water that continuously flows/moves to larger main body of water; inlet and outlet 20. Shallow Seas – oceans and continents meet; sunlight reaches the bottom levels to create diverse life in the water (p ...
Ecology
... • Detritivores feed on the remains of plants, animals and other dead matter. • Decomposers breaks down organic matter. ...
... • Detritivores feed on the remains of plants, animals and other dead matter. • Decomposers breaks down organic matter. ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Ecologists Study
... 20. ______________________ organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once living resources, such as plants and animals. 21. Consumers are also called _________________________. Hetero means “different” 22. All ecosystems depend on ________________________, because they provide the ba ...
... 20. ______________________ organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once living resources, such as plants and animals. 21. Consumers are also called _________________________. Hetero means “different” 22. All ecosystems depend on ________________________, because they provide the ba ...
Ecosystems with fill
... energy of sunlight inside Earth’s atmosphere and maintain Earth’s temperature range this is called the… ...
... energy of sunlight inside Earth’s atmosphere and maintain Earth’s temperature range this is called the… ...
Ecology 1-
... ago due to human activity (burning of fossil fuels) • The atm has not held this much Carbon for at least 420,000 years http://www.ucar.edu/ (The National Center for Atmospheric Research) ...
... ago due to human activity (burning of fossil fuels) • The atm has not held this much Carbon for at least 420,000 years http://www.ucar.edu/ (The National Center for Atmospheric Research) ...
Biology EOC Goal 5:
... 1. Explain human population graphs- both historical and potential using graph to the right. ...
... 1. Explain human population graphs- both historical and potential using graph to the right. ...
Ecology
... Population = all the individuals of one species living in a given area Community = all the populations (living things) living in a given area (all species) Ecosystem = includes all living things and non-living factors in a given area Includes the study of: I) Biotic factors = living organisms ...
... Population = all the individuals of one species living in a given area Community = all the populations (living things) living in a given area (all species) Ecosystem = includes all living things and non-living factors in a given area Includes the study of: I) Biotic factors = living organisms ...
Community Eco Part 1 Test Review
... Honors Biology Community Ecology Test Part I: Community Interactions and Energy Flow Review Sheet Test will be given in a 55 minute period. During that time you will be asked to answer multiple choice, matching, and/or diagram analysis type questions. This is one of the two parts to each test. The s ...
... Honors Biology Community Ecology Test Part I: Community Interactions and Energy Flow Review Sheet Test will be given in a 55 minute period. During that time you will be asked to answer multiple choice, matching, and/or diagram analysis type questions. This is one of the two parts to each test. The s ...