12A Relationships
... such close associations, including parasitism (a form of exploitation), mutualism, and commensalism. ...
... such close associations, including parasitism (a form of exploitation), mutualism, and commensalism. ...
Energy Flow
... produce their own food. a. photosynthesis= the process of using solar energy to produce food (Ex: plants). b. chemosynthesis= the process of using inorganic compounds or chemicals to produce food (Ex: sulfur bacteria near hydrothermal vents). Autotrophs are the foundation of all ecosystems because t ...
... produce their own food. a. photosynthesis= the process of using solar energy to produce food (Ex: plants). b. chemosynthesis= the process of using inorganic compounds or chemicals to produce food (Ex: sulfur bacteria near hydrothermal vents). Autotrophs are the foundation of all ecosystems because t ...
Think like an Ecologist… a scientist who studies the relationships
... Nonrenewable resource: Resource that exists in a fixed amount and has the potential for renewal only by geological, physical, and chemical processes taking place over hundreds of millions to billions of years. Examples are copper, aluminum, coal, and oil. Overfishing: Harvesting so many fish of a sp ...
... Nonrenewable resource: Resource that exists in a fixed amount and has the potential for renewal only by geological, physical, and chemical processes taking place over hundreds of millions to billions of years. Examples are copper, aluminum, coal, and oil. Overfishing: Harvesting so many fish of a sp ...
energy
... • Living organisms are a reservoir in which carbon exists in carbohydrates (mainly cellulose) and fats, nitrogen in protein, and phosphorus in ATP ...
... • Living organisms are a reservoir in which carbon exists in carbohydrates (mainly cellulose) and fats, nitrogen in protein, and phosphorus in ATP ...
Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow & Nutrient Cycling
... • Living organisms are a reservoir in which carbon exists in carbohydrates (mainly cellulose) and fats, nitrogen in protein, and phosphorus in ATP ...
... • Living organisms are a reservoir in which carbon exists in carbohydrates (mainly cellulose) and fats, nitrogen in protein, and phosphorus in ATP ...
Principles of Ecology
... ◦There are different parts that make up any environment: Biotic factors are all of the living ...
... ◦There are different parts that make up any environment: Biotic factors are all of the living ...
Cell Division and Mitosis
... 3rd level - Secondary consumers (primary carnivores) 4th level - Tertiary consumers (secondary carnivores & parasites) - decomposers feed on organisms from all levels ...
... 3rd level - Secondary consumers (primary carnivores) 4th level - Tertiary consumers (secondary carnivores & parasites) - decomposers feed on organisms from all levels ...
Ecosystems and Biomes
... large fish have invertebrate parasites cleaner mimic gains access to large fish and takes a bite (parasitism & deceit) ...
... large fish have invertebrate parasites cleaner mimic gains access to large fish and takes a bite (parasitism & deceit) ...
Outline - EDHSGreenSea.net
... support more organisms. If people eat at a lower trophic level (fruits, vegetables, grains directly consumed) earth can support more people. There is a large loss of energy between successive trophic levels. G. Production of biomass takes place at different rates among different ecosystems. 1. The r ...
... support more organisms. If people eat at a lower trophic level (fruits, vegetables, grains directly consumed) earth can support more people. There is a large loss of energy between successive trophic levels. G. Production of biomass takes place at different rates among different ecosystems. 1. The r ...
Ecology and Ecosystems
... needed in large amounts - CHONPS and a few others Micronutrients needed in small or trace amounts. ...
... needed in large amounts - CHONPS and a few others Micronutrients needed in small or trace amounts. ...
The Biosphere – Ch
... Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems include biotic and abiotic factors. A biotic factor is any living part of an environment. An abiotic factor is any nonliving part of an environment. ...
... Biotic and Abiotic Factors Ecosystems include biotic and abiotic factors. A biotic factor is any living part of an environment. An abiotic factor is any nonliving part of an environment. ...
Keystone Ecology Quia Quiz
... The number of deer increased because populations are always increasing. The number of deer increased because with fewer mountain lions and wolves, the deer had more food to eat. There is not enough information given in the question and diagram to tell why the deer population increased. 17. The diagr ...
... The number of deer increased because populations are always increasing. The number of deer increased because with fewer mountain lions and wolves, the deer had more food to eat. There is not enough information given in the question and diagram to tell why the deer population increased. 17. The diagr ...
Food Webs, and Energy
... More energy is available at the base of the pyramid than at its top. Energy is lost each time one organism eats another. ...
... More energy is available at the base of the pyramid than at its top. Energy is lost each time one organism eats another. ...
Populations and Ecosystems
... organisms at each level. But matter cannot be replenished like the energy from sunlight. The atoms of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and other elements make up the bodies of organisms alive today are the same atoms that have been on Earth since life began. ...
... organisms at each level. But matter cannot be replenished like the energy from sunlight. The atoms of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and other elements make up the bodies of organisms alive today are the same atoms that have been on Earth since life began. ...
16. Changes to Ecosystems
... After bushfires, the native plant population can either be replaced (OS) or can regenerate (VR). The interval between fires can affect the diversity of a plant community. If fire occurs frequently, some species may be lost. If it remains absent for a while, certain animals and plants will die as the ...
... After bushfires, the native plant population can either be replaced (OS) or can regenerate (VR). The interval between fires can affect the diversity of a plant community. If fire occurs frequently, some species may be lost. If it remains absent for a while, certain animals and plants will die as the ...
Ecology Notes - Rochester Century High School
... given area that depend on each other) 10.Ecosystem All biotic and abiotic factors in the community 11.Biome: Areas of similar climatic conditions 12.Biosphere: All areas that sustain life ...
... given area that depend on each other) 10.Ecosystem All biotic and abiotic factors in the community 11.Biome: Areas of similar climatic conditions 12.Biosphere: All areas that sustain life ...
What four areas does population size depend on?
... 13 In the water cycle, what two methods take water into the atmosphere and briefly describe each. • -Evaporation- From areas of concentration of water (Ponds, lakes etc.) • -Transpiration- H20 lost from plants ...
... 13 In the water cycle, what two methods take water into the atmosphere and briefly describe each. • -Evaporation- From areas of concentration of water (Ponds, lakes etc.) • -Transpiration- H20 lost from plants ...
review of human - Hicksville Public Schools
... Although large numbers of zebra mussels often clog water intake pipes of power plants and other industries, the mussels have a benefit. Each mussel filters about a quart of water per day, absorbing cancer-causing PCB’s from lake water in the process. The goby, a bottom-feeding fish from Europe, was ...
... Although large numbers of zebra mussels often clog water intake pipes of power plants and other industries, the mussels have a benefit. Each mussel filters about a quart of water per day, absorbing cancer-causing PCB’s from lake water in the process. The goby, a bottom-feeding fish from Europe, was ...
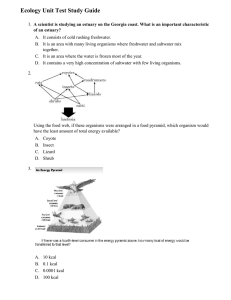
ecology unit study guide
... A. The deer supplies food and oxygen to the green plants. B. The deer supplies food and carbon dioxide to the green plants. C. The green plants supply food and carbon dioxide to the deer. D. The green plants supply food and oxygen to the deer. ...
... A. The deer supplies food and oxygen to the green plants. B. The deer supplies food and carbon dioxide to the green plants. C. The green plants supply food and carbon dioxide to the deer. D. The green plants supply food and oxygen to the deer. ...
Ecological Pyramids
... Ecological pyramids are organized with plants on the bottom, herbivores above the plants, and carnivores above the herbivores. Top carnivores will be at the apex of the ecological pyramid. There are three types of ecological pyramids, energy, numbers and biomass. When energy is passed along a food c ...
... Ecological pyramids are organized with plants on the bottom, herbivores above the plants, and carnivores above the herbivores. Top carnivores will be at the apex of the ecological pyramid. There are three types of ecological pyramids, energy, numbers and biomass. When energy is passed along a food c ...