2015 8th grade Science Study Guide Extended Version
... Ecosystem—interactive systems that include both biological (biotic) and physical (abiotic) components of the environment Population—group of organisms belonging to the same species that live in a particular area Predation—interaction between species in which one species (predator) eats the other (pr ...
... Ecosystem—interactive systems that include both biological (biotic) and physical (abiotic) components of the environment Population—group of organisms belonging to the same species that live in a particular area Predation—interaction between species in which one species (predator) eats the other (pr ...
100
... The zone separating two air masses, of which the cooler, denser mass is advancing and replacing the warmer. ...
... The zone separating two air masses, of which the cooler, denser mass is advancing and replacing the warmer. ...
Chapter 7 Sustainability Review
... 10. The maximum number of organisms in a population that can survive on available resources. 11. The struggle among organisms to access of resources such as food or territory. 12. The interaction between two different species that live together in close association. 13. Variables that affect a popul ...
... 10. The maximum number of organisms in a population that can survive on available resources. 11. The struggle among organisms to access of resources such as food or territory. 12. The interaction between two different species that live together in close association. 13. Variables that affect a popul ...
Nutrient Uptake by Duckweed
... Ecosystems provide “services” that: • control agricultural pests • maintain biodiversity • generate and preserve soils and renew their fertility • contribute to climate stability • purify the air and water • regulate disease carrying organisms • pollinate crops and natural vegetation • moderate wea ...
... Ecosystems provide “services” that: • control agricultural pests • maintain biodiversity • generate and preserve soils and renew their fertility • contribute to climate stability • purify the air and water • regulate disease carrying organisms • pollinate crops and natural vegetation • moderate wea ...
Geologic Time
... All atoms and molecules are perpetually in motion and how that motion affects changes of state There is a relationship between phase of matter and density How the periodic table is organized and how to use the periodic table in order to obtain information about the atom of an element How the periodi ...
... All atoms and molecules are perpetually in motion and how that motion affects changes of state There is a relationship between phase of matter and density How the periodic table is organized and how to use the periodic table in order to obtain information about the atom of an element How the periodi ...
No Slide Title
... Body parts of different organisms that have a similar structure, but not a similar function. ...
... Body parts of different organisms that have a similar structure, but not a similar function. ...
ecology ppt
... • Unlike energy, matter is recycled in the environment. • Matter cycles from one organism to another. • Elements like nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus are RECYCLED in the environment ...
... • Unlike energy, matter is recycled in the environment. • Matter cycles from one organism to another. • Elements like nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus are RECYCLED in the environment ...
Overall Summary of ecosystems File
... are interconnected because organisms have feeding relationships with many different other organisms. So food chains in a network known as a food web. The mass or number of organisms at different trophic levels in a food chain can be expressed visually using a pyramid of biomass or a pyramid of numbe ...
... are interconnected because organisms have feeding relationships with many different other organisms. So food chains in a network known as a food web. The mass or number of organisms at different trophic levels in a food chain can be expressed visually using a pyramid of biomass or a pyramid of numbe ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... conservation and reserve formation may not be viable, or to reverse existing damage, habitat restoration is an alternative. 37.5 Working Toward a Sustainable Society Human society in its current form is not sustainable. A sustainable society should be able to provide the same goods and services for ...
... conservation and reserve formation may not be viable, or to reverse existing damage, habitat restoration is an alternative. 37.5 Working Toward a Sustainable Society Human society in its current form is not sustainable. A sustainable society should be able to provide the same goods and services for ...
Practice AP Questions
... (a ) the increase in concentration of a pollutant as it moves up the food chain (b) certain traits becoming more pronounced through natural or artificial selection (c) growth in size of individuals when given optimum nutrition (d) increase in populations when environmental resistance is low (e) two ...
... (a ) the increase in concentration of a pollutant as it moves up the food chain (b) certain traits becoming more pronounced through natural or artificial selection (c) growth in size of individuals when given optimum nutrition (d) increase in populations when environmental resistance is low (e) two ...
EnSys. 12 Cert. - Study Guide
... bonded to a single carbon atom. Fossil fuels are formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. Emission is the term used to describe the gases and particles which are put into the air or emitted by various sources. Weather is he state of the atmosphere, to the ...
... bonded to a single carbon atom. Fossil fuels are formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. Emission is the term used to describe the gases and particles which are put into the air or emitted by various sources. Weather is he state of the atmosphere, to the ...
File - Holtville FFA The Farmer in All of Us.
... Multiple Choice: (2 points each) 11. An example of the mutualistic symbiotic relationship is: a. A tick that feeds on the blood of a deer b. A cattle egret that eats the bugs off of cattle c. A clown fish that seeks shelter in an anenome while providing food to the ...
... Multiple Choice: (2 points each) 11. An example of the mutualistic symbiotic relationship is: a. A tick that feeds on the blood of a deer b. A cattle egret that eats the bugs off of cattle c. A clown fish that seeks shelter in an anenome while providing food to the ...
Ecology
... energy is lost at each link, the further along the food chain you go, the less energy is available. We use the energy pyramid as a model to show decreasing available energy at each level in the pyramid. ...
... energy is lost at each link, the further along the food chain you go, the less energy is available. We use the energy pyramid as a model to show decreasing available energy at each level in the pyramid. ...
Ecology is the study of the interaction s among living things and
... A change in a single factor can affect an entire ecosystem. A KEYSTONE SPECIES is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
... A change in a single factor can affect an entire ecosystem. A KEYSTONE SPECIES is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
Ecology is the study of the interaction s among living things and
... A change in a single factor can affect an entire ecosystem. A KEYSTONE SPECIES is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
... A change in a single factor can affect an entire ecosystem. A KEYSTONE SPECIES is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
Go with The Flow! Food Chains, Webs, and Pyramids
... ◦ Consumers = things with mouths Primary consumer – herbivore / omnivore Secondary consumer – carnivore / omnivore Tertiary (third) consumer - carnivore ...
... ◦ Consumers = things with mouths Primary consumer – herbivore / omnivore Secondary consumer – carnivore / omnivore Tertiary (third) consumer - carnivore ...
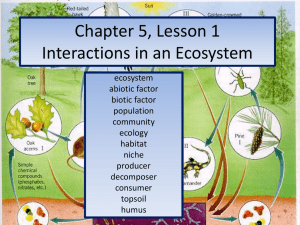
Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Interactions in an Ecosystem
... ecosystem – all the living and non-living things in an area Click to access link! ...
... ecosystem – all the living and non-living things in an area Click to access link! ...
Ecosystems Unit Review
... 21. Ecologists now think climax communities are continually changing since climates continually change over time, so therefore biotic and abiotic factors change over time. For example, long ago most of British Columbia was once covered in ice, then there was a warm period, and then it was covered in ...
... 21. Ecologists now think climax communities are continually changing since climates continually change over time, so therefore biotic and abiotic factors change over time. For example, long ago most of British Columbia was once covered in ice, then there was a warm period, and then it was covered in ...
Name - Humble ISD
... o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Omnivores: ___________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Detritivores: _______________________________________________________________________ ...
... o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Omnivores: ___________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Detritivores: _______________________________________________________________________ ...
Phosphorus and Nitrogen Cycles
... competition: two species use the same resource; they participate in a biological interaction What resources might species compete for? Water, food, nesting site, living space, light, mineral nutrients ...
... competition: two species use the same resource; they participate in a biological interaction What resources might species compete for? Water, food, nesting site, living space, light, mineral nutrients ...
Chapter 3 - Kenton County Schools
... Biome – Biosphere – It extends about _____km above the Earth’s surface to about _____km below If you could shrink earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel ...
... Biome – Biosphere – It extends about _____km above the Earth’s surface to about _____km below If you could shrink earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel ...
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work
... living organisms. It covers most of the earth and provides nutrients for plant growth. Soils are formed by a breaking down of rock, decomposing surface litter and organic matter. Bacteria and other decomposer microorganisms break down some of soil’s organic compounds into simpler inorganic compounds ...
... living organisms. It covers most of the earth and provides nutrients for plant growth. Soils are formed by a breaking down of rock, decomposing surface litter and organic matter. Bacteria and other decomposer microorganisms break down some of soil’s organic compounds into simpler inorganic compounds ...