Topic 2 - Ecology
... resources – Each species occupies its own niche, or role in the ecosystem – Resource partitioning – species use the same resources but in different ways or at different times ...
... resources – Each species occupies its own niche, or role in the ecosystem – Resource partitioning – species use the same resources but in different ways or at different times ...
8.L.3 Understand how organisms interact with and respond to the
... repeatedly and between organisms and their physical environment. As in all material systems, the total amount of matter remains constant, even though its form and location change. Students know that the flow of energy through ecosystems can be described and illustrated in food chains, food webs, and ...
... repeatedly and between organisms and their physical environment. As in all material systems, the total amount of matter remains constant, even though its form and location change. Students know that the flow of energy through ecosystems can be described and illustrated in food chains, food webs, and ...
Ecology Vocabulary Words
... 18. Host - An organism that provides a source of energy or a suitable ...
... 18. Host - An organism that provides a source of energy or a suitable ...
APES Guided Reading * Chapter 2, 3, and 4
... 5. Environmental change can drive both evolution and extinction. Explain. 6. Distinguish the terms niche and habitat. 7. Why is habitat loss the number one cause of loss of biodiversity on Earth today? 8. Would specialists or generalists do better in a human-dominated environment? Why? 9. Why do eco ...
... 5. Environmental change can drive both evolution and extinction. Explain. 6. Distinguish the terms niche and habitat. 7. Why is habitat loss the number one cause of loss of biodiversity on Earth today? 8. Would specialists or generalists do better in a human-dominated environment? Why? 9. Why do eco ...
Bio 11A
... 1. What is the biodiversity crisis? Name 4 species in our local area that are threatened or endangered. 2. What is the estimated rate of extinction today? Why is this significant? 3. Why is biodiversity important to the human population? 4. What is the geographic distribution pattern of species with ...
... 1. What is the biodiversity crisis? Name 4 species in our local area that are threatened or endangered. 2. What is the estimated rate of extinction today? Why is this significant? 3. Why is biodiversity important to the human population? 4. What is the geographic distribution pattern of species with ...
Ms. Fazio
... (2) The population size became limited due to factors such as availability of food. (3) An increase in the chipmunk population caused an increase in the producer population. (4) A predator species came to the area and occupied the same niche as the chipmunks. Energy for this ecosystem originally com ...
... (2) The population size became limited due to factors such as availability of food. (3) An increase in the chipmunk population caused an increase in the producer population. (4) A predator species came to the area and occupied the same niche as the chipmunks. Energy for this ecosystem originally com ...
Q2 Ecology PowerPoint for Marine Bio
... • Some molecules in the food source can’t be broken down. • Some energy is lost as heat. ...
... • Some molecules in the food source can’t be broken down. • Some energy is lost as heat. ...
Community Ecology
... Outline of topics 55.1 Chemicals cycle within ecosystems. • An ecosystem includes all of the organisms living in a particular place, plus the abiotic environment in which they live. (p. 1184) • Due to the Law of Conservation of Matter, all chemical elements are recycled in the environment. The Water ...
... Outline of topics 55.1 Chemicals cycle within ecosystems. • An ecosystem includes all of the organisms living in a particular place, plus the abiotic environment in which they live. (p. 1184) • Due to the Law of Conservation of Matter, all chemical elements are recycled in the environment. The Water ...
Release Test items 11th Grade Obj 3
... G Modern lizards drink more water than their ancestors did. H These lizards cool themselves by evaporation. J Modern lizards excrete more water than their ancestors did. ...
... G Modern lizards drink more water than their ancestors did. H These lizards cool themselves by evaporation. J Modern lizards excrete more water than their ancestors did. ...
Secondary Succession
... fertile enough to hold moisture – Supports the growth of herbs, grasses, and low shrubs – Creates shade which causes mosses and lichens to die – Trees replace grasses and shrubs ...
... fertile enough to hold moisture – Supports the growth of herbs, grasses, and low shrubs – Creates shade which causes mosses and lichens to die – Trees replace grasses and shrubs ...
UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY
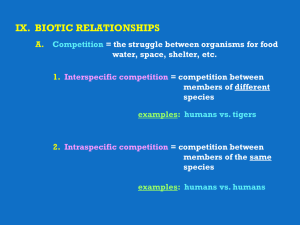
... A. Competition = the struggle between organisms for food water, space, shelter, etc. 1. Interspecific competition = competition between members of different species examples: humans vs. tigers ...
... A. Competition = the struggle between organisms for food water, space, shelter, etc. 1. Interspecific competition = competition between members of different species examples: humans vs. tigers ...
Science Careers in Sustainability
... to meet human needs for natural resources, industrial products, energy, food, transportation, shelter, and effective waste management while conserving and protecting environmental quality and the natural resource base essential for future development. Civil engineers often specialize in an area such ...
... to meet human needs for natural resources, industrial products, energy, food, transportation, shelter, and effective waste management while conserving and protecting environmental quality and the natural resource base essential for future development. Civil engineers often specialize in an area such ...
FREE Sample Here
... animals. C. These plants are actually deriving their food from dying animals, thus the pyramid is inverted. D. The pyramid appears inverted because it is based on a very short time sample, over a year the algae production would likely be ten times the zooplankton in biomass or energy. ...
... animals. C. These plants are actually deriving their food from dying animals, thus the pyramid is inverted. D. The pyramid appears inverted because it is based on a very short time sample, over a year the algae production would likely be ten times the zooplankton in biomass or energy. ...
Ecosystems and Populations Unit Test Study Guide - Parkway C-2
... Predators: ___Red Fox, Red Tailed Hawk______ Prey _____Chipmunk, Red Fox___________ Decomposers: earthworms/bacteria/fungi ...
... Predators: ___Red Fox, Red Tailed Hawk______ Prey _____Chipmunk, Red Fox___________ Decomposers: earthworms/bacteria/fungi ...
Earth`s Surface - Mentor Public Schools
... dramatically. When the environment changes, some plants and animals survive and reproduce and others die or move to new locations. An animal’s patterns of behavior are related to the environment. This includes the kinds and number of other organisms present, the availability of food and resources, a ...
... dramatically. When the environment changes, some plants and animals survive and reproduce and others die or move to new locations. An animal’s patterns of behavior are related to the environment. This includes the kinds and number of other organisms present, the availability of food and resources, a ...
File - Reedley High School Chemistry
... return the raw materials to the environment are called decomposers. As decomposers obtain energy for their own needs, they return simple molecules to the environment to be used again by other organisms. Ecologists use a diagram called a food chain to show to flow of energy from organism to organism ...
... return the raw materials to the environment are called decomposers. As decomposers obtain energy for their own needs, they return simple molecules to the environment to be used again by other organisms. Ecologists use a diagram called a food chain to show to flow of energy from organism to organism ...
Chapter 5: Biodiversity and Conservation
... Introduced species are a worldwide environmental problem. An estimated 40% of the extinctions that have occurred since 1750 are due to introduced species, and billions of dollars are spent every year in an effort to clean up or control the damage caused by ...
... Introduced species are a worldwide environmental problem. An estimated 40% of the extinctions that have occurred since 1750 are due to introduced species, and billions of dollars are spent every year in an effort to clean up or control the damage caused by ...
Ecosystems,FoodWebs,FoodChains(Review)
... Using figure 6.5 summarize the main energy flows in an ecosystem p. 95 Sun = source of all ecosystem energy Producers make food via photosynthesis Consumers eat plants and other consumers to get energy Each time energy moves from one organism to another, energy leaves the system in the form of heat ...
... Using figure 6.5 summarize the main energy flows in an ecosystem p. 95 Sun = source of all ecosystem energy Producers make food via photosynthesis Consumers eat plants and other consumers to get energy Each time energy moves from one organism to another, energy leaves the system in the form of heat ...
Environmental-Science-Jeopardy
... Ants collect food made from the Acacia tree and protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... Ants collect food made from the Acacia tree and protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
Environmental Science Jeopardy
... Ants collect food made from the Acacia tree and protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... Ants collect food made from the Acacia tree and protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
Slide 1
... • Plants receive this energy from the sun, using this solar energy and chlorophyll by a process of photosynthesis they make their own food. • Because they can make their own food (autotrophic) plants are called producers ...
... • Plants receive this energy from the sun, using this solar energy and chlorophyll by a process of photosynthesis they make their own food. • Because they can make their own food (autotrophic) plants are called producers ...
Types of competition
... • Interference competition occurs when individuals defend resources through antagonistic behaviors: – less common, requires that resources can be ...
... • Interference competition occurs when individuals defend resources through antagonistic behaviors: – less common, requires that resources can be ...
How to Conserve Biodiversity on the Farm
... This chart lays out a progression of activities that increasingly support biodiversity and the benefits it provides to the farm. Each farm has a unique set of circumstances and will begin at different places in the continuum, depending on its need and capacity for supporting nature. Whether the need ...
... This chart lays out a progression of activities that increasingly support biodiversity and the benefits it provides to the farm. Each farm has a unique set of circumstances and will begin at different places in the continuum, depending on its need and capacity for supporting nature. Whether the need ...
Term Definition Example
... parts that work together to form systems work together a whole. so that you can function. ...
... parts that work together to form systems work together a whole. so that you can function. ...