Plant Ecology 101 in 5 minutes - Rutgers Environmental Stewards
... Catastrophes are infrequent but of great significance to the survival of species. The prosperity of a species may depend upon catastrophic events that control it’s competitors or provide food. Ie. fire, flood, epizootic. etc. Succession and Climax Classic plant ecology describes an orderly progressi ...
... Catastrophes are infrequent but of great significance to the survival of species. The prosperity of a species may depend upon catastrophic events that control it’s competitors or provide food. Ie. fire, flood, epizootic. etc. Succession and Climax Classic plant ecology describes an orderly progressi ...
Effects of Climate C..
... could negatively affect habitats. Mangroves, seagrass beds, other coastal ecosystems and associated biodiversity will be affected. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater habitats Potential loss of coral reef associated species due to coral bleaching and reduced calcification rates. Inundation and flood ...
... could negatively affect habitats. Mangroves, seagrass beds, other coastal ecosystems and associated biodiversity will be affected. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater habitats Potential loss of coral reef associated species due to coral bleaching and reduced calcification rates. Inundation and flood ...
FP7 (Heinze, 5 min)
... Jan 2005, Brussels, consultation meeting on topics for FP7 2-3 Feb 06, Brussels, Symposium in memoriam Anver Ghazi 17 Feb 06, Text – input to FP7 WP 7 Apr 06, consultation for specification of acidification WP text ...
... Jan 2005, Brussels, consultation meeting on topics for FP7 2-3 Feb 06, Brussels, Symposium in memoriam Anver Ghazi 17 Feb 06, Text – input to FP7 WP 7 Apr 06, consultation for specification of acidification WP text ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 3 Energy and Ecosystems What is
... What are the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in the carbon cycle? What is nitrogen fixation? Why is it important? What are the biological and industrial forms of nitrogen fixation? What are legumes? What is their role in the nitrogen cycle?] How are bacteria symbiotic with legumes? What i ...
... What are the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in the carbon cycle? What is nitrogen fixation? Why is it important? What are the biological and industrial forms of nitrogen fixation? What are legumes? What is their role in the nitrogen cycle?] How are bacteria symbiotic with legumes? What i ...
Ecology Learning Goalsb - Coristines
... Understand the meaning of low or high abiotic measurements ( water temp, nitrogen, ammonia etc.) and discuss the significance of these to an ecosystem ...
... Understand the meaning of low or high abiotic measurements ( water temp, nitrogen, ammonia etc.) and discuss the significance of these to an ecosystem ...
Climatic Controls of Soil Carbon Cycling Across a Gradient of
... Arid and semiarid lands cover roughly 36% to 40% of global land area, highlighting the importance these ecosystems play in the global carbon cycle. The controls of arid and semiarid ecosystem carbon cycle processes, such as soil organic matter turnover and mineral weathering, remain poorly understoo ...
... Arid and semiarid lands cover roughly 36% to 40% of global land area, highlighting the importance these ecosystems play in the global carbon cycle. The controls of arid and semiarid ecosystem carbon cycle processes, such as soil organic matter turnover and mineral weathering, remain poorly understoo ...
Principles of Ecology
... matter & energy move through an ecosystem. • In a chain nutrients & energy move from autotrophs to heterotrophs & eventually to decomposers. ...
... matter & energy move through an ecosystem. • In a chain nutrients & energy move from autotrophs to heterotrophs & eventually to decomposers. ...
Intro to the Biosphere
... the biological community and the abiotic environment. • An ecosystem's abiotic and biotic composition and structure is determined by the state of interrelated environmental factors. • Changes in any of these factors (for example: nutrient availability, temperature, light intensity, grazing intensity ...
... the biological community and the abiotic environment. • An ecosystem's abiotic and biotic composition and structure is determined by the state of interrelated environmental factors. • Changes in any of these factors (for example: nutrient availability, temperature, light intensity, grazing intensity ...
Nitrogen Cycles through the Biosphere
... cycles within and among ecosystems and the biosphere, and human activities are altering these chemical cycles. ...
... cycles within and among ecosystems and the biosphere, and human activities are altering these chemical cycles. ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... supports the deciduous forest.) Explain climate and weather patterns associated with certain geographic locations and features (e.g., tornado alley, tropical hurricanes and lake effect snow). Describe how matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization in living systems and b ...
... supports the deciduous forest.) Explain climate and weather patterns associated with certain geographic locations and features (e.g., tornado alley, tropical hurricanes and lake effect snow). Describe how matter cycles and energy flows through different levels of organization in living systems and b ...
Title of Unit: Ecology Course and Grade Level: 9th Grade Biology
... State the five levels of ecological study. Compare abiotic and biotic factors and list two examples of each. Summarize the roles of producers in an ecosystem. ...
... State the five levels of ecological study. Compare abiotic and biotic factors and list two examples of each. Summarize the roles of producers in an ecosystem. ...
answers - Biology Resources
... (b) Deforestation in the tropics also leads to erosion. If followed by agriculture, it causes impoverishment of the soil. There may also be local climatic changes and a global increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Biodiversity is reduced. 8 Over-grazing leads to erosion because (i) the animals rem ...
... (b) Deforestation in the tropics also leads to erosion. If followed by agriculture, it causes impoverishment of the soil. There may also be local climatic changes and a global increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Biodiversity is reduced. 8 Over-grazing leads to erosion because (i) the animals rem ...
Chapter 4 - Department of Environmental Sciences
... -By 1940, three and a half billion American chestnuts had perished. -American chestnut stock advertised as "blight free", means it was grown in an area where no blight is present, outside the natural range or inside a greenhouse. ...
... -By 1940, three and a half billion American chestnuts had perished. -American chestnut stock advertised as "blight free", means it was grown in an area where no blight is present, outside the natural range or inside a greenhouse. ...
apes final exam fall 09
... 55.Which country has the greatest percentage of land area affected by desertification? (Russia, Brazil, Chile, US, or Australia?) 56.Which country has the largest area of temperate deciduous forests? (Russia, Brazil, Chile, US, or Australia?) 57.What is fundamentally responsible for earth’s seasons ...
... 55.Which country has the greatest percentage of land area affected by desertification? (Russia, Brazil, Chile, US, or Australia?) 56.Which country has the largest area of temperate deciduous forests? (Russia, Brazil, Chile, US, or Australia?) 57.What is fundamentally responsible for earth’s seasons ...
Ecosystems Unit Summary
... • About 90 percent of the energy taken in is used for chemical reactions and will be lost as heat to the ecosystem. • Only 10 percent of the energy is available for the next trophic level. 2. Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems • The nutrients carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus move in and out of the abioti ...
... • About 90 percent of the energy taken in is used for chemical reactions and will be lost as heat to the ecosystem. • Only 10 percent of the energy is available for the next trophic level. 2. Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems • The nutrients carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus move in and out of the abioti ...
Ecology 3
... What term is used to describe a condition where lakes become overenriched with nutrients, from excess fertiliser use and results, ultimately, in the death of aquatic organisms? ...
... What term is used to describe a condition where lakes become overenriched with nutrients, from excess fertiliser use and results, ultimately, in the death of aquatic organisms? ...
Environmental Changes2
... (perhaps due to bad weather or over-exploitation), there will be serious repercussions on all other species in the chain. But in a complex food web, changes in individual populations are likely to have a smaller impact because they are buffered by the availability of an alternative prey or host spec ...
... (perhaps due to bad weather or over-exploitation), there will be serious repercussions on all other species in the chain. But in a complex food web, changes in individual populations are likely to have a smaller impact because they are buffered by the availability of an alternative prey or host spec ...
Ecology is the study of interactions among and with their environment
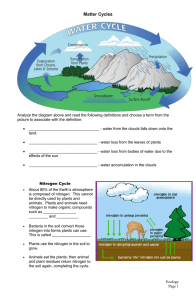
... sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. Plants that die and are buried may turn into __________________ made of carbon like coal and oil over millions of years. When humans burn fossil fuels, most of the carbon quickly enters the ____________________ as carbon ...
... sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. Plants that die and are buried may turn into __________________ made of carbon like coal and oil over millions of years. When humans burn fossil fuels, most of the carbon quickly enters the ____________________ as carbon ...
Ecosystem Ecology for Wildlife Scientists
... inputs and outputs of both energy and nutrients ¾ Energy flows in only one direction through an ecosystem ...
... inputs and outputs of both energy and nutrients ¾ Energy flows in only one direction through an ecosystem ...
Ecological Succession
... – Inhibition- species present change the environment and make it less suitable for themselves ...
... – Inhibition- species present change the environment and make it less suitable for themselves ...
Ecological Networks - ChaosAndComplexity
... and their environment • Study of ecosystems – Ecosystem- web/network of relationships of organisms to each other and their environment ...
... and their environment • Study of ecosystems – Ecosystem- web/network of relationships of organisms to each other and their environment ...
Ecosystems: Components, Energy Flow, and Matter - RHS-APES
... of interacting individuals of the same species ...
... of interacting individuals of the same species ...
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse. Agricultural and industrial nitrogen (N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle (Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide (N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector. This article is intended to give a brief review of the history of anthropogenic N inputs, and reported impacts of nitrogen inputs on selected terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.