File
... They determine whether the incoming sensory stimulus should be transmitted to the cerebrum or terminated. ...
... They determine whether the incoming sensory stimulus should be transmitted to the cerebrum or terminated. ...
Title of Presentation - Cambodian Ophthalmological Society
... *Pupillary involvement may be seen in some diabetes associated 3rd nerve palsies *Pupillary sparing does not exclude aneurysm or compressive lesion ...
... *Pupillary involvement may be seen in some diabetes associated 3rd nerve palsies *Pupillary sparing does not exclude aneurysm or compressive lesion ...
Diapositive 1
... of endocannabinoid molecules from membrane lipidss. Characteristics of endocannabinoid: 1. They are not packaged in vesicles like most other neurotransmitters; instead, they are manufactured rapidly and on-demand. 2. 2. They are small and membrane pecrneable; once synthesized, they can diffuse rapid ...
... of endocannabinoid molecules from membrane lipidss. Characteristics of endocannabinoid: 1. They are not packaged in vesicles like most other neurotransmitters; instead, they are manufactured rapidly and on-demand. 2. 2. They are small and membrane pecrneable; once synthesized, they can diffuse rapid ...
Radial Nerve - EventBuilder
... deviation with extension of the wrist Lack MP extension Splinting is similar as for radial nerve palsy ...
... deviation with extension of the wrist Lack MP extension Splinting is similar as for radial nerve palsy ...
Unit 2 PowerPoint 2.1 and 2.2
... positive charge of the nerve fiber. When the charge reaches +40 mv, the impulse is propagated down the nerve fiber. • This electrical impulse is carried down the nerve through a series of action potentials. ...
... positive charge of the nerve fiber. When the charge reaches +40 mv, the impulse is propagated down the nerve fiber. • This electrical impulse is carried down the nerve through a series of action potentials. ...
Q24 Describe the mechanism of action of the
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
Action Potentials
... Action Potentials “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with more th ...
... Action Potentials “Each neuron continuously integrates signals over both time and space as it is continually bombarded with stimuli through the thousands of synapses covering its dendrites and cell body. Remember that, although schematic diagrams of neural circuitry rarely show neurons with more th ...
The Respiratory System:
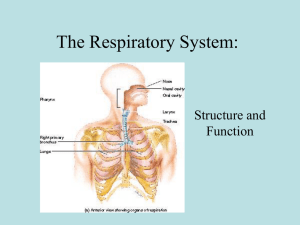
... What are the functions of the respiratory system? What tissue helps prevent the collapse of air passageways in the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles? Identify some of these by name. ...
... What are the functions of the respiratory system? What tissue helps prevent the collapse of air passageways in the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles? Identify some of these by name. ...
CNS - FIU
... The vertebrate spinal cord is a dorsal, hollow nerve cord that lies within the neural arches of the vertebral column. Like the brain, the spinal cord is covered by three membranes (the meninges), the dura mater (outer; L, tough mouth), arachnoid (middle; G&L, spider- (web-) like mother), and pia mat ...
... The vertebrate spinal cord is a dorsal, hollow nerve cord that lies within the neural arches of the vertebral column. Like the brain, the spinal cord is covered by three membranes (the meninges), the dura mater (outer; L, tough mouth), arachnoid (middle; G&L, spider- (web-) like mother), and pia mat ...
Perception Lecture unit6Perception
... For cannabis or any drug, being schedule I means: 1. It has high addiction potential 2. It is dangerous to use in any circumstances 3. It has no medical benefit 4. 1 + 2 + 3 according to federal regulators 5. 1 + 2 are true, 3 is not ...
... For cannabis or any drug, being schedule I means: 1. It has high addiction potential 2. It is dangerous to use in any circumstances 3. It has no medical benefit 4. 1 + 2 + 3 according to federal regulators 5. 1 + 2 are true, 3 is not ...
Visual organ
... The lens capsule is an elastic and transparent basal lamina that covers the entire lens and prevents wandering cells from penetrating it. Subcapsular epithelium. The height of this low cuboidal epithelium beneath the capsule on the anterior lens surface increases to columnar near the lens equator, w ...
... The lens capsule is an elastic and transparent basal lamina that covers the entire lens and prevents wandering cells from penetrating it. Subcapsular epithelium. The height of this low cuboidal epithelium beneath the capsule on the anterior lens surface increases to columnar near the lens equator, w ...
Sensory Motor Approaches with People with Mental Illness Week 5
... • Provide sensory stimulation and opportunities for ...
... • Provide sensory stimulation and opportunities for ...
Botox in ophtho - M.M.Joshi Eye Institute
... Dysthyroid orbitopathy Surgical surprises ! Infantile ET ??? Buying time ...
... Dysthyroid orbitopathy Surgical surprises ! Infantile ET ??? Buying time ...
Document
... covered by and insulated with a layer of fat cells. • Increases the speed of information which travels through the peripheral nervous system. ...
... covered by and insulated with a layer of fat cells. • Increases the speed of information which travels through the peripheral nervous system. ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... signal. The left hand is clenched later than the right, as evident in the recordings from a pressure bulb transducer squeezed by the patient. B. A patient moving his arm from a raised position to touch the tip of his nose exhibits dysmetria (inaccuracy in range and direction) and decomposition of mo ...
... signal. The left hand is clenched later than the right, as evident in the recordings from a pressure bulb transducer squeezed by the patient. B. A patient moving his arm from a raised position to touch the tip of his nose exhibits dysmetria (inaccuracy in range and direction) and decomposition of mo ...
outline28002
... i. Electrode array placed on the vitreal surface to stimulate ganglion or possibly bipolar cells. ii. Second Sight, Inc. ...
... i. Electrode array placed on the vitreal surface to stimulate ganglion or possibly bipolar cells. ii. Second Sight, Inc. ...
Chapter 22 The Nervous System Nervous System - Function 6/1/2013
... Impulse travels from the dendrites to the cell body and then along axons going away from the cell body until it reaches the end of an axon (Axon Tip) ...
... Impulse travels from the dendrites to the cell body and then along axons going away from the cell body until it reaches the end of an axon (Axon Tip) ...
Term - k20 learn
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
The Nervous System
... Impulse travels from the dendrites to the cell body and then along axons going away from the cell body until it reaches the end of an axon (Axon Tip) ...
... Impulse travels from the dendrites to the cell body and then along axons going away from the cell body until it reaches the end of an axon (Axon Tip) ...
1. The main function of myelin is to a. form a protective coating over
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
The Nervous System
... Some people have higher thresholds for pain, heat or other stimuli. This means they can tolerate a stronger stimulus before their nervous system reacts with an impulse. ...
... Some people have higher thresholds for pain, heat or other stimuli. This means they can tolerate a stronger stimulus before their nervous system reacts with an impulse. ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... The smallest change in stimulation that can be detected 50 % of the time Subliminal perception Below our level of awareness Extrasensory perception Extraordinary perception such as sensing the ...
... The smallest change in stimulation that can be detected 50 % of the time Subliminal perception Below our level of awareness Extrasensory perception Extraordinary perception such as sensing the ...
Nervous System Notes
... – If received by some body part, it will stimulate some sort of change (muscles, glands, etc.) • After neurotransmitter does its job, the receptor releases it back into synapse, and finds its way back to the neuron so it can be re-released ...
... – If received by some body part, it will stimulate some sort of change (muscles, glands, etc.) • After neurotransmitter does its job, the receptor releases it back into synapse, and finds its way back to the neuron so it can be re-released ...
A. What is a neuron? 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and
... is soon adjusted by the sodium-potassium pumps to the neuron's original concentration gradient). 9. Local anesthetic drugs (e.g., Novocain, Xylocaine, etc.) hinder the occurrence of action potentials by blocking voltage-activated Na+ gates (preventing Na+ from entering a membrane). 10. General anest ...
... is soon adjusted by the sodium-potassium pumps to the neuron's original concentration gradient). 9. Local anesthetic drugs (e.g., Novocain, Xylocaine, etc.) hinder the occurrence of action potentials by blocking voltage-activated Na+ gates (preventing Na+ from entering a membrane). 10. General anest ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.