The Spinal Cord - Lightweight OCW University of Palestine
... process. The neuron is responsible for sending and receiving impulses or signals. Each nerve cell consist of: 1. Cell body (Soma): which contains the nucleus and the other organelles necessary for cellular function. 2. Several short processes called dendrites: are the region where one neuron receive ...
... process. The neuron is responsible for sending and receiving impulses or signals. Each nerve cell consist of: 1. Cell body (Soma): which contains the nucleus and the other organelles necessary for cellular function. 2. Several short processes called dendrites: are the region where one neuron receive ...
Neurotic Overview
... d. Tonsillar: cerebellar tonsils/medulla thru foramen magnum medulla compression loss of consciousness, apnea 9. Define a. Astrocytosis: acute hyperplasia/hypertrophy b. Gliosis: chronic proliferation of astrocyte processes glial scar, common in MS c. Cavitation: occurs w/ significant neuron/g ...
... d. Tonsillar: cerebellar tonsils/medulla thru foramen magnum medulla compression loss of consciousness, apnea 9. Define a. Astrocytosis: acute hyperplasia/hypertrophy b. Gliosis: chronic proliferation of astrocyte processes glial scar, common in MS c. Cavitation: occurs w/ significant neuron/g ...
Neuron Summary - MsHughesPsychology
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
The peripheral nervous system links the brain to the “real” world
... Process where axons of nociceptors release substances that sensitize the nociceptors to stimuli that were not previously painful ...
... Process where axons of nociceptors release substances that sensitize the nociceptors to stimuli that were not previously painful ...
chapt16_lecture
... Vision and Light • Vision (sight) is perception of light emitted or reflected from objects in the environment • Visible light is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from 400 to 750 nm • Light must cause a photochemical reaction in order to produce a nerve signal our brain can notice – radiat ...
... Vision and Light • Vision (sight) is perception of light emitted or reflected from objects in the environment • Visible light is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from 400 to 750 nm • Light must cause a photochemical reaction in order to produce a nerve signal our brain can notice – radiat ...
Lecture Outline ()
... Vision and Light • Vision (sight) is perception of light emitted or reflected from objects in the environment • Visible light is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from 400 to 750 nm • Light must cause a photochemical reaction in order to produce a nerve signal our brain can notice – radiat ...
... Vision and Light • Vision (sight) is perception of light emitted or reflected from objects in the environment • Visible light is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from 400 to 750 nm • Light must cause a photochemical reaction in order to produce a nerve signal our brain can notice – radiat ...
Ear
... The speed and magnitude of rotational head movements determine the direction in which the stereocilia are bent and the hair cells stimulated. Neurotransmitter is released from the hair cells at rest, and the release changes from this resting rate according to the direction in which the hairs are ben ...
... The speed and magnitude of rotational head movements determine the direction in which the stereocilia are bent and the hair cells stimulated. Neurotransmitter is released from the hair cells at rest, and the release changes from this resting rate according to the direction in which the hairs are ben ...
Chapter 3
... insulin is secreted. This promotes the uptake of glucose by cells of non-neural tissue. Hence, times of availability are times that such cells can rely upon glucose. Compared to non-neural tissue, neurons are limited in the range of substrates from which they can derive energy. They rely largely on ...
... insulin is secreted. This promotes the uptake of glucose by cells of non-neural tissue. Hence, times of availability are times that such cells can rely upon glucose. Compared to non-neural tissue, neurons are limited in the range of substrates from which they can derive energy. They rely largely on ...
Text S1.
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
... axonal polarization along L1 at 3 DIV but, initially, any of the 4 growing neurites could have differentiated into an axon. The discrepancy between random choice at 1-2 DIV and axonal preference along L1 at 3 DIV corresponds to failures of polarization along curved lines. It is thus possible to calc ...
Neuron Preview
... V cells—approximately 10%–20% of pyramidal tract neurons (PTN) in M1—their known anatomic and functional properties can be exploited to reveal general neural processing properties. A further advantage of studying neural synchrony of CM cells is that it can be done in awake preparations. Synchrony in ...
... V cells—approximately 10%–20% of pyramidal tract neurons (PTN) in M1—their known anatomic and functional properties can be exploited to reveal general neural processing properties. A further advantage of studying neural synchrony of CM cells is that it can be done in awake preparations. Synchrony in ...
Basic Anatomy and Terminology of the Head and Brain Scalp and
... tracts along its outsides. As with all of the central nervous system, the nerve cells of the spinal cord cannot regenerate if lost or destroyed (the nerves of the peripheral nervous system can regenerate). The spinal cord sends off (and receives) peripheral nerves to the body. One pair of motor nerv ...
... tracts along its outsides. As with all of the central nervous system, the nerve cells of the spinal cord cannot regenerate if lost or destroyed (the nerves of the peripheral nervous system can regenerate). The spinal cord sends off (and receives) peripheral nerves to the body. One pair of motor nerv ...
Schwann cells
... Schwann cells hold 1 – 12 small nerve fibers in grooves on its surface membrane folds once around each fiber overlapping itself along the edges mesaxon – neurilemma wrapping of unmyelinated nerve fibers ...
... Schwann cells hold 1 – 12 small nerve fibers in grooves on its surface membrane folds once around each fiber overlapping itself along the edges mesaxon – neurilemma wrapping of unmyelinated nerve fibers ...
NeuroExam_Ross_Jim_v1 - Somatic Systems Institute
... the neuron. Each neuron has a cell body, numerous dendrites - branching processes that carry incoming nerve impulses from sense organs and other neurons toward the cell body - and a single axon, which may also branch, which carries outgoing messages to other neurons, glands and muscles. Many axons a ...
... the neuron. Each neuron has a cell body, numerous dendrites - branching processes that carry incoming nerve impulses from sense organs and other neurons toward the cell body - and a single axon, which may also branch, which carries outgoing messages to other neurons, glands and muscles. Many axons a ...
Anatomy of Brain Functions
... time. These signals are evaluated, compared, used for decision making, discarded or committed to memory as deemed appropriate. Integration takes place in the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord and is performed by interneurons. Many interneurons work together to form complex networks that provi ...
... time. These signals are evaluated, compared, used for decision making, discarded or committed to memory as deemed appropriate. Integration takes place in the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord and is performed by interneurons. Many interneurons work together to form complex networks that provi ...
rview
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
... A) It will either produce an action potential or not, depending entirely upon whether it is an excitatory or inhibitory neuron. B) It will integrate the incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals, with its rate of action potentials depending on the relative amount of each type of signal. C) It will ...
Program - Harvard Medical School
... speech, making use of acoustic mismatches between predicted and realized speech in order to correct that speech online. We investigated these processes in aphasia, a communication disorder caused by damage to language-related brain regions. Persons with aphasia (PWA) took part in two experiments des ...
... speech, making use of acoustic mismatches between predicted and realized speech in order to correct that speech online. We investigated these processes in aphasia, a communication disorder caused by damage to language-related brain regions. Persons with aphasia (PWA) took part in two experiments des ...
Nervous System - Thephysicsteacher
... (panic), delusions (paranoia) and hallucinations. Over time, marijuana can suppress the immune system, impair mental functions and lower sperm and testosterone levels. Cocaine, interferes with the normal breakdown of dopamine. Dopamine is involved with pleasurable feelings. If it is not broken dow ...
... (panic), delusions (paranoia) and hallucinations. Over time, marijuana can suppress the immune system, impair mental functions and lower sperm and testosterone levels. Cocaine, interferes with the normal breakdown of dopamine. Dopamine is involved with pleasurable feelings. If it is not broken dow ...
Lecture notes - University of Sussex
... It can only transmit a succession of brief explosive waves, and the message can only be varied by changes in the frequency and in the total number of these waves. … But this limitation is really a small matter, for in the body the nervous units do not act in isolation as they do in our experiments. ...
... It can only transmit a succession of brief explosive waves, and the message can only be varied by changes in the frequency and in the total number of these waves. … But this limitation is really a small matter, for in the body the nervous units do not act in isolation as they do in our experiments. ...
Repetitive Strain Injuries - Working
... 15 - Nerve Block. You feel nothing other than a thick weightiness as if you have been given a shot of Novocaine. Many RSI patients get this in one hand when they are asleep and are awakened by it. 25 - Reduced Grip Strength. You start to lose control of your hands. This is the first stage of reduced ...
... 15 - Nerve Block. You feel nothing other than a thick weightiness as if you have been given a shot of Novocaine. Many RSI patients get this in one hand when they are asleep and are awakened by it. 25 - Reduced Grip Strength. You start to lose control of your hands. This is the first stage of reduced ...
Local anaesthetic and additive drugs
... lipid soluble) is determined by its pKa. This non-ionized portion passes through the lipid cell membrane to the inner axon where re-ionization takes place. The re-ionized portion of the local anaesthetic blocks the sodium channels. The closer the pKa of the drug is to physiological pH (7.4), the gre ...
... lipid soluble) is determined by its pKa. This non-ionized portion passes through the lipid cell membrane to the inner axon where re-ionization takes place. The re-ionized portion of the local anaesthetic blocks the sodium channels. The closer the pKa of the drug is to physiological pH (7.4), the gre ...
The Special Senses Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
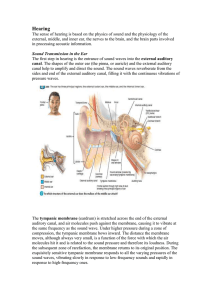
... • The ears outer, middle, and inner parts perform the functions of collecting, amplifying and transducing sound energy, respectively. • The outer ears pinna and ear canal funnel sound waves onto the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. • The ear – drum vibration is amplified 20 - fold through the lever ...
... • The ears outer, middle, and inner parts perform the functions of collecting, amplifying and transducing sound energy, respectively. • The outer ears pinna and ear canal funnel sound waves onto the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. • The ear – drum vibration is amplified 20 - fold through the lever ...
Ch. 13 Nervous System Cells Textbook
... capillaries. Small molecules (e.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, alcohol) diffuse rapidly through the barrier to reach brain neurons and other glia. Larger molecules penetrate it slowly or not at all (Box 12-1). More recent findings suggest that astrocytes may not only influence the growth of neur ...
... capillaries. Small molecules (e.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, alcohol) diffuse rapidly through the barrier to reach brain neurons and other glia. Larger molecules penetrate it slowly or not at all (Box 12-1). More recent findings suggest that astrocytes may not only influence the growth of neur ...
Nerve Transfer for Elbow Extension in Obstetrical Brachial Plexus
... The explanation of the discrepancy between the results in children and in adults might stem from both prolonged nerve regeneration in childhood, in which residual muscle vitality is maintained despite the absence of functional motion, and the augmentation of residual triceps function, otherwise too ...
... The explanation of the discrepancy between the results in children and in adults might stem from both prolonged nerve regeneration in childhood, in which residual muscle vitality is maintained despite the absence of functional motion, and the augmentation of residual triceps function, otherwise too ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 11-30
... Gustation and Olfaction (Taste and Smell) How are smell and taste clinically important? Taste intimately linked to sense of smell The number of taste buds begins declining rapidly by age 50 Sense of smell declines with ageing Elderly aren’t motivated to eat because food has little taste Pa ...
... Gustation and Olfaction (Taste and Smell) How are smell and taste clinically important? Taste intimately linked to sense of smell The number of taste buds begins declining rapidly by age 50 Sense of smell declines with ageing Elderly aren’t motivated to eat because food has little taste Pa ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.