Visual Prostheses: Current Progress and Challenges
... Vision is arguably the most important sense that we posses. Diseases that cause an impairment of this sense results in a debilitating condition. Additionally age related causes of blindness, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), are exacerbated by the increase in average lifespan especiall ...
... Vision is arguably the most important sense that we posses. Diseases that cause an impairment of this sense results in a debilitating condition. Additionally age related causes of blindness, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), are exacerbated by the increase in average lifespan especiall ...
2011 Schedule
... 4. David Gadsby Primary transporters: the sodium pump Afternoon: De Felice and Naftalin Tutorial #1 and Poster Session Evening: 5. Baruch Kanner Structure and function of neurotransmitter transporters 6. Robert Tampe ABC transporters - from self-defense to adaptive immunity May 13 Morning: 7. Franss ...
... 4. David Gadsby Primary transporters: the sodium pump Afternoon: De Felice and Naftalin Tutorial #1 and Poster Session Evening: 5. Baruch Kanner Structure and function of neurotransmitter transporters 6. Robert Tampe ABC transporters - from self-defense to adaptive immunity May 13 Morning: 7. Franss ...
Chapter 18
... i. The gray matter in the spinal cord promotes homeostasis by serving as the integrating center for spinal reflexes (the brain stem is the integrating center for cranial reflexes). ii. Reflexes are fast, predictable, automatic responses to changes in the environment that help maintain homeostasis: a ...
... i. The gray matter in the spinal cord promotes homeostasis by serving as the integrating center for spinal reflexes (the brain stem is the integrating center for cranial reflexes). ii. Reflexes are fast, predictable, automatic responses to changes in the environment that help maintain homeostasis: a ...
neuron is
... level of “depolarization” that must be reached for neuron to fire • graded potential: stimulation of dendrites was too weak to reach threshold and neuron fails to fire (depolarization just “fades away”) ...
... level of “depolarization” that must be reached for neuron to fire • graded potential: stimulation of dendrites was too weak to reach threshold and neuron fails to fire (depolarization just “fades away”) ...
Touch Pressure & Pain
... converts pressure stimulation into neural messages it sends to the brain. • Constant pressure causes sensory adaptation and it either reduces the number of signals or quits sending them all together. (like the clothes on your body) • Sensory receptors are located unevenly on the body so certain area ...
... converts pressure stimulation into neural messages it sends to the brain. • Constant pressure causes sensory adaptation and it either reduces the number of signals or quits sending them all together. (like the clothes on your body) • Sensory receptors are located unevenly on the body so certain area ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column operates as an integrative operating system d. Each column can also function as an amplifying system e. Dynamic neurons-excited at a high rate for a short period of time ...
... b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column operates as an integrative operating system d. Each column can also function as an amplifying system e. Dynamic neurons-excited at a high rate for a short period of time ...
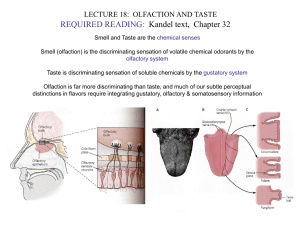
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... Olfactory sensory neurons are fairly short-lived (1-2 months), and regenerate from basal stem cells Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons r ...
... Olfactory sensory neurons are fairly short-lived (1-2 months), and regenerate from basal stem cells Each sensory neuron responds to a single odorant or a specific repertoire of chemically related odorants An odor is ENCODED by the specific combination of neurons which respond to it Sensory neurons r ...
This is all we can do!
... • ACTION POTENTIALS – Unique to animal nerve and muscle tissue – Ability to rapidly carry an ion diffusion mediated change in voltage along the cell membrane – Only neurons and muscle cells can do it – Here’s how (more or less)…. ...
... • ACTION POTENTIALS – Unique to animal nerve and muscle tissue – Ability to rapidly carry an ion diffusion mediated change in voltage along the cell membrane – Only neurons and muscle cells can do it – Here’s how (more or less)…. ...
Document
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
Chapter 50
... • Sensations and perceptions – Begin with sensory reception, the detection of stimuli (physical or chemical) by sensory receptors – Intergration of sensory information by brain is ...
... • Sensations and perceptions – Begin with sensory reception, the detection of stimuli (physical or chemical) by sensory receptors – Intergration of sensory information by brain is ...
cranial nerves
... ascending descending location of tracts information carried pathway - decussation (in some cases) - termination the big three dorsal column/medial lemniscus ALS (spinothalamic) lateral corticospinal reflex arcs ...
... ascending descending location of tracts information carried pathway - decussation (in some cases) - termination the big three dorsal column/medial lemniscus ALS (spinothalamic) lateral corticospinal reflex arcs ...
Spinal Cord Diseases of the Horse: Relevant Examination
... the recurrent laryngeal nerve to innervate the contralateral laryngeal adductor muscles. Severe cervical spinal cord disease often affects this test bilaterally, and the vagus and recurrent laryngeal nerves may be affected at the guttural pouch or within the jugular groove. It is important to note t ...
... the recurrent laryngeal nerve to innervate the contralateral laryngeal adductor muscles. Severe cervical spinal cord disease often affects this test bilaterally, and the vagus and recurrent laryngeal nerves may be affected at the guttural pouch or within the jugular groove. It is important to note t ...
Function and Metabolism of Phospholipids in the Central and
... owing to thermodynamic considerations, phospholipids can flip-flop only very slowly from one side of the membrane to the other. Would the diacylglycerol molecules be similarly restricted, and remain long enough in one-half of the bilayer to create these vesicle buddings? Moreover, are the enzymes in ...
... owing to thermodynamic considerations, phospholipids can flip-flop only very slowly from one side of the membrane to the other. Would the diacylglycerol molecules be similarly restricted, and remain long enough in one-half of the bilayer to create these vesicle buddings? Moreover, are the enzymes in ...
Nervous System Intro Part 1
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearso ...
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearso ...
Somatic Sensations: General Organization
... Thalamus has an important role in the perception of pain and temperature. ...
... Thalamus has an important role in the perception of pain and temperature. ...
TENS – a complement to wound healing
... • Antibacterial effect One study indicates that TENS increases the amount of leucocytes and phagocytes. • Effects on a cellular level The same study indicates that TENS increases protein production. ...
... • Antibacterial effect One study indicates that TENS increases the amount of leucocytes and phagocytes. • Effects on a cellular level The same study indicates that TENS increases protein production. ...
Text S1.
... associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic efficacies are modified by neural activity during a training process through long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). It is assumed that these synaptic weights have been set through repeated presentations of p different stimuli in random sequ ...
... associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic efficacies are modified by neural activity during a training process through long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). It is assumed that these synaptic weights have been set through repeated presentations of p different stimuli in random sequ ...
Biology 232
... Neurotransmitters of the ANS cholinergic neurons – release acetylcholine (ACh) all preganglionic neurons all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons a few sympathetic postganglionic neurons (eg. sweat glands) cholinergic receptors – postsynaptic integral membrane proteins 2 types: nicotinic receptors ...
... Neurotransmitters of the ANS cholinergic neurons – release acetylcholine (ACh) all preganglionic neurons all parasympathetic postganglionic neurons a few sympathetic postganglionic neurons (eg. sweat glands) cholinergic receptors – postsynaptic integral membrane proteins 2 types: nicotinic receptors ...
parasympathetic divisions
... The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons • The ANS—a system of motor neurons • Regulates visceral functions • Heart rate • Blood pressure • Digestion • Urination ...
... The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons • The ANS—a system of motor neurons • Regulates visceral functions • Heart rate • Blood pressure • Digestion • Urination ...
Cranial Nerve Locations CN I Olfactory ----------
... fibers and Golgi tendon organs) - trunk and lower limb Synapse on neurons of Clarke’s nucleus and axons ascend ipsilaterally as the posterior spinocerebellar tract to enter cerebellum through inferior cerebellar peduncle Clarke’s nucleus: group of interneurons found T1-L4, associated with propri ...
... fibers and Golgi tendon organs) - trunk and lower limb Synapse on neurons of Clarke’s nucleus and axons ascend ipsilaterally as the posterior spinocerebellar tract to enter cerebellum through inferior cerebellar peduncle Clarke’s nucleus: group of interneurons found T1-L4, associated with propri ...
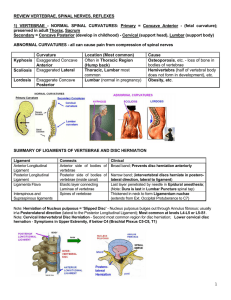
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
Neuroscience 7b – Cortical Motor Function
... scratched from heel to little toe, the toes flex i.e. curl downwards, however, in an upper motor neuron lesion this is damages and the toes extend out and flare. Consequences of Stroke Stroke is the consequence of cerebrovascular disease that interrupts blood flow to part of the brain causing ischae ...
... scratched from heel to little toe, the toes flex i.e. curl downwards, however, in an upper motor neuron lesion this is damages and the toes extend out and flare. Consequences of Stroke Stroke is the consequence of cerebrovascular disease that interrupts blood flow to part of the brain causing ischae ...
reflex
... Sir Charles Sherrington (1857-1952) was the first to introduce the word 'reflex', taking the view that sensory information going into the cord was reflected out again along the motor nerve fibres He said that the reflection of sensory information was the equivalent to a beam of light being reflected ...
... Sir Charles Sherrington (1857-1952) was the first to introduce the word 'reflex', taking the view that sensory information going into the cord was reflected out again along the motor nerve fibres He said that the reflection of sensory information was the equivalent to a beam of light being reflected ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.