Unaccusativity and Underspecification in Urdu
... 4.3. Conclusion of the debate • Concluding the above discussion, we agree with the proposals that the simple idea of unaccsativity/unergativity does not work. • Only the verb cannot decide the syntactic properties of the clauses. The other parts of the clause also contribute to grammatical validity/ ...
... 4.3. Conclusion of the debate • Concluding the above discussion, we agree with the proposals that the simple idea of unaccsativity/unergativity does not work. • Only the verb cannot decide the syntactic properties of the clauses. The other parts of the clause also contribute to grammatical validity/ ...
The verbal phrase of Northern Sotho: A morpho-syntactic
... space reasons, we however focus on the independent predicative moods in this paper: indicative, situative and relative (for an overview of the Northern Sotho moods, see e.g. (Lombard, 1985, p. 144)). These moods all appear in the three tenses future, present and past and all may be negated. To mark ...
... space reasons, we however focus on the independent predicative moods in this paper: indicative, situative and relative (for an overview of the Northern Sotho moods, see e.g. (Lombard, 1985, p. 144)). These moods all appear in the three tenses future, present and past and all may be negated. To mark ...
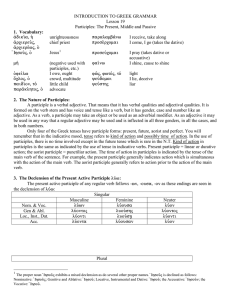
INTRODUCTION TO GREEK GRAMMAR Lesson 19 Participles: The
... formed on the verb stem and has voice and tense like a verb, but it has gender, case and number like an adjective. As a verb, a participle may take an object or be used as an adverbial modifier. As an adjective it may be used in any way that a regular adjective may be used and is inflected in all th ...
... formed on the verb stem and has voice and tense like a verb, but it has gender, case and number like an adjective. As a verb, a participle may take an object or be used as an adverbial modifier. As an adjective it may be used in any way that a regular adjective may be used and is inflected in all th ...
Spanish Intro 2 - Niles Township High Schools District 219
... I can comprehend (at a literal level) a passage of prosefiction or nonfiction, containing structures and vocabulary presented in the course. OverArching Vocabulary Target I can recognize and use vocabulary found in Realidades , chapters 5A to 6B Subtargets ● I can can recognize and use vocabular ...
... I can comprehend (at a literal level) a passage of prosefiction or nonfiction, containing structures and vocabulary presented in the course. OverArching Vocabulary Target I can recognize and use vocabulary found in Realidades , chapters 5A to 6B Subtargets ● I can can recognize and use vocabular ...
GRS LX 700 Language Acquisition and Linguistic Theory
... was there a post-negation inflected verb (she doesn’t go vs. *she not goes). The actual infinitive morpheme in English is Ø, so we can’t differentiate bare forms between infinitives and other bare forms. The infinitive morpheme seems to carry modal meaning—in languages where you can see it you can t ...
... was there a post-negation inflected verb (she doesn’t go vs. *she not goes). The actual infinitive morpheme in English is Ø, so we can’t differentiate bare forms between infinitives and other bare forms. The infinitive morpheme seems to carry modal meaning—in languages where you can see it you can t ...
PDF sample
... INDIRECT QUESTION used to tell someone else about a question and introduced by a verb such as ask, tell or wonder, for example, He asked me what the time was; I wonder who he is. INFINITIVE the form of the verb with to in front of it and without any endings added, for example, to walk, to have, to b ...
... INDIRECT QUESTION used to tell someone else about a question and introduced by a verb such as ask, tell or wonder, for example, He asked me what the time was; I wonder who he is. INFINITIVE the form of the verb with to in front of it and without any endings added, for example, to walk, to have, to b ...
Participles
... A participle is a verb form that acts as an adjective. It modifies a noun or pronoun. There are two kinds of participle: present participles and past participles. The present participle always ends in -ing. A cheering crowd distracts him. (The present participle cheering modifies crowd.) ...
... A participle is a verb form that acts as an adjective. It modifies a noun or pronoun. There are two kinds of participle: present participles and past participles. The present participle always ends in -ing. A cheering crowd distracts him. (The present participle cheering modifies crowd.) ...
Document
... a)Angela Duffy is a schoolgirl from Brighton. She wants to be a doctor. "I'm going to medical school next year. It's a long course- but I'm going to work very hard. It's a difficult job,but I like working with people, and I like the idea of working in a caring profession." She says that later she wo ...
... a)Angela Duffy is a schoolgirl from Brighton. She wants to be a doctor. "I'm going to medical school next year. It's a long course- but I'm going to work very hard. It's a difficult job,but I like working with people, and I like the idea of working in a caring profession." She says that later she wo ...
Phil1_12 - Amador Bible Studies
... HOTI, used to introduce indirect discourse. It is translated “that” and introduces the content of a previous verb of mental action (“I want you to know”). Then we have the nominative subject from the neuter plural article, meaning “the things.” With this we have the KATA plus the accusative of relat ...
... HOTI, used to introduce indirect discourse. It is translated “that” and introduces the content of a previous verb of mental action (“I want you to know”). Then we have the nominative subject from the neuter plural article, meaning “the things.” With this we have the KATA plus the accusative of relat ...
Action Verb
... Complete each sentence by writing a predicate complement in the blank. In the parentheses following the sentence, write PN if you added a predicate noun or PA if you added a predicate adjective. 1. The brown cowboy boots with the pointy toes look ________________. (____) 2. My favorite shoes are my ...
... Complete each sentence by writing a predicate complement in the blank. In the parentheses following the sentence, write PN if you added a predicate noun or PA if you added a predicate adjective. 1. The brown cowboy boots with the pointy toes look ________________. (____) 2. My favorite shoes are my ...
APUNTES – ESPAÑOL II NOMBRE Impersonal Se
... Start the sentence with “se” – it doesn’t translate, but tells us that it’s an impersonal sentence. Then conjugate the verb in the él, ella, Ud. form. o Se trabaja mucho en esa clase. o Se vive bien en esa ciudad. The passive se Is very similar to the impersonal se – that’s why they are taught toget ...
... Start the sentence with “se” – it doesn’t translate, but tells us that it’s an impersonal sentence. Then conjugate the verb in the él, ella, Ud. form. o Se trabaja mucho en esa clase. o Se vive bien en esa ciudad. The passive se Is very similar to the impersonal se – that’s why they are taught toget ...
An FST grammar for verb chain transfer in a
... Finite verbs, in Basque, can be synthetic, consisting of a single word (noa / (I) am going, dakit / (I) know it) or analytical, consisting of a participial form and an auxiliary (joaten naiz / (I) go, jakingo dut / (I) will know). The structure of finite forms (synthetic and auxiliary verb) in Basqu ...
... Finite verbs, in Basque, can be synthetic, consisting of a single word (noa / (I) am going, dakit / (I) know it) or analytical, consisting of a participial form and an auxiliary (joaten naiz / (I) go, jakingo dut / (I) will know). The structure of finite forms (synthetic and auxiliary verb) in Basqu ...
Grammar Rules for Writing in Schwarz`s class
... Verbs are said to be either active (The executive committee approved the new policy) or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sente ...
... Verbs are said to be either active (The executive committee approved the new policy) or passive (The new policy was approved by the executive committee) in voice. In the active voice, the subject and verb relationship is straightforward: the subject is a be-er or a do-er and the verb moves the sente ...
Task 3
... The rules given below are a guide only. You will find that there is considerable variety in the literature you read. However, if you use them to guide your own writing, you should always be correct. When the focus of your citation is on the INFORMATION i.e. there is no reference to researcher activi ...
... The rules given below are a guide only. You will find that there is considerable variety in the literature you read. However, if you use them to guide your own writing, you should always be correct. When the focus of your citation is on the INFORMATION i.e. there is no reference to researcher activi ...
past progressive tense
... Desire: Clara would like to go to the moon. Condition: Clara must know how to build a rocket. Clara would go to the moon if she knew how to build a rocket. ...
... Desire: Clara would like to go to the moon. Condition: Clara must know how to build a rocket. Clara would go to the moon if she knew how to build a rocket. ...
Production of verbs in base position by Dutch agrammatic
... are due to the finiteness as such, or to inflection as such. The second reason was that past participles, as the name shows, whether or not in combination with an auxiliary, refer to the past, just like past tense (Palmer, 1987). In this way, the past participle (from now on ‘participle’) can be seen ...
... are due to the finiteness as such, or to inflection as such. The second reason was that past participles, as the name shows, whether or not in combination with an auxiliary, refer to the past, just like past tense (Palmer, 1987). In this way, the past participle (from now on ‘participle’) can be seen ...
PECULIARITIES OF USING ACTIVE, PASSIVE AND MIDDLE VOICES
... shaved by Fred". This doesn’t need to be reflexive, as in "my clothes soaked in detergent overnight". The English language used to have a distinct form, called the passival, which was displaced over the early 19th century by the passive progressive (progressive passive), and is no longer used in Eng ...
... shaved by Fred". This doesn’t need to be reflexive, as in "my clothes soaked in detergent overnight". The English language used to have a distinct form, called the passival, which was displaced over the early 19th century by the passive progressive (progressive passive), and is no longer used in Eng ...
FREN 2201 - New York City College of Technology
... ability to understand and use French through practice and conversation, writing and reading from French literature and civilization. It includes a systematic review of the essentials of grammar. COURSE OBJECTIVES: The course is intended to increase the student’s ability to understand and use French ...
... ability to understand and use French through practice and conversation, writing and reading from French literature and civilization. It includes a systematic review of the essentials of grammar. COURSE OBJECTIVES: The course is intended to increase the student’s ability to understand and use French ...
1 Variation in Appalachian non-present verb forms 1. Overview. For
... forms should reflect specialization for simple past vs. compound tense. Related to this, it also doesn’t follow that when speakers exhibit more than one non-present form, there are only two. Previous research on variation in non-present verb forms in English (e.g. Anderwald 2009; Eisikovits 1987; By ...
... forms should reflect specialization for simple past vs. compound tense. Related to this, it also doesn’t follow that when speakers exhibit more than one non-present form, there are only two. Previous research on variation in non-present verb forms in English (e.g. Anderwald 2009; Eisikovits 1987; By ...
Russian Grammar: Participles (Прича́стия)
... • Present active participles in Russian can only be used to describe something that is actually performing the action, thus it can be used with active constructions, not passive ones. • Я поговорил с покупающей женщиной. ...
... • Present active participles in Russian can only be used to describe something that is actually performing the action, thus it can be used with active constructions, not passive ones. • Я поговорил с покупающей женщиной. ...
Jingulu - UQ eSpace
... aspect, mood, and associated motion. The appearance of these morphemes on nominals is discussed in section 2, where it is shown that, in the nominal context, these morphemes do not reflect any verbal/inflectional properties of the clause, but rather serve as markers of definiteness or deixis. In thi ...
... aspect, mood, and associated motion. The appearance of these morphemes on nominals is discussed in section 2, where it is shown that, in the nominal context, these morphemes do not reflect any verbal/inflectional properties of the clause, but rather serve as markers of definiteness or deixis. In thi ...
Active and Passive Voice
... "to be" , often called linking verbs, so that they can easily identify the passive voice in their work. Review the forms of "to be": ...
... "to be" , often called linking verbs, so that they can easily identify the passive voice in their work. Review the forms of "to be": ...