Document
... VI. The Senses A. Your senses enable you to hear, see, taste, touch, and smell whatever comes into your environment. B. The energy that stimulates your sense organs may be in the form of light rays, heat, sound waves, chemicals, or pressure. C. Five categories of sensory receptors: ...
... VI. The Senses A. Your senses enable you to hear, see, taste, touch, and smell whatever comes into your environment. B. The energy that stimulates your sense organs may be in the form of light rays, heat, sound waves, chemicals, or pressure. C. Five categories of sensory receptors: ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy 12
... Once olfactory receptors are stimulated, nerve impulses travel through • olfactory nerves olfactory bulbs olfactory tracts limbic system (for emotions) and olfactory cortex (for interpretation) ...
... Once olfactory receptors are stimulated, nerve impulses travel through • olfactory nerves olfactory bulbs olfactory tracts limbic system (for emotions) and olfactory cortex (for interpretation) ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... Messages are sent from the axon terminals of one neuron to the dendrites of other neurons. In order for a message to be sent from one neuron to another neuron, it must cross the synapse. The synapse is a junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. Messages ...
... Messages are sent from the axon terminals of one neuron to the dendrites of other neurons. In order for a message to be sent from one neuron to another neuron, it must cross the synapse. The synapse is a junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. Messages ...
Microcircuits in visual cortex Kevan AC Martin
... Schematic of connectivity within the orientation map of visual cortex. Optical recordings of intrinsic signals rendered in false color provide striking images of the tangential organization of the cortical orientation map. The maps are generated by presenting stimuli at different orientations and re ...
... Schematic of connectivity within the orientation map of visual cortex. Optical recordings of intrinsic signals rendered in false color provide striking images of the tangential organization of the cortical orientation map. The maps are generated by presenting stimuli at different orientations and re ...
Types of Neurons of ANS
... Thoracic splanchnic nerves (a) Location of the sympathetic trunk Figure 14.5a ...
... Thoracic splanchnic nerves (a) Location of the sympathetic trunk Figure 14.5a ...
Canonical computations of cerebral cortex
... from studies of the ventral stream in vision. First, there is a hierarchy of cortical areas, in which neurons in ‘higher’, more anterior areas of the hierarchy are sensitive to the presence of more complex aspects of objects across larger regions of sensory space and with greater ability to recogniz ...
... from studies of the ventral stream in vision. First, there is a hierarchy of cortical areas, in which neurons in ‘higher’, more anterior areas of the hierarchy are sensitive to the presence of more complex aspects of objects across larger regions of sensory space and with greater ability to recogniz ...
Ch 15 Notes: The Autonomic Nervous System 2012
... fibers release acetylcholine and postganglionic fibers release acetylcholine or norepinephrine. The output (efferent) part of the ANS is divided into two principal parts: the SYMPATHETIC and the PARASYMPATHETIC divisions. Organs that receive impulses from both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers ...
... fibers release acetylcholine and postganglionic fibers release acetylcholine or norepinephrine. The output (efferent) part of the ANS is divided into two principal parts: the SYMPATHETIC and the PARASYMPATHETIC divisions. Organs that receive impulses from both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... positive charge, so the neuron becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential t ...
... positive charge, so the neuron becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential t ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VIII. Apoptosis: Neuronal Hari
... occur during periods of cell genesis, it has been difficult to assess how much apoptosis occurs during CNS development. However, advances in methods for labeling dying cells in situ have led to current estimates that cell death removes more than half of the cells that are born during development. Wh ...
... occur during periods of cell genesis, it has been difficult to assess how much apoptosis occurs during CNS development. However, advances in methods for labeling dying cells in situ have led to current estimates that cell death removes more than half of the cells that are born during development. Wh ...
Document
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
Document
... Autonomic responses are coordinated with one another and with behavioral responses and emotions through the hypothalamus in the CNS ...
... Autonomic responses are coordinated with one another and with behavioral responses and emotions through the hypothalamus in the CNS ...
2
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
16. Taste, smell
... - less old pathway passes through portions of limbic system (amygdaloid nuclei and hippocampus) as well as medial cortex of temporal lobe (paleocortex), bypassing thalamus; appears responsible for development of food preferences or aversions - newer pathway passes through thalamus (dorsomedial nucle ...
... - less old pathway passes through portions of limbic system (amygdaloid nuclei and hippocampus) as well as medial cortex of temporal lobe (paleocortex), bypassing thalamus; appears responsible for development of food preferences or aversions - newer pathway passes through thalamus (dorsomedial nucle ...
Direct Reprogramming: Bypassing Stem Cells for
... The adult mammalian heart heals focal injury, such as that which occurs in myocardial infarction, by scar formation, but scar does not contract, leading to systolic dysfunction and adverse remodeling. Direct reprogramming can convert fibroblasts within the heart into functioning cardiomyocytes.4 The ...
... The adult mammalian heart heals focal injury, such as that which occurs in myocardial infarction, by scar formation, but scar does not contract, leading to systolic dysfunction and adverse remodeling. Direct reprogramming can convert fibroblasts within the heart into functioning cardiomyocytes.4 The ...
Discuss two effects of the environment on physiological processes
... •MRI scans showed no structural differences in groups' brains before juggling. •There was an increase in volume of two regions of the jugglers' brains associated with the retention of visually detected movement information of learning • This difference decreased after 3 months of no practice. Conclu ...
... •MRI scans showed no structural differences in groups' brains before juggling. •There was an increase in volume of two regions of the jugglers' brains associated with the retention of visually detected movement information of learning • This difference decreased after 3 months of no practice. Conclu ...
Slide ()
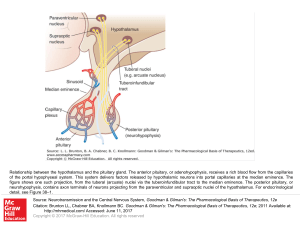
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
endocrine system
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
view - Queen`s University
... by evidence9,10 suggesting that the brain supports more-complex sensorimotor processing than the spinal cord, so high-gain control is processed through brain pathways. Faster, ...
... by evidence9,10 suggesting that the brain supports more-complex sensorimotor processing than the spinal cord, so high-gain control is processed through brain pathways. Faster, ...
Bypassing V1: a direct geniculate input to area MT
... STS. The extensive retrograde labeling of neurons in layer 4B of V1 (Fig. 1c,d)27 confirmed that this injection was in MT. We can rule out the possibility that CTB was transported from leakage along the pipette track in adjacent area V4 because there were no CTB-labeled cells in layer 2/3, the only ...
... STS. The extensive retrograde labeling of neurons in layer 4B of V1 (Fig. 1c,d)27 confirmed that this injection was in MT. We can rule out the possibility that CTB was transported from leakage along the pipette track in adjacent area V4 because there were no CTB-labeled cells in layer 2/3, the only ...
The Nervous System
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) A. all of the nerves outside of the central nervous system including the spinal and cranial nerves which connect the brain and spinal cord to other body parts B. made up of ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) A. all of the nerves outside of the central nervous system including the spinal and cranial nerves which connect the brain and spinal cord to other body parts B. made up of ...