Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS
... • A chemical must be present in this space in order for the signal to be transmitted • The signal will always move in the same direction: from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of the next. ...
... • A chemical must be present in this space in order for the signal to be transmitted • The signal will always move in the same direction: from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of the next. ...
SHH - bthsresearch
... Today’s Goals • Realize that Nervous system is patterned on A-P and D-V axis • Describe mechanisms by which this pattern is set-up – Identify important signaling pathways involved ...
... Today’s Goals • Realize that Nervous system is patterned on A-P and D-V axis • Describe mechanisms by which this pattern is set-up – Identify important signaling pathways involved ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... A. The firing of PMC neurons occurs precisely at the onset of a muscle contraction <––– B. PMC neurons can be directionally selective C. The firing rate of a PMC neuron codes for or contributes to the force of a movement D. The directional control of a movement is coded by the activity of a populati ...
... A. The firing of PMC neurons occurs precisely at the onset of a muscle contraction <––– B. PMC neurons can be directionally selective C. The firing rate of a PMC neuron codes for or contributes to the force of a movement D. The directional control of a movement is coded by the activity of a populati ...
Zoology Assignment - Wikimedia Commons
... eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in a slightly different direction from the others as a result of the eye’s overall convex shape. The visual field of a compound eye is very wide, as anyone who has tried to catch a fly knows. Each ommatidium has its own nerve tract leading to a l ...
... eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in a slightly different direction from the others as a result of the eye’s overall convex shape. The visual field of a compound eye is very wide, as anyone who has tried to catch a fly knows. Each ommatidium has its own nerve tract leading to a l ...
nervous systems
... that receive, encode, and transmit information. Neurons with their support cells (glial cells) make up nervous systems. Modified neurons called sensory cells receive information and convert or transduce it into electrical signals that are transmitted and processed by other neurons. To cause behavior ...
... that receive, encode, and transmit information. Neurons with their support cells (glial cells) make up nervous systems. Modified neurons called sensory cells receive information and convert or transduce it into electrical signals that are transmitted and processed by other neurons. To cause behavior ...
PATHOLOGY/HISTOLOGY TEST KIT 6C: MORE BRAIN (26 vials)
... The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater that is occupied by spongy tissue consisting of trabeculae (delicate connective tissue filaments) and intercommunicating channels in which the cerebrospinal fluid is contained. The superior parietal lobule is involved with spatial orientation, r ...
... The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater that is occupied by spongy tissue consisting of trabeculae (delicate connective tissue filaments) and intercommunicating channels in which the cerebrospinal fluid is contained. The superior parietal lobule is involved with spatial orientation, r ...
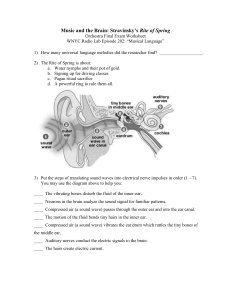
Music and the Brain: Stravinsky`s Rite of Spring
... b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. They booed the performers b. They threw punches c. Old women attacked one another with canes. d. All of the above 8) The auditory cortical fugal network adjusts neur ...
... b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. They booed the performers b. They threw punches c. Old women attacked one another with canes. d. All of the above 8) The auditory cortical fugal network adjusts neur ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
... the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 1. Given what you know about hormones, be able to name three hormones produced by the pituitary, their targets, and their effects. 2. Harry has a biking accident and injures his back. He is examined by a ...
... 1. Given what you know about hormones, be able to name three hormones produced by the pituitary, their targets, and their effects. 2. Harry has a biking accident and injures his back. He is examined by a ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • Which of the following statements best describes the corpus callosum? • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures t ...
... • Which of the following statements best describes the corpus callosum? • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures t ...
FUNCTIONAL COGNITIVE NETWORKS IN PRIMATES
... 2) the archicortex and paleocortex of the limbic system, which are involved in coordination of memory and the control of emotions and drives; and 3) the neocortex of mammals, which processes a broad array of information. Close parallels in morphology, physiology, and neurochemistry remain between th ...
... 2) the archicortex and paleocortex of the limbic system, which are involved in coordination of memory and the control of emotions and drives; and 3) the neocortex of mammals, which processes a broad array of information. Close parallels in morphology, physiology, and neurochemistry remain between th ...
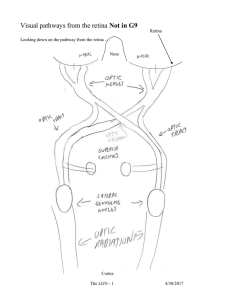
Why light
... That is, the activity generated by stimulus A is at the same end of both LGN layers. The activity generated by stimulus B is right next to A in to layers. The activity generated by stimulus C is at the opposite end in both layers. The layers are in registration with each other. Registration carries ...
... That is, the activity generated by stimulus A is at the same end of both LGN layers. The activity generated by stimulus B is right next to A in to layers. The activity generated by stimulus C is at the opposite end in both layers. The layers are in registration with each other. Registration carries ...
Your Name Here______________________________
... 1. The location where nerve impulses are transmitted from one neuron to the next is the a. receptor b. neurilemma c. synapse c. effector e. axon 2. The depolarization of a neuron is caused by a. K+ diffusing into it. b. Na+ diffusing into it. c. K+ diffusing out of it d. Na+ diffusing out of it. 3. ...
... 1. The location where nerve impulses are transmitted from one neuron to the next is the a. receptor b. neurilemma c. synapse c. effector e. axon 2. The depolarization of a neuron is caused by a. K+ diffusing into it. b. Na+ diffusing into it. c. K+ diffusing out of it d. Na+ diffusing out of it. 3. ...
Webb et al 2002 - User Web Areas at the University of York
... (approximately 100 impulses0s) than the suppression of the spontaneous activity. With V1 ablated, the response of a LGN neuron to a grating covering its classical receptive field was lower (Fig. 1A, right) than in the example recorded with V1 intact, but the degree of suppression caused by the prese ...
... (approximately 100 impulses0s) than the suppression of the spontaneous activity. With V1 ablated, the response of a LGN neuron to a grating covering its classical receptive field was lower (Fig. 1A, right) than in the example recorded with V1 intact, but the degree of suppression caused by the prese ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... •Saltatory conduction can be compared with a line of marbles pushing on each other - when poking the marble in one end then each marble only moves slightly, but this small effect on the marble in the other end is almost instantaneous, like a one-way Newton's cradle. So the signal moves at the speed ...
... •Saltatory conduction can be compared with a line of marbles pushing on each other - when poking the marble in one end then each marble only moves slightly, but this small effect on the marble in the other end is almost instantaneous, like a one-way Newton's cradle. So the signal moves at the speed ...
The Nervous System
... hemispheres together and quickens communication b/t the two sides. Gyri (sing. gyrus) are the folds or mountains on the cerebral cortex Sulci (sing. sulcus) are the dips or cracks on the cortex. These peaks and dips are used expand the surface area of the ...
... hemispheres together and quickens communication b/t the two sides. Gyri (sing. gyrus) are the folds or mountains on the cerebral cortex Sulci (sing. sulcus) are the dips or cracks on the cortex. These peaks and dips are used expand the surface area of the ...
Nervous System
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
Power Point CH 14
... Cytology of Nervous Tissue There are two distinct types of cells within the nervous system: 1. Neurons (nerve cells)—electrically excitable cells that initiate, transmit, and receive nerve impulses 2. Glial cells—nonexcitable cells that support and protect the neurons ...
... Cytology of Nervous Tissue There are two distinct types of cells within the nervous system: 1. Neurons (nerve cells)—electrically excitable cells that initiate, transmit, and receive nerve impulses 2. Glial cells—nonexcitable cells that support and protect the neurons ...
Chapter 27 Lecture notes
... C. The graph traces the electrical changes over time at one point along an axon. These changes can lead to an action potential (Figure 28.4). D. A typical action potential shows the following changes relative to the resting potential of 270 mV. Following a stimulus, the voltage rises to the threshol ...
... C. The graph traces the electrical changes over time at one point along an axon. These changes can lead to an action potential (Figure 28.4). D. A typical action potential shows the following changes relative to the resting potential of 270 mV. Following a stimulus, the voltage rises to the threshol ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 4. Myelinated axons send nerve impulses faster than unmyelinated axons. 5. The diameter of an axon also affects the speed of a nerve impulse. V. Impulse Processing A. Neuronal Pools 1. Neuronal pools are groups of neurons that make synaptic connections with each other and work together to perform a ...
... 4. Myelinated axons send nerve impulses faster than unmyelinated axons. 5. The diameter of an axon also affects the speed of a nerve impulse. V. Impulse Processing A. Neuronal Pools 1. Neuronal pools are groups of neurons that make synaptic connections with each other and work together to perform a ...
Document
... CELLS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary types of cells: ...
... CELLS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary types of cells: ...
Nervous System
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches ...