Richard G. Schuster, DO
... Under some circumstances they are activated and release compounds that sensitize neurons in nociceptive pathways. ...
... Under some circumstances they are activated and release compounds that sensitize neurons in nociceptive pathways. ...
BUILDING AN ARTIFICIAL BRAIN
... • Create a complex functionality without any a priori knowledge of how to achieve it… • Requires the desired Input/Output function! ...
... • Create a complex functionality without any a priori knowledge of how to achieve it… • Requires the desired Input/Output function! ...
22 reflexes 1 - The reflex arc
... At the sensory organ, the response is a NONPROPAGATED GRADED RESPONSE If it reaches threshold, it is interpreted into an ALL-OR-NONE ACTION POTENTIAL This travels along the afferent neuron The frequency of the action potentials is what determines the intensity of the stimulus At the synapse, the act ...
... At the sensory organ, the response is a NONPROPAGATED GRADED RESPONSE If it reaches threshold, it is interpreted into an ALL-OR-NONE ACTION POTENTIAL This travels along the afferent neuron The frequency of the action potentials is what determines the intensity of the stimulus At the synapse, the act ...
22-4 EUBANK
... The cerebellum, often called the “Little Brain,” has as its major function being proprioception (the unconscious awareness of the body’s position in space).2,5 It analyzes and adjusts the body for precise movement and balance. It also sends information to the thalamus via the superior peduncles, whi ...
... The cerebellum, often called the “Little Brain,” has as its major function being proprioception (the unconscious awareness of the body’s position in space).2,5 It analyzes and adjusts the body for precise movement and balance. It also sends information to the thalamus via the superior peduncles, whi ...
The Nervous System
... axon to speed up the signal transfer • Synaptic Terminal = end of the neuron • Synapse = gap/space between neurons where neurotransmitters transfer ...
... axon to speed up the signal transfer • Synaptic Terminal = end of the neuron • Synapse = gap/space between neurons where neurotransmitters transfer ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... motor learning and adaptation in response to changing conditions, such as external forces or muscle fatigue. More specifically, the cerebellumhasbeenhypothesizedtoprovideforward internal models, that is, predictions about what body movements will result from motor commands. It has further been propo ...
... motor learning and adaptation in response to changing conditions, such as external forces or muscle fatigue. More specifically, the cerebellumhasbeenhypothesizedtoprovideforward internal models, that is, predictions about what body movements will result from motor commands. It has further been propo ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... a particular direction. Direction of each line represents the cell’s preferred direction and its length represents the cell’s firing rate. Red solid arrows are the population vectors; black thin arrows are the direction of movement of the target limb (Georgopoulos, 1982) ...
... a particular direction. Direction of each line represents the cell’s preferred direction and its length represents the cell’s firing rate. Red solid arrows are the population vectors; black thin arrows are the direction of movement of the target limb (Georgopoulos, 1982) ...
Modeling and Imagery
... • So signal transmission is complex, determined by total strength of arriving signal and subsequent strength of descending signal ...
... • So signal transmission is complex, determined by total strength of arriving signal and subsequent strength of descending signal ...
Ch5slides - Blackwell Publishing
... depletion of the cellular, rather than the extracellular, thirst system that accounts for the greater part of the drinking, typically around 75 per cent. ...
... depletion of the cellular, rather than the extracellular, thirst system that accounts for the greater part of the drinking, typically around 75 per cent. ...
Unit 5- Nervous
... - I can discuss the anatomical and functional characteristics of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system - I can classify sense organs as special or general and explain the basic differences between the two groups. - I can discuss how a stimulus is converted into sensation. - I can list th ...
... - I can discuss the anatomical and functional characteristics of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system - I can classify sense organs as special or general and explain the basic differences between the two groups. - I can discuss how a stimulus is converted into sensation. - I can list th ...
the limbic system
... gives it a much higher efficiency. … it takes about 100-200 msec for the brain to recognize a familiar face … this simple task causes great problems to the computer - if it can do it at all. {efforts at developing AI have been disappointing} ...
... gives it a much higher efficiency. … it takes about 100-200 msec for the brain to recognize a familiar face … this simple task causes great problems to the computer - if it can do it at all. {efforts at developing AI have been disappointing} ...
Paternal transmission of subcortical band heterotopia through DCX
... only the mutated allele and tend to express a more severe phenotype, while females are heterozygous showing usually a milder phenotype [1]. Thus, in the case of a female patient with SBH this usually means two possibilities: a de novo mutation or an inherited mutation from a heterozygous asymptomati ...
... only the mutated allele and tend to express a more severe phenotype, while females are heterozygous showing usually a milder phenotype [1]. Thus, in the case of a female patient with SBH this usually means two possibilities: a de novo mutation or an inherited mutation from a heterozygous asymptomati ...
Nervous System
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
questions from - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... 4. As you watch a friend walk away from you, your retinal image of your friend gets smaller. Despite this, you do not perceive him to be shrinking. This is an example of 5. The reversible figure to the right illustrates the Gestalt organizing principle of 6. Which of the following is true about rods ...
... 4. As you watch a friend walk away from you, your retinal image of your friend gets smaller. Despite this, you do not perceive him to be shrinking. This is an example of 5. The reversible figure to the right illustrates the Gestalt organizing principle of 6. Which of the following is true about rods ...
Internal Regulation
... of baroreceptor activity, which stimulates the vasomotor center in the medulla to activate various nuclei in the hypothalamus to generate the desire to drink and conserve water (release of ADH). Hypovolemia also causes the kidneys to release renin, which ultimately leads to synthesis of ...
... of baroreceptor activity, which stimulates the vasomotor center in the medulla to activate various nuclei in the hypothalamus to generate the desire to drink and conserve water (release of ADH). Hypovolemia also causes the kidneys to release renin, which ultimately leads to synthesis of ...
nerves
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
Sensation and Perception Unit IV
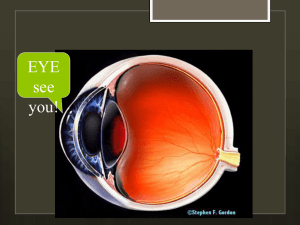
... • Retina- the light sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information • Accommodation- the process by which the eye’s lends changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina * ...
... • Retina- the light sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information • Accommodation- the process by which the eye’s lends changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina * ...
Vision - APPsychBCA
... other areas of the cortex for higher-level processing These areas – called supercell clusters – work in teams to determine familiar patterns – such as faces (processed in the right-side of temporal lobe) ...
... other areas of the cortex for higher-level processing These areas – called supercell clusters – work in teams to determine familiar patterns – such as faces (processed in the right-side of temporal lobe) ...
30. Autonomic NS. Sympathetic nervous system
... – Autonomic motor neurons to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands Where in the CNS? Hypothalamus and brain stem ...
... – Autonomic motor neurons to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands Where in the CNS? Hypothalamus and brain stem ...
Central Nervous System
... • Maintains water balance • Endocrine function – release hormones that regulate actions of the anterior pituitary gland • Waking state (alert and arousal) • Regulating appetite • Maintaining normal body temperature ...
... • Maintains water balance • Endocrine function – release hormones that regulate actions of the anterior pituitary gland • Waking state (alert and arousal) • Regulating appetite • Maintaining normal body temperature ...
ch15 autonomic nervous system
... sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Usually one division causes excitation and one causes inhibition resulting in autonomic tone. B. The sympathetic responses prepare the body for emergency situations (the fight-or-flight responses). 1. Sympathetic responses are stimulated by the four E’s (Em ...
... sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Usually one division causes excitation and one causes inhibition resulting in autonomic tone. B. The sympathetic responses prepare the body for emergency situations (the fight-or-flight responses). 1. Sympathetic responses are stimulated by the four E’s (Em ...
Neurotoxicity
... CO may also produce white matter damage. Systemic hypotension is the best predictor of these lesions following ...
... CO may also produce white matter damage. Systemic hypotension is the best predictor of these lesions following ...
Notes
... Nerves are composed of smaller structures called neurons. Neurons consist of 1. Cell Body: This contains the nucleus and other metabolic structures required to keep the cell alive. 2. Dendrites: This branch out from the cell body to receive electrical signals from other neurons. 3. Axon or Nerve Fib ...
... Nerves are composed of smaller structures called neurons. Neurons consist of 1. Cell Body: This contains the nucleus and other metabolic structures required to keep the cell alive. 2. Dendrites: This branch out from the cell body to receive electrical signals from other neurons. 3. Axon or Nerve Fib ...
Parts of the Brain - University of Peradeniya
... • Nervous system consists of nerve tissues: neurons and glia • Brain and spinal cord belongs to CNS • In CNS, macroscopically white and gray matter are identifiable • These white and gray matter are arranged into different areas of the brain and spinal cord ...
... • Nervous system consists of nerve tissues: neurons and glia • Brain and spinal cord belongs to CNS • In CNS, macroscopically white and gray matter are identifiable • These white and gray matter are arranged into different areas of the brain and spinal cord ...
nerve impulse
... Five major types of glia (cont.) Schwann cells (in PNS) • Found only in peripheral neurons • Support nerve fibers and form myelin sheaths (Figure 124) • Myelin sheath gaps are often called nodes of Ranvier • Neurilemma is formed by cytoplasm of Schwann cell (neurolemmocyte) wrapped around the myel ...
... Five major types of glia (cont.) Schwann cells (in PNS) • Found only in peripheral neurons • Support nerve fibers and form myelin sheaths (Figure 124) • Myelin sheath gaps are often called nodes of Ranvier • Neurilemma is formed by cytoplasm of Schwann cell (neurolemmocyte) wrapped around the myel ...