Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters of peripheral neuronal cell bodies Motor endings—axon terminals of motor neurons Innervate effectors (muscle fibers and glands) Cranial Nerves Attach to the brain and pass through foramina of the skull Numbered from I–XII Cranial ...
... Nerves and ganglia Nerves—bundles of peripheral axons Ganglia—clusters of peripheral neuronal cell bodies Motor endings—axon terminals of motor neurons Innervate effectors (muscle fibers and glands) Cranial Nerves Attach to the brain and pass through foramina of the skull Numbered from I–XII Cranial ...
Autonomic nervous system
... their target organs (see below “Function”): sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric. Sympathetic ganglia are located in two sympathetic chains close to the spinal cord: the prevertebral and pre-aortic chains. Parasympathetic ganglia, in contrast, are located in close proximity to the target organ: ...
... their target organs (see below “Function”): sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric. Sympathetic ganglia are located in two sympathetic chains close to the spinal cord: the prevertebral and pre-aortic chains. Parasympathetic ganglia, in contrast, are located in close proximity to the target organ: ...
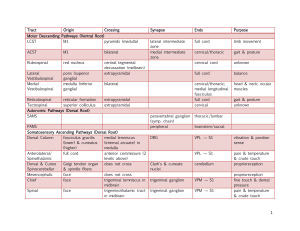
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... headache (from swelling, hydrocephalus, usually occipital) SCA has brainstem involvement while PICA does not ataxia: peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
... headache (from swelling, hydrocephalus, usually occipital) SCA has brainstem involvement while PICA does not ataxia: peduncle/pontine lesions; hydrocephalus; prefrontal cortex; spinal cord disorder; contralateral ataxia-hemiparesis ...
Stages of Brain Development
... This migration which results in cells being arranged in a particular alignment with other cells by layer and direction is called aggregation. Theoretically, each cell in the human body carries with it the entire DNA coding of the individual and can therefore differentiate into any cell type required ...
... This migration which results in cells being arranged in a particular alignment with other cells by layer and direction is called aggregation. Theoretically, each cell in the human body carries with it the entire DNA coding of the individual and can therefore differentiate into any cell type required ...
Neurophysiology
... where sensation and its location are perceived - Crossing to other side, decussation, occurs either at level of entry into spinal cord (spinothalamic) or in the medulla (posterior column – medial lemniscal). ...
... where sensation and its location are perceived - Crossing to other side, decussation, occurs either at level of entry into spinal cord (spinothalamic) or in the medulla (posterior column – medial lemniscal). ...
Modeling cortical maps with Topographica
... that is available freely at topographica.org. Here the user is studying the behavior of an orientation map in the primary visual cortex (V1), using a model similar to the one depicted in figure 1. The window at the bottom labeled “Orientation” shows the self-organized orientation map and the orienta ...
... that is available freely at topographica.org. Here the user is studying the behavior of an orientation map in the primary visual cortex (V1), using a model similar to the one depicted in figure 1. The window at the bottom labeled “Orientation” shows the self-organized orientation map and the orienta ...
Large-scale recording of neuronal ensembles
... Furthermore, understanding how the cooperative activity of different classes of neurons gives rise to collective ensemble behavior requires their separation and identification. Because most anatomical wiring is local, the majority of neuronal interactions, and thus computation, occur in a small volu ...
... Furthermore, understanding how the cooperative activity of different classes of neurons gives rise to collective ensemble behavior requires their separation and identification. Because most anatomical wiring is local, the majority of neuronal interactions, and thus computation, occur in a small volu ...
Untitled 2
... synthesise proteins and other materials Cell body's protein- and membrane-making machinery consist of clustered free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum - most active and most developed in the body Rough ER, also called chromatophilic substance stain darkly with basic dyes Golgi apparatus is w ...
... synthesise proteins and other materials Cell body's protein- and membrane-making machinery consist of clustered free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum - most active and most developed in the body Rough ER, also called chromatophilic substance stain darkly with basic dyes Golgi apparatus is w ...
Nervous Regulation
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon ...
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon ...
Nerve Growth Factor-7S (N0513) - Datasheet - Sigma
... neurons.6 NGF induces the formation of neurite-like filaments from chick embryo dorsal root ganglia2 and from rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells.7 In vivo NGF may be involved in fetal development8,9 and nerve regeneration.10 NGF may also play a physiological role within the central nervous system.8,11, ...
... neurons.6 NGF induces the formation of neurite-like filaments from chick embryo dorsal root ganglia2 and from rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells.7 In vivo NGF may be involved in fetal development8,9 and nerve regeneration.10 NGF may also play a physiological role within the central nervous system.8,11, ...
mspn1a
... muscle spindle (See Muscle Spindle Question). Cells in this area are organized into motor pools with somatotopic organization in regard to the muscles they innervate (See Question 2). b. Dorsal Horn The dorsal horn has a somatosensory function. It receives input from the dorsal root ganglia and othe ...
... muscle spindle (See Muscle Spindle Question). Cells in this area are organized into motor pools with somatotopic organization in regard to the muscles they innervate (See Question 2). b. Dorsal Horn The dorsal horn has a somatosensory function. It receives input from the dorsal root ganglia and othe ...
Development of Nervous System
... processing of serial sequences of information, and visual and auditory details. Specializes in detailed activities required for motor control. ...
... processing of serial sequences of information, and visual and auditory details. Specializes in detailed activities required for motor control. ...
Document
... metabotropic receptors, which are expressed by neurons and astrocytes stimulation of glutamate receptors may induce calcium signaling over stimulation with glutamate leads to neuronal death, glutamate induced neurotoxicity is the major damage in ischemia ...
... metabotropic receptors, which are expressed by neurons and astrocytes stimulation of glutamate receptors may induce calcium signaling over stimulation with glutamate leads to neuronal death, glutamate induced neurotoxicity is the major damage in ischemia ...
A Stereoscopic Look at Visual Cortex
... published study (Janssen et al. 2003) demonstrating that neurons in macaque IT discard anti-correlated signals and from a preliminary report (Fujita et al. 2003) that signals in IT show high choice probabilities in a fine stereoacuity task. However, IT [being a terminal station in the ventral stream ...
... published study (Janssen et al. 2003) demonstrating that neurons in macaque IT discard anti-correlated signals and from a preliminary report (Fujita et al. 2003) that signals in IT show high choice probabilities in a fine stereoacuity task. However, IT [being a terminal station in the ventral stream ...
What is a moment? `Cortical` sensory integration over a brief interval
... view of the fact that the animal’s ‘training’ had been based on a single example from another speaker. More surprising is the fact that the cell generalized from a single utterance of the training speaker to many utterances of more than half of the other speakers. ...
... view of the fact that the animal’s ‘training’ had been based on a single example from another speaker. More surprising is the fact that the cell generalized from a single utterance of the training speaker to many utterances of more than half of the other speakers. ...
(Figure 4B) in 12 month old Cln5-/- mice. To survey effects on glial
... nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss of their target neurons in lamina IV of somatosensory cortex. Our preliminary data suggest that this vulnerability of thalamic neurons is ...
... nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss of their target neurons in lamina IV of somatosensory cortex. Our preliminary data suggest that this vulnerability of thalamic neurons is ...
Taste and Smell
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
... • Specialized to detect chemicals dissolved in a fluid • The fluid may be saliva, mucous, or blood plasma • Rely on receptors that interact with specific molecules to generate an action potential • Receptors are integrated with two or more tissue types making them fit the definition of “organ” ...
Williams Syndrome Neuronal Size and Neuronal-Packing Density in Primary Visual Cortex
... receptive field size, sensitivity to color and light contrast, and timing properties. The parvo system is ideally suited for form, texture, and color analysis, while magno processes larger sections of space and appears better designed to calculate spatial location and motion. Anatomically, the magno ...
... receptive field size, sensitivity to color and light contrast, and timing properties. The parvo system is ideally suited for form, texture, and color analysis, while magno processes larger sections of space and appears better designed to calculate spatial location and motion. Anatomically, the magno ...
Brainstem*s involvement in Motor process
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
Sensory feedback for upper limb prostheses
... intrafusal muscles. While these afferents are clearly needed for controlling muscle length, their role in perception is less clear since they do not seem to carry accurate measurements of joint angle and velocity (Dimitriou and Edin, 2008). However, there is convincing evidence that some aspect of j ...
... intrafusal muscles. While these afferents are clearly needed for controlling muscle length, their role in perception is less clear since they do not seem to carry accurate measurements of joint angle and velocity (Dimitriou and Edin, 2008). However, there is convincing evidence that some aspect of j ...
I. Nerve Organization
... vertebrates, coordination of sensory input, motor dexterity, and possibly mental dexterity ...
... vertebrates, coordination of sensory input, motor dexterity, and possibly mental dexterity ...
Investigating neural correlates of conscious perception by frequency
... recent psychophysical studies have demonstrated that perceptual rivalry can occur even when both stimuli are presented through the same eye or when they are alternated between the eyes (2). Furthermore, single-unit recordings during binocular rivalry in monkeys indicate that, while the firing of mos ...
... recent psychophysical studies have demonstrated that perceptual rivalry can occur even when both stimuli are presented through the same eye or when they are alternated between the eyes (2). Furthermore, single-unit recordings during binocular rivalry in monkeys indicate that, while the firing of mos ...
Program booklet - Munich Center for NeuroSciences
... The detection of visual motion, both the movement of objects in a visual scene and of the visual scene itself, helps animals to spot prey, predators or mates and to navigate in their environment. Yet visual motion is not directly detected by photoreceptors in the retina, but has to be computed from ...
... The detection of visual motion, both the movement of objects in a visual scene and of the visual scene itself, helps animals to spot prey, predators or mates and to navigate in their environment. Yet visual motion is not directly detected by photoreceptors in the retina, but has to be computed from ...