Unit 3 - Biological Bases - Bearcat Social Studies Corner
... 18. The part of the neuron that receives information from neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicle (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 19. The part of the neuron that sends information to neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicles (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 2 ...
... 18. The part of the neuron that receives information from neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicle (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 19. The part of the neuron that sends information to neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicles (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 2 ...
Biological_Neuroscience
... 18. The part of the neuron that receives information from neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicle (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 19. The part of the neuron that sends information to neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicles (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 2 ...
... 18. The part of the neuron that receives information from neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicle (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 19. The part of the neuron that sends information to neighboring cells is called the (A) membrane (B) axons (C) vesicles (D) nucleus (E) dendrites 2 ...
Stereoscopic Mechanisms in Monkey Visual Cortex: Binocular
... The brain utilizes the signalsfrom the 2 eyes to recover the relative depth of objects.Wheatstone (1838) first demonstrated that a difference, or disparity, in the relative horizontal position of the object’s imagesin the 2 eyescan generatean impression of depth and solidity. Julesz(1960, 1971)later ...
... The brain utilizes the signalsfrom the 2 eyes to recover the relative depth of objects.Wheatstone (1838) first demonstrated that a difference, or disparity, in the relative horizontal position of the object’s imagesin the 2 eyescan generatean impression of depth and solidity. Julesz(1960, 1971)later ...
II./2.6. Examination of the sensory system
... points is varied by the examiner. The smallest distance is determined where the patient is still able to recognize the two points as separate. f.) Stereognosis: everyday objects (pen, key) are placed in the hand of the patient, which should be named by the patient wth closed eyes. The skin area supp ...
... points is varied by the examiner. The smallest distance is determined where the patient is still able to recognize the two points as separate. f.) Stereognosis: everyday objects (pen, key) are placed in the hand of the patient, which should be named by the patient wth closed eyes. The skin area supp ...
File
... Broca’s Area: Speak (can still sing and understand speech) Wernicker’s Area: Speech comprehension and expression (gibberish) Angular Gyrus: Reading aloud Connections (e.g. reading allowed requires visual info, turned into auditory info, then made into meaning, then spoken ...
... Broca’s Area: Speak (can still sing and understand speech) Wernicker’s Area: Speech comprehension and expression (gibberish) Angular Gyrus: Reading aloud Connections (e.g. reading allowed requires visual info, turned into auditory info, then made into meaning, then spoken ...
Programming task 5
... the desired transfer function (use an extra input parameter which decides the approximation criteria) with a Genetic Algorithm. When finding the least square- or the minimax-filter, the only thing that has to be modified is the definition of the error function. • Run the Genetic Algorithm with the d ...
... the desired transfer function (use an extra input parameter which decides the approximation criteria) with a Genetic Algorithm. When finding the least square- or the minimax-filter, the only thing that has to be modified is the definition of the error function. • Run the Genetic Algorithm with the d ...
High-Level Visual Processing: Cognitive Influences
... The Inferior Temporal Cortex Is Part of a Network of Cortical Areas Involved in Object Recognition Object recognition is intimately intertwined with visual categorization, visual memory, and emotion (see Figure 27–2), and the outputs of the inferior temporal cortex contribute to these functions. Amo ...
... The Inferior Temporal Cortex Is Part of a Network of Cortical Areas Involved in Object Recognition Object recognition is intimately intertwined with visual categorization, visual memory, and emotion (see Figure 27–2), and the outputs of the inferior temporal cortex contribute to these functions. Amo ...
A cellular mechanism for cortical associations: an organizing
... that although small (sub-threshold) signals contribute only to their respective spike initiation zones, the fact that input has reached threshold in one zone is quickly signaled to the other zone. This provides the possibility for associative interactions within the neuron by which the activity of o ...
... that although small (sub-threshold) signals contribute only to their respective spike initiation zones, the fact that input has reached threshold in one zone is quickly signaled to the other zone. This provides the possibility for associative interactions within the neuron by which the activity of o ...
Robo1 Regulates the Migration and Laminar Distribution of Upper
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...
... Indeed, an increasing number of genes have been identified that control the early phase of radial migration (Caviness and Rakic 1978; Gupta et al. 2002; Nadarajah and Parnavelas 2002; Tsai and Gleeson 2005; Cooper 2008; Huang 2009; Honda et al. 2011). In contrast, much less is known about how the ter ...
Physiological Psychology
... The Nervous System The nervous system can be simply described as collection of neurons which are arranged to work in a coordinated function. One of the most important functions of the nervous system is to process incoming information in such a way that appropriate mental and motor responses will occ ...
... The Nervous System The nervous system can be simply described as collection of neurons which are arranged to work in a coordinated function. One of the most important functions of the nervous system is to process incoming information in such a way that appropriate mental and motor responses will occ ...
On the importance of the transient visual response in the superior
... required to stimulate immediate action, either towards stimuli of interest (e.g. prey) or away from perilous stimuli (e.g. large looming things). The SC mediates these two fast responses through access to different motor output channels [4,5]. Unlike other parts of the visual orienting network (see ...
... required to stimulate immediate action, either towards stimuli of interest (e.g. prey) or away from perilous stimuli (e.g. large looming things). The SC mediates these two fast responses through access to different motor output channels [4,5]. Unlike other parts of the visual orienting network (see ...
The vocabulary of nerve cells
... what they will transport and what they will not: Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++,etc. Channels also differ in what causes them to open and/or close: Chemicals outside cell Chemicals inside cell Mechanical deformation of the membrane Etc. ...
... what they will transport and what they will not: Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++,etc. Channels also differ in what causes them to open and/or close: Chemicals outside cell Chemicals inside cell Mechanical deformation of the membrane Etc. ...
Biology 232
... Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; operate at all times, usually without conscious control or perception operates mainly via reflex arcs Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems ...
... Autonomic Nervous System – regulates activities of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; operate at all times, usually without conscious control or perception operates mainly via reflex arcs Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 1. The cerebellum is separated from the brain stem by the fourth ventricle. 2. The cerebellum is in two portions joined by a narrow median portion. 3. The cerebellum integrates impulses from higher centers to coordinate muscle actions, maintain equilibrium and muscle tone, and sustain normal posture ...
... 1. The cerebellum is separated from the brain stem by the fourth ventricle. 2. The cerebellum is in two portions joined by a narrow median portion. 3. The cerebellum integrates impulses from higher centers to coordinate muscle actions, maintain equilibrium and muscle tone, and sustain normal posture ...
Development of the Auditory Areas
... The prominent radial neurogenetic gradient between deep and superficial layers is shown after [3H] thymidine injections on E17 and EI8 (Figs. 12-2 and 12-3). Practically all of the neurons in layer VI and many of the neurons in layer V (especially anteriorly, Fig. 12-2) are unlabeled, while the majo ...
... The prominent radial neurogenetic gradient between deep and superficial layers is shown after [3H] thymidine injections on E17 and EI8 (Figs. 12-2 and 12-3). Practically all of the neurons in layer VI and many of the neurons in layer V (especially anteriorly, Fig. 12-2) are unlabeled, while the majo ...
Moving Colors in the Lime Light Minireview
... visual pathway. Signals from the K pathway could potentially reach area MT from the V1 blobs via V2 (see Merigan and Maunsell, 1993, for details regarding projections between these areas). Alternatively, the direct (yet sparse) connections known to exist between K layers in the LGN and area MT (Figu ...
... visual pathway. Signals from the K pathway could potentially reach area MT from the V1 blobs via V2 (see Merigan and Maunsell, 1993, for details regarding projections between these areas). Alternatively, the direct (yet sparse) connections known to exist between K layers in the LGN and area MT (Figu ...
on Brain/ Behavior
... aggressive and fear-based behaviors Area in the parietal lobe close to the temporal lobe; visual processing, mathematics, cognition, high-language functions like understanding metaphors, and vestibular (balance) sensations; transforms visual representation into auditory code; Subjects of researchers ...
... aggressive and fear-based behaviors Area in the parietal lobe close to the temporal lobe; visual processing, mathematics, cognition, high-language functions like understanding metaphors, and vestibular (balance) sensations; transforms visual representation into auditory code; Subjects of researchers ...
Case Study 48
... edema, no significant mass effect or midline shift. No hemorrhage is seen on T1 and there is no abnormal contrast enhancement. (There is also a small enhancing left retromastoid lesion with underlying meningeal enhancement felt to be a hemangioma.) L’hermitte-duclos disease was strongly suspected ba ...
... edema, no significant mass effect or midline shift. No hemorrhage is seen on T1 and there is no abnormal contrast enhancement. (There is also a small enhancing left retromastoid lesion with underlying meningeal enhancement felt to be a hemangioma.) L’hermitte-duclos disease was strongly suspected ba ...
Consciousness_12
... brain stem. Each geniculate axon terminates in the visual cortex, primarily in layer 4. The cells in each layer have their own patterns of connections with other subcortical regions. Cells in the visual cortex are arranged in into orientation-specific columns, ocular dominance columns, and blobs. So ...
... brain stem. Each geniculate axon terminates in the visual cortex, primarily in layer 4. The cells in each layer have their own patterns of connections with other subcortical regions. Cells in the visual cortex are arranged in into orientation-specific columns, ocular dominance columns, and blobs. So ...
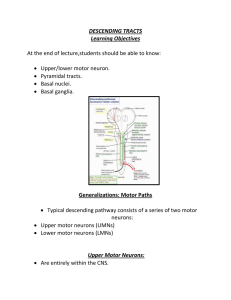
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Includes descending motor tracts that do not pass through medullary pyramids or corticobulbar tracts. Includes: Rubrospinal tracts Vestibulospinal tracts Reticulospinal tracts Rubrospinal Tract Begins in red nucleus. Decussates in midbrain. Descends in lateral funiculus (column). ...
... Includes descending motor tracts that do not pass through medullary pyramids or corticobulbar tracts. Includes: Rubrospinal tracts Vestibulospinal tracts Reticulospinal tracts Rubrospinal Tract Begins in red nucleus. Decussates in midbrain. Descends in lateral funiculus (column). ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... is called a neuron ( Figure 1.1). The messages carried by neurons are called nerve impulses. Nerve impulses can travel very quickly because they are electrical impulses. Think about flipping on a light switch when you enter a room. When you flip the switch, the electricity flows to the light through ...
... is called a neuron ( Figure 1.1). The messages carried by neurons are called nerve impulses. Nerve impulses can travel very quickly because they are electrical impulses. Think about flipping on a light switch when you enter a room. When you flip the switch, the electricity flows to the light through ...
Categorical perception of somesthetic stimuli: psychophysical
... stimulus speeds (categorical neurons). In a light instruction task, we tested the possibility that the categorical neurons (n = 71) were associated with the intention to press, or with the trajectory of the hand to one of the two target switches used to indicate categorization. In this situation, ea ...
... stimulus speeds (categorical neurons). In a light instruction task, we tested the possibility that the categorical neurons (n = 71) were associated with the intention to press, or with the trajectory of the hand to one of the two target switches used to indicate categorization. In this situation, ea ...
cp_kellermann_launay_17092010
... How does Prozac act? By acting on the microRNA… The response time to antidepressants, such as Prozac, is around three weeks. How can we explain this? The adaptation mechanisms of the neurons to antidepressants has, until now, remained enigmatic. Research, published this week by the teams of Odile Ke ...
... How does Prozac act? By acting on the microRNA… The response time to antidepressants, such as Prozac, is around three weeks. How can we explain this? The adaptation mechanisms of the neurons to antidepressants has, until now, remained enigmatic. Research, published this week by the teams of Odile Ke ...
Population vectors and motor cortex: neural coding or
... molecule. The WNT factors are a family of secreted signaling proteins, and are known to be involved in early developmental patterning. Several are also expressed in the brain, and the presence of WNT-7a in cerebellar granule cells during the period of synaptogenesis prompted the authors to examine a ...
... molecule. The WNT factors are a family of secreted signaling proteins, and are known to be involved in early developmental patterning. Several are also expressed in the brain, and the presence of WNT-7a in cerebellar granule cells during the period of synaptogenesis prompted the authors to examine a ...
Chapter 14 - WordPress.com
... Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing messages o Cervical enlargement o Lumbar enlargement Conus medullaris + filum terminale = cauda equina The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments, each associated with a pair of o Dorsal root ganglia- contain cell bodies of sensory n ...
... Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing messages o Cervical enlargement o Lumbar enlargement Conus medullaris + filum terminale = cauda equina The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments, each associated with a pair of o Dorsal root ganglia- contain cell bodies of sensory n ...