Pathophysiology of Pain
... horn, travel ventrally, and terminate in lamina III and deeper. C fibers (small unmyelinated afferents) penetrate directly and generally terminate no deeper than lamina II. However, after peripheral nerve injury there is a prominent sprouting of large afferents dorsally from lamina III into laminae ...
... horn, travel ventrally, and terminate in lamina III and deeper. C fibers (small unmyelinated afferents) penetrate directly and generally terminate no deeper than lamina II. However, after peripheral nerve injury there is a prominent sprouting of large afferents dorsally from lamina III into laminae ...
Exam I
... 11) In order for a presynaptic neuron to send a bigger signal to a postsynaptic neuron it must… A) send larger action potentials. B) increase the frequency with which it is sending action potentials. C) All of the above. D) None of the above. Use the following figure of an action potential to answer ...
... 11) In order for a presynaptic neuron to send a bigger signal to a postsynaptic neuron it must… A) send larger action potentials. B) increase the frequency with which it is sending action potentials. C) All of the above. D) None of the above. Use the following figure of an action potential to answer ...
04-21-06
... • Sea stars have a nerve net in each arm connected by radial nerves to a central nerve ring. No Photosensitive Organs ...
... • Sea stars have a nerve net in each arm connected by radial nerves to a central nerve ring. No Photosensitive Organs ...
Test yourself on lesions in section pictures
... spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralateral body occurs due to elimination of the lateral spinothalamic tract. This tract crossed back in th ...
... spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralateral body occurs due to elimination of the lateral spinothalamic tract. This tract crossed back in th ...
Neurology
... Every living organism must be able to react appropriately to changes in its environment if it is to survive. The nervous system monitors and controls almost every organ system through a series of positive and negative feedback loops. The nervous system consists of brain, nerves and spinal cord. The ...
... Every living organism must be able to react appropriately to changes in its environment if it is to survive. The nervous system monitors and controls almost every organ system through a series of positive and negative feedback loops. The nervous system consists of brain, nerves and spinal cord. The ...
The Nervous System - teacheroftruth.net
... Further investigations revealed that one of the patients was a doctor working at the clinic despite having had his medical licence revoked. He had diluted the neurotoxin before injecting it into himself and three patients. The incident is described in the Journal of the American Medical Association ...
... Further investigations revealed that one of the patients was a doctor working at the clinic despite having had his medical licence revoked. He had diluted the neurotoxin before injecting it into himself and three patients. The incident is described in the Journal of the American Medical Association ...
Role of Feedforward and Feedback Projections in Figure
... stimulus evoked response of a cell. The prominence of contextual information processing is reflected by the fact that the majority of neurons in the primary visual cortex are sensitive to such contextual influences from surrounding regions. Surrounding stimuli outside the classical receptive field d ...
... stimulus evoked response of a cell. The prominence of contextual information processing is reflected by the fact that the majority of neurons in the primary visual cortex are sensitive to such contextual influences from surrounding regions. Surrounding stimuli outside the classical receptive field d ...
sponges_and_cnidarians
... No cell wall and few specialized cells Live their entire life attached to a surface They eat by sifting microscopic food in water • Choanocytes are specialized structures that help move water through their body cavity • Water enters through pores and leaves through the osculum (a large hole at the t ...
... No cell wall and few specialized cells Live their entire life attached to a surface They eat by sifting microscopic food in water • Choanocytes are specialized structures that help move water through their body cavity • Water enters through pores and leaves through the osculum (a large hole at the t ...
Untitled - inetTeacher
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters that naturally reduce pain and boost mood. Flooding the brain with painkillers, antidepressants, or other drugs may cause the brain to stop producing endorphins. When such drug(s) is discontinued, a person may experience a period of discomfort—ranging from mild to ag ...
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters that naturally reduce pain and boost mood. Flooding the brain with painkillers, antidepressants, or other drugs may cause the brain to stop producing endorphins. When such drug(s) is discontinued, a person may experience a period of discomfort—ranging from mild to ag ...
Brains of Primitive Chordates - CIHR Research Group in Sensory
... is the hagfish, Myxine) have a brain that develops from invaginated ectoderm that becomes completely transformed into nervous tissue but remains confined within the former epithelial basement membrane. Major subdivisions that can be identified on the basis of external and internal features include ( ...
... is the hagfish, Myxine) have a brain that develops from invaginated ectoderm that becomes completely transformed into nervous tissue but remains confined within the former epithelial basement membrane. Major subdivisions that can be identified on the basis of external and internal features include ( ...
Remembering or Forgetting: The Lifetime of Memories
... the group improves memory while removing them accelerates forgetting. A special type of neuron in the brain controls the size of these groups. We think that this process regulates the lifetime of memories. ...
... the group improves memory while removing them accelerates forgetting. A special type of neuron in the brain controls the size of these groups. We think that this process regulates the lifetime of memories. ...
J. Neurophysiol. - Nonlinear Dynamics Group
... the firing activity of specific populations of neurons to animal behaviors, defining sites with neuronal activity in particular behavioral contexts as the functional areas corresponding to those behaviors. Although such observations are interesting in themselves, these studies do not necessarily exa ...
... the firing activity of specific populations of neurons to animal behaviors, defining sites with neuronal activity in particular behavioral contexts as the functional areas corresponding to those behaviors. Although such observations are interesting in themselves, these studies do not necessarily exa ...
GABA A Receptor
... Ions channels are not suitable for causing prolonged postsynaptic neuronal changes (such as those needed for memory and other prolonged changes) because they close within millisecond Activation of second messenger systems in the postsynaptic neuronal cell itself achieves long term effects The most c ...
... Ions channels are not suitable for causing prolonged postsynaptic neuronal changes (such as those needed for memory and other prolonged changes) because they close within millisecond Activation of second messenger systems in the postsynaptic neuronal cell itself achieves long term effects The most c ...
Decoding visual consciousness from human
... natural link to recent developments in experimental neuroscience based on multivariate decoding and pattern recognition [9–24]. This promising approach could yield a much tighter link between hypothetical NCCs and conscious experiences. ...
... natural link to recent developments in experimental neuroscience based on multivariate decoding and pattern recognition [9–24]. This promising approach could yield a much tighter link between hypothetical NCCs and conscious experiences. ...
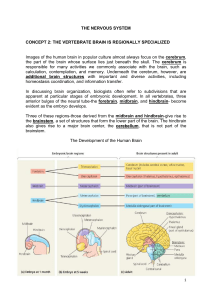
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... damaged, the eyes can follow a moving object, but they will not stop at the same place as the object. ...
... damaged, the eyes can follow a moving object, but they will not stop at the same place as the object. ...
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... Neurons are organized into networks. ● Connections are one or two-way communication links between neurons ● Weights are the strength of connections. A weight wij is a real number than indicates the influence neuron ui has on neuron uj ...
... Neurons are organized into networks. ● Connections are one or two-way communication links between neurons ● Weights are the strength of connections. A weight wij is a real number than indicates the influence neuron ui has on neuron uj ...
At the root of embodied cognition: Cognitive science meets
... 1997). This classification reveals the role of motor neurons in actions that are required for interaction with an object, action finalized towards reaching a determined goal. In fact, mirror neurons are intended for an actionÕs underlying purpose and not for the single movements required or the effecto ...
... 1997). This classification reveals the role of motor neurons in actions that are required for interaction with an object, action finalized towards reaching a determined goal. In fact, mirror neurons are intended for an actionÕs underlying purpose and not for the single movements required or the effecto ...
doc Practice midterm
... c. Both establish reflex connections with some component of the trigeminal sensory complex d. Neither innervate branchiomeric muscles 13. Which of the following structures reveive direct synaptic connections from first order sensory ganglion cells : ...
... c. Both establish reflex connections with some component of the trigeminal sensory complex d. Neither innervate branchiomeric muscles 13. Which of the following structures reveive direct synaptic connections from first order sensory ganglion cells : ...
Towards understanding of the cortical network underlying
... IT cortex. In one type of neuron, the strongest and the second strongest responses during the cue period were ascribed to particular paired pictures (‘pair-coding neuron’; figure 1d,e). The other type of neuron, which had the strongest response to optimal stimulus during the cue period, exhibited st ...
... IT cortex. In one type of neuron, the strongest and the second strongest responses during the cue period were ascribed to particular paired pictures (‘pair-coding neuron’; figure 1d,e). The other type of neuron, which had the strongest response to optimal stimulus during the cue period, exhibited st ...
Spinal Reflexes
... • Believed that simple reflexes activated by receptors in the skin and muscles were the basic units of movement. • Also, complex sequences of movement were the combinations of simple reflexes. ...
... • Believed that simple reflexes activated by receptors in the skin and muscles were the basic units of movement. • Also, complex sequences of movement were the combinations of simple reflexes. ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH
... The goal of the present application is to determine the action of purinergic neurotransmission, especially that mediated by P2X4 receptors, in brain areas related to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of alcohol. My portion of the project involves the investigation of the interaction of ATP an ...
... The goal of the present application is to determine the action of purinergic neurotransmission, especially that mediated by P2X4 receptors, in brain areas related to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of alcohol. My portion of the project involves the investigation of the interaction of ATP an ...
Cells in human postmortem brain tissue slices remain alive for
... Key Words: aging 䡠 Alzheimer’s disease 䡠 human brain 䡠 tissue culture 䡠 transgene expression Brain disorders are complex diseases often associated with multiple genetic, environmental, and agerelated risk factors (1–5). Although animal models have contributed greatly to our understanding of human ne ...
... Key Words: aging 䡠 Alzheimer’s disease 䡠 human brain 䡠 tissue culture 䡠 transgene expression Brain disorders are complex diseases often associated with multiple genetic, environmental, and agerelated risk factors (1–5). Although animal models have contributed greatly to our understanding of human ne ...
animal nervous system - mf011
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla ...
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla ...
MF011_fhs_lnt_008a_Jan11
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla ...
... The brainstem coordinates and conducts information between brain centers The brainstem has three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata The midbrain contains centers for receipt and integration of sensory information The pons regulates breathing centers in the medulla ...