primary motor cortex - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Major point of departure of signals from cortex Somatotopic – more cortex is devoted to body parts that make more movements (eg. face vs elbow) ...
... Major point of departure of signals from cortex Somatotopic – more cortex is devoted to body parts that make more movements (eg. face vs elbow) ...
The Nervous System
... • Most neuron cell bodies are found in the central nervous system • Gray matter—cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers • Nuclei—clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system • Ganglia—collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
... • Most neuron cell bodies are found in the central nervous system • Gray matter—cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers • Nuclei—clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system • Ganglia—collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
9e_CH_02 - Biloxi Public Schools
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguisti ...
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguisti ...
3.13
... and developed a mathematical model for neuron activity. Their work appeared in a series of papers in 1952. It is an excellent example of how experimental and theoretical research can be combined to gain a thorough understanding of a natural system. In 1963, Hodgkin and Huxley were awarded the Nobel ...
... and developed a mathematical model for neuron activity. Their work appeared in a series of papers in 1952. It is an excellent example of how experimental and theoretical research can be combined to gain a thorough understanding of a natural system. In 1963, Hodgkin and Huxley were awarded the Nobel ...
... up all the different areas and messages are constantly passing between them from sensory areas to motor areas via association areas. This allows the brain to make an integrated response based on all the collective information. The cerebrum is also able to recoil stored memories and then alter future ...
STEM CELLS OF THE BRAIN
... implanting stem cells into a damaged area has been shown some promising recovery for strokes in studies done on rodents (Srivastava, 2009). The stem cells that already exist in the brain of both human and animals are not sufficient enough to repair damage alone. In order to help the brains’ ability ...
... implanting stem cells into a damaged area has been shown some promising recovery for strokes in studies done on rodents (Srivastava, 2009). The stem cells that already exist in the brain of both human and animals are not sufficient enough to repair damage alone. In order to help the brains’ ability ...
full abstracts in word format
... Ceramic optical detectors based on the photo-ferroelectrics effect are being developed for direct implantation into the eyes of patients with retinal dystrophies. In retinal dystrophies where the optic nerve and retinal ganglia are intact (such as Retinitis Pigmentosa), direct retinal implant of an ...
... Ceramic optical detectors based on the photo-ferroelectrics effect are being developed for direct implantation into the eyes of patients with retinal dystrophies. In retinal dystrophies where the optic nerve and retinal ganglia are intact (such as Retinitis Pigmentosa), direct retinal implant of an ...
Psychobiology—Behavioral Problems Seeking Biological Solutions
... the problem of the biological bases of behavior, both human and nonhuman. Michael Gazzaniga and Colin Blakemore have provided a survey of much of this field in the Handbook of Psychobiology. While hoping to impart the vitality and indicate the rapid developments of psychobiology, the authors have al ...
... the problem of the biological bases of behavior, both human and nonhuman. Michael Gazzaniga and Colin Blakemore have provided a survey of much of this field in the Handbook of Psychobiology. While hoping to impart the vitality and indicate the rapid developments of psychobiology, the authors have al ...
Active vision system for embodied intelligence based
... ◘ Use images organized in time sequences to obtain feedback connections for invariance building ◘ Process the input data from layer N-1 and calculate the correlations ◘ For each neuron, find out the best correlated set of neurons, and create connections to those neurons ● Local winners are used to a ...
... ◘ Use images organized in time sequences to obtain feedback connections for invariance building ◘ Process the input data from layer N-1 and calculate the correlations ◘ For each neuron, find out the best correlated set of neurons, and create connections to those neurons ● Local winners are used to a ...
The Nervous System - Gordon State College
... neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the lower body. The spinal cord also controls some automatic, involuntary responses to sensory stimuli cal ...
... neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the lower body. The spinal cord also controls some automatic, involuntary responses to sensory stimuli cal ...
The Central Nervous System
... Sensory Areas of the Cerebrum • Sensory association cortex – Posterior to the primary sensory cortex in the parietal lobe – Integrates sensory inputs (temperature, pressure etc, not special senses) from the primary sensory cortex – Produces an understanding of an object being felt: its size, textur ...
... Sensory Areas of the Cerebrum • Sensory association cortex – Posterior to the primary sensory cortex in the parietal lobe – Integrates sensory inputs (temperature, pressure etc, not special senses) from the primary sensory cortex – Produces an understanding of an object being felt: its size, textur ...
Lecture slides from 2007
... Skeletal Joints Joints can rotate along: •One axis (knee) •Two axes (wrist) •Three axes (hip) ...
... Skeletal Joints Joints can rotate along: •One axis (knee) •Two axes (wrist) •Three axes (hip) ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • try to relate them to molecular properties in synapses, various receptors, ion channels (pore forming proteins), membrane properties; • try to find markers for specific abnormalities. ...
... • try to relate them to molecular properties in synapses, various receptors, ion channels (pore forming proteins), membrane properties; • try to find markers for specific abnormalities. ...
Central Nervous System
... After inside flooded with Na+, K+ gates open (they are slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
... After inside flooded with Na+, K+ gates open (they are slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
File - Joris Vangeneugden
... technique of in-vivo fluorescence microendoscopy. This technique measures fluorescence excitation elicited by underlying neural activity and is able to capture > 75 cells simultaneously in awake and freely moving mice. Finally we will investigate in more detail the large inter-subject variability in ...
... technique of in-vivo fluorescence microendoscopy. This technique measures fluorescence excitation elicited by underlying neural activity and is able to capture > 75 cells simultaneously in awake and freely moving mice. Finally we will investigate in more detail the large inter-subject variability in ...
Nervous System Organization
... You touch a hot stove and jerk your hand back. Sensory input, integration, motor output ...
... You touch a hot stove and jerk your hand back. Sensory input, integration, motor output ...
primary motor Cortex
... gradients and not due to the original stimulus itself. Given that action potentials are always of a similar magnitude, how can stimuli of varied strengths be distinguished? A suprathreshold stimulus, one that is larger than necessary to depolarize the membrane simply to threshold, does not produce a ...
... gradients and not due to the original stimulus itself. Given that action potentials are always of a similar magnitude, how can stimuli of varied strengths be distinguished? A suprathreshold stimulus, one that is larger than necessary to depolarize the membrane simply to threshold, does not produce a ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
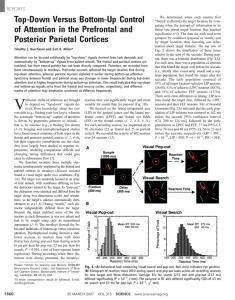
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
Abstract
... features including symptoms of disrupted colonic motility and visceral pain. To better understand and treat these conditions, it is necessary to elucidate the neural mechanisms responsible for altered gut functions and to develop targeted therapeutic strategies. The objectives of my dissertation stu ...
... features including symptoms of disrupted colonic motility and visceral pain. To better understand and treat these conditions, it is necessary to elucidate the neural mechanisms responsible for altered gut functions and to develop targeted therapeutic strategies. The objectives of my dissertation stu ...
Nervous System Function
... Base unit that has very simple function – “decide” whether to transmit signal or not ...
... Base unit that has very simple function – “decide” whether to transmit signal or not ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Somatosensory Feedback a. Vertical columnar arrangement of the neurons in the motor cortex b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column operates as an integrative operating system d. Each column can also function ...
... • Somatosensory Feedback a. Vertical columnar arrangement of the neurons in the motor cortex b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column operates as an integrative operating system d. Each column can also function ...
pdf file. - Harvard Vision Lab
... Each of our movements activates our own sensory receptors, and therefore keeping track of self-movement is a necessary part of analysing sensory input. One way in which the brain keeps track of self-movement is by monitoring an internal copy, or corollary discharge, of motor commands1–13. This conce ...
... Each of our movements activates our own sensory receptors, and therefore keeping track of self-movement is a necessary part of analysing sensory input. One way in which the brain keeps track of self-movement is by monitoring an internal copy, or corollary discharge, of motor commands1–13. This conce ...
Spatial Responsiveness of Monkey Hippocampal Neurons to
... Of 1,047 neurons recorded, 106 (10.1%) responded to some stimuli from one or more directions. Of these 106 neurons with directionally differentiating responsiveness, 49 responded to visual stimulation, 35 to auditory stimulation, and 22 to both. Among 81 neurons, each tested with more than 10 differ ...
... Of 1,047 neurons recorded, 106 (10.1%) responded to some stimuli from one or more directions. Of these 106 neurons with directionally differentiating responsiveness, 49 responded to visual stimulation, 35 to auditory stimulation, and 22 to both. Among 81 neurons, each tested with more than 10 differ ...