reflex
... the afferent neuron in the PNS. The afferent neuron then transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. The impulse will transmit through the ganglion then to the gray matter in the spinal cord. (Ganglion is a structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies). ...
... the afferent neuron in the PNS. The afferent neuron then transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. The impulse will transmit through the ganglion then to the gray matter in the spinal cord. (Ganglion is a structure containing a number of nerve cell bodies). ...
Chapter 12 - apsubiology.org
... electrical stimulation elicits different responses includes defensive posturing (rage); others inspire timidity ...
... electrical stimulation elicits different responses includes defensive posturing (rage); others inspire timidity ...
What's a cerebellar circuit doing in the auditory system?
... Department of Physiology, University of Wisconsin, 1300 University Avenue, Madison, WI 53706, USA Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, 720 Rutland Avenue, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA ...
... Department of Physiology, University of Wisconsin, 1300 University Avenue, Madison, WI 53706, USA Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, 720 Rutland Avenue, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA ...
Case Study: John Woodbury - Harvard Life Science Outreach Program
... What is your hypothesis? (Keep in mind this is simply a starting point and you will get more information later that will most likely change your hypothesis). ...
... What is your hypothesis? (Keep in mind this is simply a starting point and you will get more information later that will most likely change your hypothesis). ...
Do distinct populations of dorsal root ganglion neurons account for
... mechanisms to be studied further to putatively explain neurogenic CGRP release being so effective in ameliorating hypertensive kidney damage (3, 31). One major problem in this respect lies in the fact that afferent sensory nerve fibers, mainly C-fibers, are extremely difficult to record (4). Further ...
... mechanisms to be studied further to putatively explain neurogenic CGRP release being so effective in ameliorating hypertensive kidney damage (3, 31). One major problem in this respect lies in the fact that afferent sensory nerve fibers, mainly C-fibers, are extremely difficult to record (4). Further ...
Chapter 12 – Auditory Localization and Organization
... But if a sound strikes L first, then strikes R shortly afterward, L’s action potential will reach the end of its axon first and much much later (in neural time) R’s action potential will reach the end of its axon, resulting in insufficient neurotransmitter to cause the MSO neuron to respond. Note th ...
... But if a sound strikes L first, then strikes R shortly afterward, L’s action potential will reach the end of its axon first and much much later (in neural time) R’s action potential will reach the end of its axon, resulting in insufficient neurotransmitter to cause the MSO neuron to respond. Note th ...
Radial migration: Retinal neurons hold on for the ride
... and forth, instead of progressing basally. A second role of the apical process may be to control the mode of migration. When the basal process was experimentally ablated, RGC migration was initially stymied but the authors noticed that, later in the imaging session, most RGCs detached their apical p ...
... and forth, instead of progressing basally. A second role of the apical process may be to control the mode of migration. When the basal process was experimentally ablated, RGC migration was initially stymied but the authors noticed that, later in the imaging session, most RGCs detached their apical p ...
No Slide Title
... BIFURCATION OF COMMON CAROTID BLOOD SUPPLY-EXTERNAL CAROTID VENOUS DRAIN-INT JUGULAR NERVE SUPPLY- IX NERVE ...
... BIFURCATION OF COMMON CAROTID BLOOD SUPPLY-EXTERNAL CAROTID VENOUS DRAIN-INT JUGULAR NERVE SUPPLY- IX NERVE ...
The horizontal brain slice preparation: a novel approach for
... recorded. We find that the horizontal brain slice preparation stays healthy on the rig for ⬃2 h (no perfusion required). A minor drawback of this preparation is that, even though the afferent sensory inputs are preserved, removing the most outside edge of tectum (which corresponds to the most dorsal ...
... recorded. We find that the horizontal brain slice preparation stays healthy on the rig for ⬃2 h (no perfusion required). A minor drawback of this preparation is that, even though the afferent sensory inputs are preserved, removing the most outside edge of tectum (which corresponds to the most dorsal ...
Common Neurotransmitters: Criteria for Neurotransmitters, Key
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
The Neurons that Control Axial Movements in a Frog Embryo1
... The simplest hypothesis to explain this evidence suggests that three types of spinal would be for the central synapses of the neuron control at least the flexure and trigeminal sensory cells involved to release swimming responses (see also Roberts et al., an inhibitory transmitter (Roberts, 1980). 1 ...
... The simplest hypothesis to explain this evidence suggests that three types of spinal would be for the central synapses of the neuron control at least the flexure and trigeminal sensory cells involved to release swimming responses (see also Roberts et al., an inhibitory transmitter (Roberts, 1980). 1 ...
Ingestive Behaviour Chapter 12
... • Tryptophan is a precursor of 5-HT, and increases in brain tryptophan lead to increases in brain 5-HT. • Increase in brain 5-HT leads to decreased consumption of carbohydrates. – Carb consumption, insulin injection, and tryptophan levels all increase brain 5-HT. – 5-HT agonists decrease carb intake ...
... • Tryptophan is a precursor of 5-HT, and increases in brain tryptophan lead to increases in brain 5-HT. • Increase in brain 5-HT leads to decreased consumption of carbohydrates. – Carb consumption, insulin injection, and tryptophan levels all increase brain 5-HT. – 5-HT agonists decrease carb intake ...
File
... In the PNS, the myelin sheath is formed by ________________________ cells. o The __________________________ cells wrap themselves around the _________________ and lay down multiple _________________________ of _________________________________. o The nucleus and cytoplasm are in the ________________ ...
... In the PNS, the myelin sheath is formed by ________________________ cells. o The __________________________ cells wrap themselves around the _________________ and lay down multiple _________________________ of _________________________________. o The nucleus and cytoplasm are in the ________________ ...
Neural Correlates for Perception of 3D Surface Orientation from
... 0.10). Thus, the neural coding of surface orientation based on texture gradient was as precise as that based on disparity gradient in CIP neurons. After the unit recording, we conducted a behavioral test to confirm that monkeys perceive depth from texture gradient. Although psychophysical studies su ...
... 0.10). Thus, the neural coding of surface orientation based on texture gradient was as precise as that based on disparity gradient in CIP neurons. After the unit recording, we conducted a behavioral test to confirm that monkeys perceive depth from texture gradient. Although psychophysical studies su ...
olfaction and limbic system
... Smells are surer than sounds and sights to make your heart-strings crack. - Rudyard Kipling ...
... Smells are surer than sounds and sights to make your heart-strings crack. - Rudyard Kipling ...
Understanding trigeminal pain pathways: lessons from teeth
... TMJ pain: intra-capsular injection of Freund’s adjuvant (Thut et al. 2007); single molar tooth crown that caused occlusal interference (Cao et al. 2009). Obstructive parotitis: Freund’s adjuvant injected along the parotid duct and papilla sealed (Ogawa et al. 2003). Neuropathic pain: Ligation/sectio ...
... TMJ pain: intra-capsular injection of Freund’s adjuvant (Thut et al. 2007); single molar tooth crown that caused occlusal interference (Cao et al. 2009). Obstructive parotitis: Freund’s adjuvant injected along the parotid duct and papilla sealed (Ogawa et al. 2003). Neuropathic pain: Ligation/sectio ...
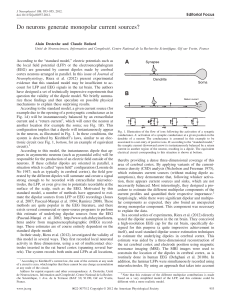
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... thereby providing a dense three-dimensional coverage of this area of cerebral cortex. By applying variants of the currentsource density (CSD) analysis (Nicholson and Freeman 1975), which estimates current sources (without making dipole assumptions), they demonstrate that, following whisker activatio ...
... thereby providing a dense three-dimensional coverage of this area of cerebral cortex. By applying variants of the currentsource density (CSD) analysis (Nicholson and Freeman 1975), which estimates current sources (without making dipole assumptions), they demonstrate that, following whisker activatio ...
Reduction III: Mechanistic Reduction
... requires identifying the parts and operations that interact to produce the phenomenon This requires discovering productive continuity between the operations of the different parts In many cases the entities identified by ruthless reduction in explaining cognitive activities such as learning are mult ...
... requires identifying the parts and operations that interact to produce the phenomenon This requires discovering productive continuity between the operations of the different parts In many cases the entities identified by ruthless reduction in explaining cognitive activities such as learning are mult ...
The Importance of the Nervous System
... • ensures action potential travels in one direction only ...
... • ensures action potential travels in one direction only ...
NAlab08_DescMotor
... the most medial to the face and larynx, and the intermediate fibers to the upper extremity. What cranial nerve exits from the brain at the medial border of the basis pedunculi? Which other major descending tracts take origin from structures shown in this slide? M-3 Horizontal—cerebral hemisphere; tr ...
... the most medial to the face and larynx, and the intermediate fibers to the upper extremity. What cranial nerve exits from the brain at the medial border of the basis pedunculi? Which other major descending tracts take origin from structures shown in this slide? M-3 Horizontal—cerebral hemisphere; tr ...
Descending Motor Pathways Objective • To learn the functional
... the most medial to the face and larynx, and the intermediate fibers to the upper extremity. What cranial nerve exits from the brain at the medial border of the basis pedunculi? Which other major descending tracts take origin from structures shown in this slide? M-3 Horizontal—cerebral hemisphere; tr ...
... the most medial to the face and larynx, and the intermediate fibers to the upper extremity. What cranial nerve exits from the brain at the medial border of the basis pedunculi? Which other major descending tracts take origin from structures shown in this slide? M-3 Horizontal—cerebral hemisphere; tr ...
Sonic Hedgehog Expression in Corticofugal Projection Neurons
... decreased in the Shh conditional null animals, while mEPSC frequency in layer II/III (Figures 3J and 3K) was not significantly different. We also observed a 1.6-fold increase in the input resistance of conditional mutants, but no change in mEPSC amplitude between the groups, consistent with a decrea ...
... decreased in the Shh conditional null animals, while mEPSC frequency in layer II/III (Figures 3J and 3K) was not significantly different. We also observed a 1.6-fold increase in the input resistance of conditional mutants, but no change in mEPSC amplitude between the groups, consistent with a decrea ...
Neurobiology
... The most striking differences between humans and other animals are in the size and the complexity of our brains. With our big brains we have acquired a rich culture, which far exceeds that of any other species in scope and complexity. We have developed science to understand how and why an immensity ...
... The most striking differences between humans and other animals are in the size and the complexity of our brains. With our big brains we have acquired a rich culture, which far exceeds that of any other species in scope and complexity. We have developed science to understand how and why an immensity ...
DIENCEPHALON
... The left thalamus and right thalamus are separated by the third ventricle. A projection of gray matter called the intermediate mass extends into the ventricle from each side. ...
... The left thalamus and right thalamus are separated by the third ventricle. A projection of gray matter called the intermediate mass extends into the ventricle from each side. ...