introduction - HAL
... expressed in mature, -tubulin III-positive neurons. Altogether, these results demonstrate that ES cell- ...
... expressed in mature, -tubulin III-positive neurons. Altogether, these results demonstrate that ES cell- ...
Light and Electron Microscopic Localization of a Cell Surface
... Copyright 0 1987 Society for Neuroscience ...
... Copyright 0 1987 Society for Neuroscience ...
Sensory Pathways and Emotional Context for Action
... organization within the prefrontal cortex. However, prefrontal areas also receive projections from polymodal temporal association cortices. Moreover, neighboring prefrontal cortices are interconnected (27), allowing exchange of information, as in sensory cortices (28). This evidence suggests a bias, ...
... organization within the prefrontal cortex. However, prefrontal areas also receive projections from polymodal temporal association cortices. Moreover, neighboring prefrontal cortices are interconnected (27), allowing exchange of information, as in sensory cortices (28). This evidence suggests a bias, ...
The non-classical auditory pathways are involved in hearing in
... non-classical pathways that diminished with age, thus probably a sign of normal maturation. The fact that some of the individuals that we studied experienced an increase in loudness when their median nerve was stimulated while a few individuals experienced a decrease in loudness is in agreement with ...
... non-classical pathways that diminished with age, thus probably a sign of normal maturation. The fact that some of the individuals that we studied experienced an increase in loudness when their median nerve was stimulated while a few individuals experienced a decrease in loudness is in agreement with ...
Septins promote dendrite and axon development by negatively
... recombination system. This approach reveals obvious neuritogenesis defects in vivo for the first time in vertebrates, and enables us to further investigate this mechanism in neurons dissociated in vitro, an experimental system which is more amenable to rigorous morphometry, molecular pharmacology, in ...
... recombination system. This approach reveals obvious neuritogenesis defects in vivo for the first time in vertebrates, and enables us to further investigate this mechanism in neurons dissociated in vitro, an experimental system which is more amenable to rigorous morphometry, molecular pharmacology, in ...
somatic sensory system
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
... lie lateral to the fibers of the medial lemniscus make synapses in the reticular formation have arisen from cells in the dorsal column nuclei have arisen from cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord decussate (cross the midline) ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY B.Sc. Counselling Psychology
... depth or distance in vision. Both processes involve spatial aspects of sensory input. Many features contribute to auditory localization of which the following are most important: Having two ears In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so ...
... depth or distance in vision. Both processes involve spatial aspects of sensory input. Many features contribute to auditory localization of which the following are most important: Having two ears In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so ...
Physiology Lecture Outline: Membrane Potential and Neurophysiology
... *excitable tissue (responds to electrical stimulation). The excitable tissues have various RMP's, for example; neurons have a RMP of -70mV whereas most cardiac muscle cells have a RMP of -90mV. Excitable means that they are capable of producing electrical signals when excited (stimulated). As we may ...
... *excitable tissue (responds to electrical stimulation). The excitable tissues have various RMP's, for example; neurons have a RMP of -70mV whereas most cardiac muscle cells have a RMP of -90mV. Excitable means that they are capable of producing electrical signals when excited (stimulated). As we may ...
Dynamic expression of ATF3 as a novel tool to study activation and
... nervous system remains to be clarified. The expression of ATF3 by rat ependymal SPCs is dynamically regulated: when the ependymal stem cells become activated in vitro, the ATF3 immunostaining changes from cytoplasmic to nuclear, which provides the unique possibility to detect and quantify activated ...
... nervous system remains to be clarified. The expression of ATF3 by rat ependymal SPCs is dynamically regulated: when the ependymal stem cells become activated in vitro, the ATF3 immunostaining changes from cytoplasmic to nuclear, which provides the unique possibility to detect and quantify activated ...
Two Phylogenetic Specializations in the Human Brain
... error-correcting information to other parts of the brain. The spindle cells are located in layer 5, which typically relays the output of cortical processing to other cortical areas and subcortical structures. The axons of the spindle cells are known to project into the underlying white matter (Nimch ...
... error-correcting information to other parts of the brain. The spindle cells are located in layer 5, which typically relays the output of cortical processing to other cortical areas and subcortical structures. The axons of the spindle cells are known to project into the underlying white matter (Nimch ...
Neuronal Migration
... The signal transduction pathway mediating neuronal migratory responses to Slit is only beginning to be understood. The intracellular part of Robo interacts with proteins that regulate the Rho family of guanosine triphosphatases (RhoGTPases). The RhoGTPases are well known regulators of a diverse arra ...
... The signal transduction pathway mediating neuronal migratory responses to Slit is only beginning to be understood. The intracellular part of Robo interacts with proteins that regulate the Rho family of guanosine triphosphatases (RhoGTPases). The RhoGTPases are well known regulators of a diverse arra ...
Identification of neural circuits involved in female genital responses
... Sections were rinsed several times in KPBS and then incubated for 1 h in primary antibody directed against PRV at room temperature followed by 48 h at 4°C. Secondary and ABC reactions were as stated above. PRV was visualized as a brown reaction product using a 3,3⬘-DAB solution containing 0.08% hydr ...
... Sections were rinsed several times in KPBS and then incubated for 1 h in primary antibody directed against PRV at room temperature followed by 48 h at 4°C. Secondary and ABC reactions were as stated above. PRV was visualized as a brown reaction product using a 3,3⬘-DAB solution containing 0.08% hydr ...
neuronal coding of prediction errors
... from the properties of the prediction error. As the error (k1RV) is zero, or at least of a small magnitude on AX episodes, little associative strength accrues to signal X. By contrast, the error on the initial AY episode has a larger value, thereby producing increments on the associative strength of ...
... from the properties of the prediction error. As the error (k1RV) is zero, or at least of a small magnitude on AX episodes, little associative strength accrues to signal X. By contrast, the error on the initial AY episode has a larger value, thereby producing increments on the associative strength of ...
Biology and Behavior
... effects of endorphins on the body are also quite similar to the effects produced by the opioid compounds. In fact, the name 'endorphin' is actually the short form for 'endogenous morphine'. Like opioids, endorphins can reduce pain, stress, and promote calmness and serenity. The opioid drugs produce ...
... effects of endorphins on the body are also quite similar to the effects produced by the opioid compounds. In fact, the name 'endorphin' is actually the short form for 'endogenous morphine'. Like opioids, endorphins can reduce pain, stress, and promote calmness and serenity. The opioid drugs produce ...
Anatomy Review
... a. action potential b. synaptic potential 18. (Page 5.) Label the diagrams on page 5. 19. (Page 5.) In the brain, a variety of synapses have evolved to serve complex transmission needs between neurons. Synapses located between axon terminals of one neuron and ______, ______, or ______ of another are ...
... a. action potential b. synaptic potential 18. (Page 5.) Label the diagrams on page 5. 19. (Page 5.) In the brain, a variety of synapses have evolved to serve complex transmission needs between neurons. Synapses located between axon terminals of one neuron and ______, ______, or ______ of another are ...
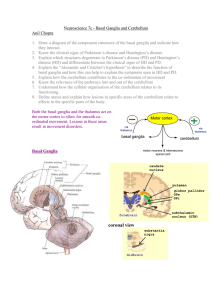
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... known as corticopontine connections and cross over after synapsing at the pons Functions of the Cerbellar Divisions The cerebellum is involved in the co-ordination of movement. It compares what you thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do ( ...
... known as corticopontine connections and cross over after synapsing at the pons Functions of the Cerbellar Divisions The cerebellum is involved in the co-ordination of movement. It compares what you thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do ( ...
Neuronal basis of contrast discrimination
... with a mid-gray field of equal mean luminance. Voxels with correlations above a liberal threshold (r \0.23 with 0–9 s time lag) were included in further analyses. This correlation threshold of r\0.23 corresponds to a PB 0.025 (one-tailed) significance level with n =72 given that the 72 points in the ...
... with a mid-gray field of equal mean luminance. Voxels with correlations above a liberal threshold (r \0.23 with 0–9 s time lag) were included in further analyses. This correlation threshold of r\0.23 corresponds to a PB 0.025 (one-tailed) significance level with n =72 given that the 72 points in the ...
Chapter 4
... – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
... – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
Chapter 4
... – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
... – The brain’s ability to change and adapt in response to experience (e.g., reorganizing or growing new neural connections) – Behavioural deficits that occur as a result of brain damage may be lessened by enriching environments people live in (e.g., Kolb et al., 1991) ...
File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
... • proprioception: joints, muscleswhite ramus communicans Somatic motor activity sympathetic gray: ramus innervate skeletal muscles ganglion communicans ...
... • proprioception: joints, muscleswhite ramus communicans Somatic motor activity sympathetic gray: ramus innervate skeletal muscles ganglion communicans ...
Ganglion Cells Specificity of Cone Inputs to Macaque Retinal
... S-cone axis, and a constant L- and M-cone axis (DKL space). For each linear visual neuron, there exists a single null plane through white that contains all the lights that can be exchanged without inducing a response. Derrington et al. inferred cone inputs from cells’ null planes. If a cell receives ...
... S-cone axis, and a constant L- and M-cone axis (DKL space). For each linear visual neuron, there exists a single null plane through white that contains all the lights that can be exchanged without inducing a response. Derrington et al. inferred cone inputs from cells’ null planes. If a cell receives ...
Master Thesis - Laboratory of Cerebral Cortex Development
... sheet of proliferating neuroblasts, Later, it consists of several areas, each characterized by peculiar anatomical and functional properties. These areas form a map that is similar from one individual to another and displays large topological commonalities across mammalian species. Two models have b ...
... sheet of proliferating neuroblasts, Later, it consists of several areas, each characterized by peculiar anatomical and functional properties. These areas form a map that is similar from one individual to another and displays large topological commonalities across mammalian species. Two models have b ...
Action Potentials
... base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...
... base of the axon hillock where they are summed • Two EPSPs in rapid succession at one synapse are additive • Same for IPSPs ...