Teacher: Date: Subject:
... Students will: *Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. *U ...
... Students will: *Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. *U ...
Newton-Raphson Method Nonlinear Equations
... Drawbacks – Oscillations near local maximum and minimum 3. Oscillations near local maximum and minimum Results obtained from the Newton-Raphson method may oscillate about the local maximum or minimum without converging on a root but converging on the local maximum or ...
... Drawbacks – Oscillations near local maximum and minimum 3. Oscillations near local maximum and minimum Results obtained from the Newton-Raphson method may oscillate about the local maximum or minimum without converging on a root but converging on the local maximum or ...
Determine whether each trinomial is a perfect square trinomial. Write
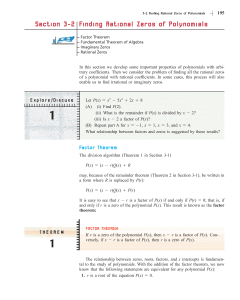
... Factor each polynomial, if possible. If the polynomial cannot be factored, write prime . ...
... Factor each polynomial, if possible. If the polynomial cannot be factored, write prime . ...
Add, Subtract, Multiply Polynomials
... The additive inverse of the polynomial x2 + 3x + 2 is – (x2 + 3x + 2). This is equivalent to the additive inverse of each of the terms. – (x2 + 3x + 2) = – x2 – 3x – 2 To subtract two polynomials, add the additive inverse of the second polynomial to the first. ...
... The additive inverse of the polynomial x2 + 3x + 2 is – (x2 + 3x + 2). This is equivalent to the additive inverse of each of the terms. – (x2 + 3x + 2) = – x2 – 3x – 2 To subtract two polynomials, add the additive inverse of the second polynomial to the first. ...
Prerequisites - Friedrich Von Steuben Metropolitan Science Center
... The number associated with a point is the coordinate of the point. As long as the context is clear, we will follow the standard convention of using the real number for both the name of the point and its coordinate. ...
... The number associated with a point is the coordinate of the point. As long as the context is clear, we will follow the standard convention of using the real number for both the name of the point and its coordinate. ...
finm221F08smpKey.pdf
... Instructions: Show your work in the spaces provided below for full credit. Clearly identify answers and show supporting work to receive any credit. Give exact answers (e.g., π ) rather than inexact (e.g., 3.14); make obvious simpli cations, e.g., 0 rather than sin π . Point values are in parentheses ...
... Instructions: Show your work in the spaces provided below for full credit. Clearly identify answers and show supporting work to receive any credit. Give exact answers (e.g., π ) rather than inexact (e.g., 3.14); make obvious simpli cations, e.g., 0 rather than sin π . Point values are in parentheses ...