Quarter 1
... computation with whole numbers and fractions. MP. 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them ...
... computation with whole numbers and fractions. MP. 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them ...
Section 2
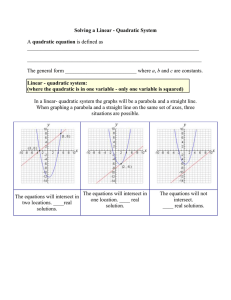
... A quadratic equation in x is an equation that can be written in the general form. ax 2 bx c 0 where a, b, and c are real numbers, with a 0 . It is also called a second-degree polynomial equation in x. *Solving Quadratic Equation by Factoring The Zero-Product Principle If AB 0 , then A 0 ...
... A quadratic equation in x is an equation that can be written in the general form. ax 2 bx c 0 where a, b, and c are real numbers, with a 0 . It is also called a second-degree polynomial equation in x. *Solving Quadratic Equation by Factoring The Zero-Product Principle If AB 0 , then A 0 ...
10 Questions & Answers[1].
... • Absolute value of a number x, is written like this IxI, is the distance the number is from 0 on a number line. Always remember absolute value is always nonnegative. The distance between -4 and 0 is 4, so I-4I=4 ...
... • Absolute value of a number x, is written like this IxI, is the distance the number is from 0 on a number line. Always remember absolute value is always nonnegative. The distance between -4 and 0 is 4, so I-4I=4 ...
Day 6: Worksheet
... Explain what the coordinates tell you about the numbers of adult and student memberships sold. 3. Consider the graph of the equation that relates x and y to the $400 income. Could a point that is not on this graph be a solution to the equation? 4. Could there be a common solution for both of your eq ...
... Explain what the coordinates tell you about the numbers of adult and student memberships sold. 3. Consider the graph of the equation that relates x and y to the $400 income. Could a point that is not on this graph be a solution to the equation? 4. Could there be a common solution for both of your eq ...
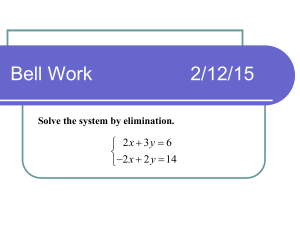
Solving Equations Using Multiplication and Division
... “What Do Opticians, Optometrists, and Opthamologists Have In Common?” ...
... “What Do Opticians, Optometrists, and Opthamologists Have In Common?” ...
Solve Quadratic Equations
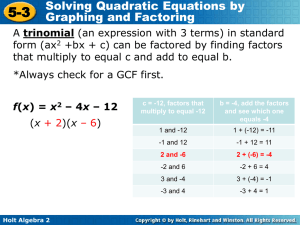
... Solve Quadratic Equations If there is more than 1 variable, with different exponents, try to solve the problem by factoring. The equation must be set equal to zero to use the zero product property. When two or more factors multiply together and the result is zero, then one of the factors must be zer ...
... Solve Quadratic Equations If there is more than 1 variable, with different exponents, try to solve the problem by factoring. The equation must be set equal to zero to use the zero product property. When two or more factors multiply together and the result is zero, then one of the factors must be zer ...
6_M2306_Hist_chapter6 - Nipissing University Word
... of the form a+√b where a and b are rational • Euclid: study of numbers of the form a b • No progress in the theory of irrationals until the Renaissance, except for Fibonacci result (1225): roots of x3+2x2+10x=20 are not any of Euclid’s irrationals • Fibonacci did not prove that these roots are not ...
... of the form a+√b where a and b are rational • Euclid: study of numbers of the form a b • No progress in the theory of irrationals until the Renaissance, except for Fibonacci result (1225): roots of x3+2x2+10x=20 are not any of Euclid’s irrationals • Fibonacci did not prove that these roots are not ...


![10 Questions & Answers[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008474122_1-913b0bc5b28ab2d292606c5c2aed9267-300x300.png)