* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch1-Section 1.4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
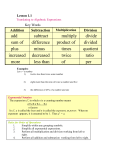
§ 1.4 Introduction to Variable Expressions and Equations Exponents Exponential notation is used to write repeated multiplication in a more compact form. 3333 3 4 34 exponent base The expression 34 is called an exponential expression. Example: Evaluate 26. 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 64 6 Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 2 Order of Operations Order of Operations Simplify expressions using the order below. If grouping symbols such as parentheses are present, simplify expressions within those first, starting with the innermost set. If fraction bars are present, simplify the numerator and the denominator separately. 1. Evaluate exponential expressions 2. Perform multiplication or division in order from left to right. 3. Perform addition or subtraction in order from left to right. Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 3 Using the Order of Operations Example: 6 9 3 Simplify the expression. 32 693 6 9 3 2 9 3 63 9 Simplify numerator and denominator separately Divide. 9 9 Add. 1 Simplify. Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 4 Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Definition Variable: A symbol used to represent a number. Algebraic Expression: A collection of numbers, variables, operation symbols, and grouping symbols. Evaluating an Algebraic Expression: Finding its numerical value once we know the values of the variables. Example Evaluate: 7 + 3z when z = – 3 7 3z 7 3(3) 7 (9) 7 9 2 Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 5 Determining Whether a Number is a Solution Definition Equation: A mathematical statement that two expressions have equal value. Example 5x = 10 4 + y = 2y – 5 Solving: In an equation Solve the equation for a. containing a variable, finding x + 2 = 16 which values of the variable make x = 14 the equation a true statement. Solution: In an equation, a value for the variable that makes the equation a true statement. Is –7 a solution of: a + 23 = –16? a 23 16 (7) 23 16 – 7 is not a solution. Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 6 Translating Phrases Addition (+) Sum Plus Added to More than Increased by Total Subtraction (–) Difference Minus Subtract Less than Decreased by Less Multiplication (·) Product Times Multiply Twice Of Division () Quotient Divide Into Ratio Divided by Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed Equality (=) Equals Gives Is/was/should be Yields Amounts to Represents 7 Translating Phrases Example: Write as an algebraic expression. Let x to represent the unknown number. a.) 5 decreased by a number b.) The quotient of a number and 12 a.) In words: Translate: 5 5 decreased by – a number x The quotient of b.) In words: Translate: a number x and 12 x or 12 12 Martin-Gay, Beginning and Intermediate Algebra, 4ed 8