New Era University
... none for the colleges except for the College of Education which is Basic Math A course in Algebra which focuses on topics such as introductory set theory, real number, algebraic expressions, relations and function system, rational exponents, quadratic equations systems of linear equations, geometric ...
... none for the colleges except for the College of Education which is Basic Math A course in Algebra which focuses on topics such as introductory set theory, real number, algebraic expressions, relations and function system, rational exponents, quadratic equations systems of linear equations, geometric ...
Full text
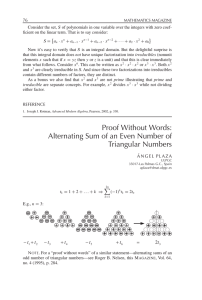
... second kinds if the positive sign is taken in the equation and to the Pell and Pell-Lucas polynomials if the negative sign is taken in the equation. It may be of interest to note that Bhaskara II, another Indian mathematician of the twelfth century dealt extensively with the positive integer solutio ...
... second kinds if the positive sign is taken in the equation and to the Pell and Pell-Lucas polynomials if the negative sign is taken in the equation. It may be of interest to note that Bhaskara II, another Indian mathematician of the twelfth century dealt extensively with the positive integer solutio ...
Linear Systems
... The latter system can easily be solved using back-substitution: z = −2 → y = 1 − z = 1 − (−2) = 3 → x = 4 − 2y + z = 4 − 2(3) + (−2) = −4. There are three elementary row operations that can be performed on a system and still have an equivalent system: ...
... The latter system can easily be solved using back-substitution: z = −2 → y = 1 − z = 1 − (−2) = 3 → x = 4 − 2y + z = 4 − 2(3) + (−2) = −4. There are three elementary row operations that can be performed on a system and still have an equivalent system: ...