Document
... • A number of languages have extensive nonconcatenative morphology, in which morphemes are combined in more complex ways. • Another kind of non-concatenative morphology is called templatic morphology or root-and-pattern morphology. • Example: Read Chapter 3. ...
... • A number of languages have extensive nonconcatenative morphology, in which morphemes are combined in more complex ways. • Another kind of non-concatenative morphology is called templatic morphology or root-and-pattern morphology. • Example: Read Chapter 3. ...
How Many Word-Classes Are There After All?
... • But: no longer circular, because these are features relevant at another/different level: syntax, affixation, etc. • What we have called word-classes are but instructions for the item as to what to combine with • Classical word-classes are (equivalent to) sets or clusters of formal syntactic featur ...
... • But: no longer circular, because these are features relevant at another/different level: syntax, affixation, etc. • What we have called word-classes are but instructions for the item as to what to combine with • Classical word-classes are (equivalent to) sets or clusters of formal syntactic featur ...
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
... representations, and also using the well-known features of unification morphology; in a dynamically expandable structure. Furthermore it is possible to define the meaning (intension) of a morpheme by linking optional number of morphemes from different languages. In our system not only the phonologic ...
... representations, and also using the well-known features of unification morphology; in a dynamically expandable structure. Furthermore it is possible to define the meaning (intension) of a morpheme by linking optional number of morphemes from different languages. In our system not only the phonologic ...
Systemic Linguistics: Core Linguistics
... relationships by word position in the sentence (= word order) • synthetic languages signal grammatical relationships by the shape of the words (=inflectional endings) • 1500 years ago, English was much more synthetic than it is today. It has changed into a more analytic language ...
... relationships by word position in the sentence (= word order) • synthetic languages signal grammatical relationships by the shape of the words (=inflectional endings) • 1500 years ago, English was much more synthetic than it is today. It has changed into a more analytic language ...
essentials of morphology
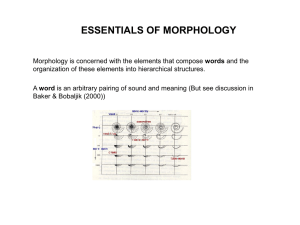
... organization of these elements into hierarchical structures. A word is an arbitrary pairing of sound and meaning (But see discussion in ...
... organization of these elements into hierarchical structures. A word is an arbitrary pairing of sound and meaning (But see discussion in ...
The term *morphology* is a Greek based word from the word morphe
... not simply a subject. A category, by contrast, is a class of expressions which are grammatically alike. An NP is (setting aside a narrow range of exceptions) simply a phrase with a noun as head (it's not the NP of anything, it's just an NP). The class of NPs thus includes an indefinitely large set o ...
... not simply a subject. A category, by contrast, is a class of expressions which are grammatically alike. An NP is (setting aside a narrow range of exceptions) simply a phrase with a noun as head (it's not the NP of anything, it's just an NP). The class of NPs thus includes an indefinitely large set o ...
Syntax - Serwis Informacyjny WSJO
... A sound change might have - No/little effect on the phonological system - Change the allophones of a phoneme - Decrease the number of phonemes - Increase the number of phonemes ...
... A sound change might have - No/little effect on the phonological system - Change the allophones of a phoneme - Decrease the number of phonemes - Increase the number of phonemes ...
Morphology - CSE, IIT Bombay
... • Property of a morphological process to give rise to new formations on a systematic basis Transitive Verb ...
... • Property of a morphological process to give rise to new formations on a systematic basis Transitive Verb ...
Morphology (CS 626-449)
... • Property of a morphological process to give rise to new formations on a systematic basis Transitive Verb ...
... • Property of a morphological process to give rise to new formations on a systematic basis Transitive Verb ...
Morphology
... • It consists of nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. • Sometimes, content words are called openclass words, because the kind of word can be added, improved, or vanished. ...
... • It consists of nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. • Sometimes, content words are called openclass words, because the kind of word can be added, improved, or vanished. ...
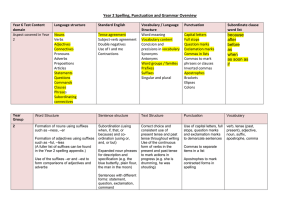
Year 2 Grammar and spelling
... Formation of adjectives using suffixes such as –ful, –less (A fuller list of suffixes can be found in the Year 2 spelling appendix.) Use of the suffixes –er and –est to form comparisons of adjectives and adverbs ...
... Formation of adjectives using suffixes such as –ful, –less (A fuller list of suffixes can be found in the Year 2 spelling appendix.) Use of the suffixes –er and –est to form comparisons of adjectives and adverbs ...
ppt
... Orthographic word: between two spaces. Clitic: part of the phonological word, but syntactically an independent unit (e.g., articles, French preverbal pronouns, etc.). ...
... Orthographic word: between two spaces. Clitic: part of the phonological word, but syntactically an independent unit (e.g., articles, French preverbal pronouns, etc.). ...
Definition of Syntax and Morphology
... 1. Definition of Morphology morphology (mɔːˈfɒlədʒɪ) n 1. (Biology) the branch of biology concerned with the form and structure of organisms 2. (Linguistics) the form and structure of words in a language, esp the consistent patterns of inflection, combination, derivation and change, etc, that may be ...
... 1. Definition of Morphology morphology (mɔːˈfɒlədʒɪ) n 1. (Biology) the branch of biology concerned with the form and structure of organisms 2. (Linguistics) the form and structure of words in a language, esp the consistent patterns of inflection, combination, derivation and change, etc, that may be ...
Morphology - Oral Language and Literacy
... • “Explain the function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) in general and their function in particular sentences.” (grade 8) ...
... • “Explain the function of verbals (gerunds, participles, infinitives) in general and their function in particular sentences.” (grade 8) ...
Composing Music with Grammars
... Chomsky’s four types of grammars Free (type 0) – imposes no restrictions on the form of the production rule. Intermediate strings can expand and contract in length. Allows for infinite strings and null strings. Context-sensitive (type 1) – A α B → A β B. alpha produces beta in the context of A and ...
... Chomsky’s four types of grammars Free (type 0) – imposes no restrictions on the form of the production rule. Intermediate strings can expand and contract in length. Allows for infinite strings and null strings. Context-sensitive (type 1) – A α B → A β B. alpha produces beta in the context of A and ...
University of Prince Salman Ibn Abdelaziz
... This is the dog that chased the cat, That killed the rat, …etc. endless recursion. Grammar must provide for this fact. Grammar should also be capable of revealing ...
... This is the dog that chased the cat, That killed the rat, …etc. endless recursion. Grammar must provide for this fact. Grammar should also be capable of revealing ...
Lecture
... Find all the possible outputs (all paths) and return them all (without choosing) Bias the search so that only one or a few likely paths are explored ...
... Find all the possible outputs (all paths) and return them all (without choosing) Bias the search so that only one or a few likely paths are explored ...
Morphemes, morpheme classification, inflectional
... Derivational morphology creates new words from old ones. The core meaning might change significantly, and the syntactic category of the word may change too. Also, the new word will require additional inflectional morphology required by the grammar, e.g.: ...
... Derivational morphology creates new words from old ones. The core meaning might change significantly, and the syntactic category of the word may change too. Also, the new word will require additional inflectional morphology required by the grammar, e.g.: ...
Slide 1
... Language is very difficult to put into words. -- Voltaire What do we mean by “language”? A system used to convey meaning made up of arbitrary elements that are organized using a set of rules. -- Rader ...
... Language is very difficult to put into words. -- Voltaire What do we mean by “language”? A system used to convey meaning made up of arbitrary elements that are organized using a set of rules. -- Rader ...
Example - PRAXIS-Study
... – bow, the front part of a ship – bow, to bend – bow, a decorative knot ...
... – bow, the front part of a ship – bow, to bend – bow, a decorative knot ...
(a set of meaningful linguistic units). Allomorphs vary in shape or
... English has several morphemes that vary in sound but not in meaning. Examples include the past tense and the plural morphemes. For example, in English, a past tense morpheme is -ed. It occurs in several allomorphs depending on its phonological environment, ...
... English has several morphemes that vary in sound but not in meaning. Examples include the past tense and the plural morphemes. For example, in English, a past tense morpheme is -ed. It occurs in several allomorphs depending on its phonological environment, ...
Reconstruction the Lexical Domain with a Single Generative
... All composition is syntactic; the internal structure of words is created by the same mechanisms of construction as the internal structure of sentences. The internal semantic structure of roots (atoms for construction, along with the universally available grammatical features), whatever it may be and ...
... All composition is syntactic; the internal structure of words is created by the same mechanisms of construction as the internal structure of sentences. The internal semantic structure of roots (atoms for construction, along with the universally available grammatical features), whatever it may be and ...
mt2revupdated
... concepts to each other. Be familiar with details of experiments which tested these principles. What are some proposed biases or constraints on how kids learn word meaning? What are overextension and underextension? What are some reasons kids might over/underextend even if they know better? What is t ...
... concepts to each other. Be familiar with details of experiments which tested these principles. What are some proposed biases or constraints on how kids learn word meaning? What are overextension and underextension? What are some reasons kids might over/underextend even if they know better? What is t ...
PSY 369: Psycholinguistics - Illinois State University Department of
... So we NP’s can be embedded within PP’s which in turn may be embedded within NP’s. ...
... So we NP’s can be embedded within PP’s which in turn may be embedded within NP’s. ...
ppt
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...
... ‘my father is looking for the cows’ • Here, the meaning of the phrase “look for cows” is expressed in a single word (they can express it with a separate noun as well). • This is similar in many ways to what happens in compounding in English; remember truck driver. In English, though we can’t use thi ...