1 Outer/inner morphology: The dichotomy of Japanese renyoo verbs
... associated with the lexical/syntactic dichotomy (e.g. lexical vs. syntactic causatives, taken up in Fodor 1970, Harley 1995, Miyagawa 1998, Shibatani 1990, and Travis 2000, among others). However, according to Marantz (2007), there is no such lexical/syntactic division in grammar, and such ‘irregula ...
... associated with the lexical/syntactic dichotomy (e.g. lexical vs. syntactic causatives, taken up in Fodor 1970, Harley 1995, Miyagawa 1998, Shibatani 1990, and Travis 2000, among others). However, according to Marantz (2007), there is no such lexical/syntactic division in grammar, and such ‘irregula ...
NEXT MEETING: _ Look up the other terms not covered. _ Prepare
... word-like form (‘ve) that must be attached to some word because it cannot occur in isolation. PHRASE STRUCTURE _ phrase is a syntactic unit; one or more words built around a skeleton consisting of two levels: phrase level and a word level. NP VP AP PP phrase level ...
... word-like form (‘ve) that must be attached to some word because it cannot occur in isolation. PHRASE STRUCTURE _ phrase is a syntactic unit; one or more words built around a skeleton consisting of two levels: phrase level and a word level. NP VP AP PP phrase level ...
Literacy overview y56
... Identifying how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning Discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader Distinguish between statements of fact and opinion Retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction P ...
... Identifying how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning Discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader Distinguish between statements of fact and opinion Retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction P ...
Ottenheimer Chapter 4 Words and Sentences Overview • When we
... For instance, the word helper can be broken down into smaller units (of meaning) • Help The action of giving assistance • -er The person who does the action • Helper Combine to mean a person who gives assistance o These meaningful units are called morphemes. • Morphemes o Phonemes make a diffe ...
... For instance, the word helper can be broken down into smaller units (of meaning) • Help The action of giving assistance • -er The person who does the action • Helper Combine to mean a person who gives assistance o These meaningful units are called morphemes. • Morphemes o Phonemes make a diffe ...
Year 6 Writing - St. John`s Church of England Primary School
... Considering how authors have developed characters and settings in what I plan my writing by considering how other authors have pupils have read, listened to or seen performed in narratives. developed characters and settings. ...
... Considering how authors have developed characters and settings in what I plan my writing by considering how other authors have pupils have read, listened to or seen performed in narratives. developed characters and settings. ...
Syntax, lexical categories, and morphology - Assets
... a reading is. This sentence is ungrammatical because it violates some of the word order rules for English, that is (i) basic word order in English clauses is subject–verb–object, (ii) articles like the and a precede the noun they modify, and (iii) auxiliary verbs like is precede the main verb, in th ...
... a reading is. This sentence is ungrammatical because it violates some of the word order rules for English, that is (i) basic word order in English clauses is subject–verb–object, (ii) articles like the and a precede the noun they modify, and (iii) auxiliary verbs like is precede the main verb, in th ...
the morphology-syntax interface - University of the Basque Country
... rules and a related set of phonological operations. Whenever a morphological operation of a given level takes place, the output of this word formation operation is submitted to the set of phonological rules that are associated with that lexical level. Within this model, Kiparsky establishes a clear ...
... rules and a related set of phonological operations. Whenever a morphological operation of a given level takes place, the output of this word formation operation is submitted to the set of phonological rules that are associated with that lexical level. Within this model, Kiparsky establishes a clear ...
THE WORD-GROUP THEORIES - Кам`янець
... first mentioned in practical grammar books. A pure scientific theory of a wordgroup was worked out by home scholars F.F. Fortunov, A.A. Shakhmatov, A.M. Peshkovsky. Any syntactically arranged unit, irrespective of its composition and types of syntactic relations between its constituents was consider ...
... first mentioned in practical grammar books. A pure scientific theory of a wordgroup was worked out by home scholars F.F. Fortunov, A.A. Shakhmatov, A.M. Peshkovsky. Any syntactically arranged unit, irrespective of its composition and types of syntactic relations between its constituents was consider ...
Customizing the XTAG System for Efficient Grammar
... language is to construct rules that generate sentences in the language at a formal level. From an implementational point of view, the grammar should be described in a consistent and efficient way. The XTAG system helps us to pursue both these goals, but the complicated inflection system mentioned ab ...
... language is to construct rules that generate sentences in the language at a formal level. From an implementational point of view, the grammar should be described in a consistent and efficient way. The XTAG system helps us to pursue both these goals, but the complicated inflection system mentioned ab ...
Chapter 3 Distributed Morphology and the Pieces of Inflection Morris
... been pursuing independently for a number of years.3 It shares important traits with traditional morphology (e.g., in its insistence that hierarchically organized pieces are present at all levels of representation of a word), but deviates from traditional morphology in other respects (most especially ...
... been pursuing independently for a number of years.3 It shares important traits with traditional morphology (e.g., in its insistence that hierarchically organized pieces are present at all levels of representation of a word), but deviates from traditional morphology in other respects (most especially ...
Syntax: Introduction
... phrasal (syntactic) category: contains a noun or pronoun as its head, and functions as the subject or as various objects in a sentence Verb phrase (VP) phrasal (syntactic) category: contains a verb as its head along with its complements such as noun phrases and prepositional phrases Adjective phrase ...
... phrasal (syntactic) category: contains a noun or pronoun as its head, and functions as the subject or as various objects in a sentence Verb phrase (VP) phrasal (syntactic) category: contains a verb as its head along with its complements such as noun phrases and prepositional phrases Adjective phrase ...
NOUN
... • Handles what is an isolated form in written text • Grouping of phonemes into morphemes – sequence deliverables → deliver, able and s (3 units) – could as well be some “ID” numbers: • e.g. deliver ~ 23987, s ~ 12, able ~ 3456 • Morpheme Combination – certain combinations/sequencing possible, other ...
... • Handles what is an isolated form in written text • Grouping of phonemes into morphemes – sequence deliverables → deliver, able and s (3 units) – could as well be some “ID” numbers: • e.g. deliver ~ 23987, s ~ 12, able ~ 3456 • Morpheme Combination – certain combinations/sequencing possible, other ...
NOUN
... • Handles what is an isolated form in written text • Grouping of phonemes into morphemes – sequence deliverables → deliver, able and s (3 units) – could as well be some “ID” numbers: • e.g. deliver ~ 23987, s ~ 12, able ~ 3456 • Morpheme Combination – certain combinations/sequencing possible, other ...
... • Handles what is an isolated form in written text • Grouping of phonemes into morphemes – sequence deliverables → deliver, able and s (3 units) – could as well be some “ID” numbers: • e.g. deliver ~ 23987, s ~ 12, able ~ 3456 • Morpheme Combination – certain combinations/sequencing possible, other ...
e30_15-16_7_learning-words-grammar-and
... matter for meaning. Without attention to form, form will not be learnt accurately. Form-focused instruction is particularly relevant for those featuresof the FL, grammar that are different from the L1 or are not very noticeable. ...
... matter for meaning. Without attention to form, form will not be learnt accurately. Form-focused instruction is particularly relevant for those featuresof the FL, grammar that are different from the L1 or are not very noticeable. ...
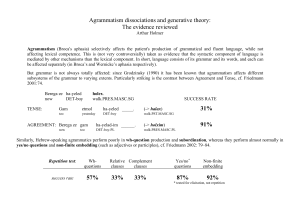
Arthur Holmer
... dissociations depend on the fact that Tense values are inherently underspecified (Tense Underspecification Hypothesis: TUH). A reason for this underspecification would be that Tense establishes a relation between event time and the speech act itself, while agreement only establishes a relation withi ...
... dissociations depend on the fact that Tense values are inherently underspecified (Tense Underspecification Hypothesis: TUH). A reason for this underspecification would be that Tense establishes a relation between event time and the speech act itself, while agreement only establishes a relation withi ...
Word - Morpheme balance in dictionary-making
... All these derivatives should be treated as word/morpheme combinations; juxtaposing the properties of words and morphemes. The word properties are numerous: each has denotational meaning/s derived from the extralinguistic world (the main ones are given in the example). Each belongs to specific gramma ...
... All these derivatives should be treated as word/morpheme combinations; juxtaposing the properties of words and morphemes. The word properties are numerous: each has denotational meaning/s derived from the extralinguistic world (the main ones are given in the example). Each belongs to specific gramma ...
幻灯片 1
... • agent (the one who performs something, as the farmer above), • patient (the one to whom things happen, the ducklings above), • experiencer and theme (I and him respectively in I saw him, where I do not really do anything, and nothing actually happens to him), • recipient, and source and goal (wher ...
... • agent (the one who performs something, as the farmer above), • patient (the one to whom things happen, the ducklings above), • experiencer and theme (I and him respectively in I saw him, where I do not really do anything, and nothing actually happens to him), • recipient, and source and goal (wher ...
Roots and Lexicality In Distributed Morphology
... have no morphosyntactic category, no gender, and no form of class affiliation'; emphasis mine). In addition to these conceptual arguments, there is also empirical evidence that roots should not carry diacritics, in particular class diacritics like declension and conjugation class. Suppose they do: t ...
... have no morphosyntactic category, no gender, and no form of class affiliation'; emphasis mine). In addition to these conceptual arguments, there is also empirical evidence that roots should not carry diacritics, in particular class diacritics like declension and conjugation class. Suppose they do: t ...
The counterpoint of phonology and morphology(音系学和形态学的
... 词), general ordinals(一般顺序词): next, last, past, (an)other, additional and other quantifiers like many, a few, several, much, little, a lot of, plenty of, a great deal of, a great number of When different sub-classes of determiners occur together, they ...
... 词), general ordinals(一般顺序词): next, last, past, (an)other, additional and other quantifiers like many, a few, several, much, little, a lot of, plenty of, a great deal of, a great number of When different sub-classes of determiners occur together, they ...
Chapter one Invitations to Linguistics
... language that unite sounds with meaning. Morphology is defined as the study of the internal structure and the formation of words. ...
... language that unite sounds with meaning. Morphology is defined as the study of the internal structure and the formation of words. ...
Linguistics 403/404 Lecture Notes No.4
... strongly and consistently into stems, stems can function on a one-to-one level without syntax determining word-order meaning. Otherwise, syntax must be employed. If we see that morphemes, like words, may also undergo movement (and are relatively unconstrained by syntax) then the question to ask is s ...
... strongly and consistently into stems, stems can function on a one-to-one level without syntax determining word-order meaning. Otherwise, syntax must be employed. If we see that morphemes, like words, may also undergo movement (and are relatively unconstrained by syntax) then the question to ask is s ...
Categorial Grammar – Introduction
... of word-combining rules. Rather, the lexical categories of words such as verbs and adjectives constitute functions that determine how these words can combine with other categories. For example, a lexical item such as ‘nice,’ an adjective, is in a category corresponding to a function that maps from t ...
... of word-combining rules. Rather, the lexical categories of words such as verbs and adjectives constitute functions that determine how these words can combine with other categories. For example, a lexical item such as ‘nice,’ an adjective, is in a category corresponding to a function that maps from t ...