Ch 12
... – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS • A nucleus is a mass of nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside the CNS. Principles of ...
... – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS • A nucleus is a mass of nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside the CNS. Principles of ...
Chapter 3
... – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS • A nucleus is a mass of nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside the CNS. Principles of ...
... – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS • A nucleus is a mass of nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside the CNS. Principles of ...
Changes in descending motor pathway connectivity after
... using dark field illumination, under which axon tracts appear bright. By studying the appearance of landmarks such as the inferior olive, together with the estimated stereotaxic location of the tissue block and the number of the section, we estimated the rostro-caudal location of each section. This ...
... using dark field illumination, under which axon tracts appear bright. By studying the appearance of landmarks such as the inferior olive, together with the estimated stereotaxic location of the tissue block and the number of the section, we estimated the rostro-caudal location of each section. This ...
Solving the Problem of Negative Synaptic Weights in Cortical Models
... arbitrary transformations on the encoded variables. Conveniently, the same methods can be employed. Instead of finding decoders φ to decode an estimate of x (i.e., computing the identity function), the same linear leastsquares method can be used to provide decoders φ g(x) for some arbitrary function ...
... arbitrary transformations on the encoded variables. Conveniently, the same methods can be employed. Instead of finding decoders φ to decode an estimate of x (i.e., computing the identity function), the same linear leastsquares method can be used to provide decoders φ g(x) for some arbitrary function ...
- TestbankU
... c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde axoplasmic transport. e. Transport of materials occurs only in one direction. Difficulty: 3 Question ID: 2.1-26 Page Ref: 35 Topic: Neurons Skill: Conceptual Answer: d. Retr ...
... c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde axoplasmic transport. e. Transport of materials occurs only in one direction. Difficulty: 3 Question ID: 2.1-26 Page Ref: 35 Topic: Neurons Skill: Conceptual Answer: d. Retr ...
Number and Laminar Distribution of Neurons in a
... the number of neurons in such a projection column. Together with the data on TC projections, these numbers are then used to compute the average TC innervation of excitatory neurons in a cortical column as presented in the subsequent article (Meyer et al. 2010). The number of neurons in a cortical co ...
... the number of neurons in such a projection column. Together with the data on TC projections, these numbers are then used to compute the average TC innervation of excitatory neurons in a cortical column as presented in the subsequent article (Meyer et al. 2010). The number of neurons in a cortical co ...
Artificial Neural Networks - University of Northampton
... Non-linearly separable problems If a problem is not linearly separable, then it is ...
... Non-linearly separable problems If a problem is not linearly separable, then it is ...
A part of the cholinergic fibers in mouse superior cervical ganglia
... immunoreactivities observed in fibers of the SCG, SIF-like cells in the sympathetic trunk showed a GABA-like immunoreactivity, and there were few GABA-like neurons in the spinal cord. Because their argument was based upon indirect evidence, further direct evidence is needed to elucidate the source o ...
... immunoreactivities observed in fibers of the SCG, SIF-like cells in the sympathetic trunk showed a GABA-like immunoreactivity, and there were few GABA-like neurons in the spinal cord. Because their argument was based upon indirect evidence, further direct evidence is needed to elucidate the source o ...
Aging reduces total neuron number in the dorsal component of the
... vPFC. The number of cells stained with antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) was also reduced in aged rats. The changes in prefrontal cortical neuron number were not correlated with behavioral impairment in the assessment of hippocampus-dependent spatial memory, consistent with t ...
... vPFC. The number of cells stained with antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) was also reduced in aged rats. The changes in prefrontal cortical neuron number were not correlated with behavioral impairment in the assessment of hippocampus-dependent spatial memory, consistent with t ...
A Beginner`s Guide to the Mathematics of Neural Networks
... membrane potential and ring state). Right: close-up of a typical synapse. decrease. In the rst case the arriving signal will increase the probability of the receiving neuron to start ring itself, therefore such a synapse is called excitatory. In the second case the arriving signal will decrease t ...
... membrane potential and ring state). Right: close-up of a typical synapse. decrease. In the rst case the arriving signal will increase the probability of the receiving neuron to start ring itself, therefore such a synapse is called excitatory. In the second case the arriving signal will decrease t ...
Chaper 1. A Brief History of Cognitive Neuroscience
... made during a different behavioral state. This allowed researchers to isolate relevant brain regions. ...
... made during a different behavioral state. This allowed researchers to isolate relevant brain regions. ...
Cortical Action Potential Backpropagation Explains Spike Threshold
... Cortical neurons initiate action potentials in their axon initial segments under a wide variety of conditions. These action potentials then propagate antidromically (backpropagate) through the soma and to variable degrees into the dendritic arbor (Stuart et al., 1997b; Palmer and Stuart, 2006; Shu e ...
... Cortical neurons initiate action potentials in their axon initial segments under a wide variety of conditions. These action potentials then propagate antidromically (backpropagate) through the soma and to variable degrees into the dendritic arbor (Stuart et al., 1997b; Palmer and Stuart, 2006; Shu e ...
Canonical Neural Computation: A Summary and a Roadmap A
... behaving animal. An important observation about the neocortex is that very different brain functions, ranging from extracting orientation information in primary visual cortex to computations of economic value in parietal cortex and motor planning in the Frontal Eye Fields, are all computed by the a ...
... behaving animal. An important observation about the neocortex is that very different brain functions, ranging from extracting orientation information in primary visual cortex to computations of economic value in parietal cortex and motor planning in the Frontal Eye Fields, are all computed by the a ...
The Biological Perspective
... human body, how are they kept separated? The answer is simple. One special type of glial cell, called a Schwann cell, generates a layer of fatty substances called myelin. Myelin wraps around the shaft of the axons, forming a protective sheath. It’s really the axons that do the bulk of the travelling ...
... human body, how are they kept separated? The answer is simple. One special type of glial cell, called a Schwann cell, generates a layer of fatty substances called myelin. Myelin wraps around the shaft of the axons, forming a protective sheath. It’s really the axons that do the bulk of the travelling ...
An ontology-based search engine for digital
... across and within animal species, developmental stages, brain regions, and cell types. This diversity is functionally important because neuronal structure strongly affects synaptic integration, spiking dynamics, and network connectivity. Digital reconstructions of axonal and dendritic arbors are thu ...
... across and within animal species, developmental stages, brain regions, and cell types. This diversity is functionally important because neuronal structure strongly affects synaptic integration, spiking dynamics, and network connectivity. Digital reconstructions of axonal and dendritic arbors are thu ...
NMDA Receptors Contribute to Primary Visceral Afferent
... and superior laryngeal nerve inspiratory shortening reflex pathways (Karius et al. 1994). These variable findings regarding the role of non-NMDA and NMDA receptors in synaptic transmission in the NTS may be due to true differences in the glutamate receptor subtypes activated in these different auton ...
... and superior laryngeal nerve inspiratory shortening reflex pathways (Karius et al. 1994). These variable findings regarding the role of non-NMDA and NMDA receptors in synaptic transmission in the NTS may be due to true differences in the glutamate receptor subtypes activated in these different auton ...
Chapter Two: Brain and Behavior
... One-Minute Motivator 2.1: Firing of the Neuron To conceptualize the firing of the neuron, students often need analogies to concrete objects. Possible analogies include: a radio, a telephone, a fax machine, a stereo system, the process of sending mail, etc. The analogy must be developed carefully: It ...
... One-Minute Motivator 2.1: Firing of the Neuron To conceptualize the firing of the neuron, students often need analogies to concrete objects. Possible analogies include: a radio, a telephone, a fax machine, a stereo system, the process of sending mail, etc. The analogy must be developed carefully: It ...
Overview Synaptic plasticity Synaptic strength
... • Maximal conductance g associated with one synaptic vesicle ...
... • Maximal conductance g associated with one synaptic vesicle ...
Brain and Behavior
... One-Minute Motivator 2.1: Firing of the Neuron To conceptualize the firing of the neuron, students often need analogies to concrete objects. Possible analogies include: a radio, a telephone, a fax machine, a stereo system, the process of sending mail, etc. The analogy must be developed carefully: It ...
... One-Minute Motivator 2.1: Firing of the Neuron To conceptualize the firing of the neuron, students often need analogies to concrete objects. Possible analogies include: a radio, a telephone, a fax machine, a stereo system, the process of sending mail, etc. The analogy must be developed carefully: It ...
Neuronal migration
... migration is orthogonal to subpial migration. Both processes can be activated sequentially in the same cell, for example in cerebellar granule cells, and lead to extension of axonal and dendritic processes in different directions. An important, unresolved question concerns the mechanisms that direct ...
... migration is orthogonal to subpial migration. Both processes can be activated sequentially in the same cell, for example in cerebellar granule cells, and lead to extension of axonal and dendritic processes in different directions. An important, unresolved question concerns the mechanisms that direct ...
nerve impulse patterns and reflex control in the motor system
... cycles of input are needed before the output begins. During the steady response which finally develops the output may consist of multiple discharges due to a single input shock. These doublets and triplets resemble in temporal characteristics those recorded from the intact animal, the separating int ...
... cycles of input are needed before the output begins. During the steady response which finally develops the output may consist of multiple discharges due to a single input shock. These doublets and triplets resemble in temporal characteristics those recorded from the intact animal, the separating int ...
FREE Sample Here
... c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde axoplasmic transport. e. Transport of materials occurs only in one direction. Difficulty: 3 Question ID: 2.1-26 Page Ref: 35 Topic: Neurons Skill: Conceptual Answer: d. Retr ...
... c. The kinesin molecule is involved in retrograde axoplasmic transport. d. Retrograde transport is half as fast as anterograde axoplasmic transport. e. Transport of materials occurs only in one direction. Difficulty: 3 Question ID: 2.1-26 Page Ref: 35 Topic: Neurons Skill: Conceptual Answer: d. Retr ...
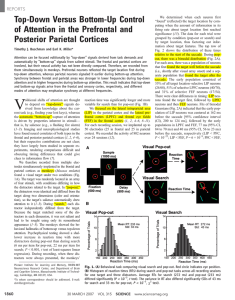
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
Fast Readout of Object Identity from Macaque Inferior Temporal Cortex
... the classifier to learn the map between neuronal responses and scale or position, irrespective of object identity (fig. S4A). Reading out object position or scale had a similar time course to the readout of object category (fig. S4B). There was little correlation between the ability of each IT site ...
... the classifier to learn the map between neuronal responses and scale or position, irrespective of object identity (fig. S4A). Reading out object position or scale had a similar time course to the readout of object category (fig. S4B). There was little correlation between the ability of each IT site ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...
... is driven by properties inherent in stimuli— that is, by salience (e.g., a flashing fire alarm) (1–3). Imaging and neurophysiological studies have found neural correlates of both types in the frontal and posterior parietal cortices (1, 2, 4–6), but their respective contributions are not clear; they ...