Physiology Ch 45 p543-557 [4-25
... -can elicit immediate reactions from brain or be stored as memories for up to years -somatic portion of sensory nervous system transmits sensory information from receptors of entire body surface and from some deep structures -and conducts through spinal cord at all levels, reticular substance of med ...
... -can elicit immediate reactions from brain or be stored as memories for up to years -somatic portion of sensory nervous system transmits sensory information from receptors of entire body surface and from some deep structures -and conducts through spinal cord at all levels, reticular substance of med ...
File
... neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that is not part of an ion channel. • This binding activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in the postsynaptic cell. • Effects of indirect synaptic transmission have a ...
... neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that is not part of an ion channel. • This binding activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in the postsynaptic cell. • Effects of indirect synaptic transmission have a ...
Biology 12 - Excretion
... peripheral nervous system: the nerves leaving spinal chord and brain central nervous system: spinal chord and brain collections of cell bodies bundle of nerve fibers one of 12 nerves that attaches to the brain collection of sensory neuron cell bodies encased in bone on dorsal side of spinal chord. r ...
... peripheral nervous system: the nerves leaving spinal chord and brain central nervous system: spinal chord and brain collections of cell bodies bundle of nerve fibers one of 12 nerves that attaches to the brain collection of sensory neuron cell bodies encased in bone on dorsal side of spinal chord. r ...
The Nervous System
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
... • A bundle of processes in the PNS is a nerve. • Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by an endoneurium (too small to see on the photomicrograph) – a layer of loose CT. • Groups of fibers are bound ...
Nervous System Notes
... • These neurons “sense” your surroundings and send the message to your SPINAL CORD or BRAIN! They sense pressure or heat and ...
... • These neurons “sense” your surroundings and send the message to your SPINAL CORD or BRAIN! They sense pressure or heat and ...
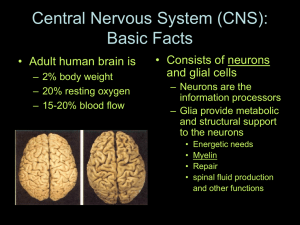
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
ch 48 clicker questions
... Adding a poison that specifically disables the Na+/K+ pumps to a culture of neurons will cause a) the resting membrane potential to drop to 0 mV. b) the inside of the neuron to become more negative relative to the outside. c) the inside of the neuron to become positively charged relative to the out ...
... Adding a poison that specifically disables the Na+/K+ pumps to a culture of neurons will cause a) the resting membrane potential to drop to 0 mV. b) the inside of the neuron to become more negative relative to the outside. c) the inside of the neuron to become positively charged relative to the out ...
Nervous System
... Getting the impulse from one neuron to the next. Adjacent neurons in a nerve fiber do not actually touch end to end. The junction between them is called a ________________. The gap is called a ________________________________. The gap between the terminal axon of one neuron and the dendrite ...
... Getting the impulse from one neuron to the next. Adjacent neurons in a nerve fiber do not actually touch end to end. The junction between them is called a ________________. The gap is called a ________________________________. The gap between the terminal axon of one neuron and the dendrite ...
The biological basis of behavior
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
Chapter 48 - cloudfront.net
... fuse with the terminal membrane which results in the release of neurotransmitters to the postsynaptic cells. 14. The postsynaptic cells contain ligand-gated ion channels that allow the binding of transmitted neurotransmitters. The binding of neurotransmitters may cause the opening of certain ion cha ...
... fuse with the terminal membrane which results in the release of neurotransmitters to the postsynaptic cells. 14. The postsynaptic cells contain ligand-gated ion channels that allow the binding of transmitted neurotransmitters. The binding of neurotransmitters may cause the opening of certain ion cha ...
The Nervous System
... 4. K+ ions are more concentrated on the inside of the axon. 5. This uneven distribution of K and Na ions is maintained by active transport across Na+/K+ pumps which operate whenever the neuron is not conducting an impulse. 6. Must work all the time, because the membrane is partially permeable to the ...
... 4. K+ ions are more concentrated on the inside of the axon. 5. This uneven distribution of K and Na ions is maintained by active transport across Na+/K+ pumps which operate whenever the neuron is not conducting an impulse. 6. Must work all the time, because the membrane is partially permeable to the ...
Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... tips communicate with the dendrites, axons and cell bodies of other neurons across tiny gaps called synapses. Scientists have classified neurons into four main groups based on differences in shape. Multipolar neurons are the most common neuron in the vertebrate nervous system and their structure mo ...
... tips communicate with the dendrites, axons and cell bodies of other neurons across tiny gaps called synapses. Scientists have classified neurons into four main groups based on differences in shape. Multipolar neurons are the most common neuron in the vertebrate nervous system and their structure mo ...
chapter48
... THE NATURE OF THE NERVE IMPULSE Most animal cells have a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane: more negative on the inside and more positive on the outside of the cell, in the fluid. ...
... THE NATURE OF THE NERVE IMPULSE Most animal cells have a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane: more negative on the inside and more positive on the outside of the cell, in the fluid. ...
Physiology Lecture Outline: Membrane Potential and Neurophysiology
... drop in Tb will significantly slow down neuronal transmission. For example, if a person falls into the very cold water of a frozen over lake, all of their nervous responses will be significantly slowed. 3. Myelination of Axon The myelin sheath that covers some axon is made from the cytoplasm of glia ...
... drop in Tb will significantly slow down neuronal transmission. For example, if a person falls into the very cold water of a frozen over lake, all of their nervous responses will be significantly slowed. 3. Myelination of Axon The myelin sheath that covers some axon is made from the cytoplasm of glia ...
Project Self-Discovery
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
... • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • motor (efferent)—send outgoing messages from brain to move muscles • sensory (afferent)—rece ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System Ch 33 and Brain
... Brains of early vertebrates had 3 principal divisions (see Fig. 33.13, p. 323): 1. Forebrain (= prosencephalon) (smell) 2. Midbrain (= mesencephalon) (vision) 3. Hindbrain (+ rhombencephalon) (hearing and balance) Different vertebrate groups have evolved different kinds of brains over time; Comparis ...
... Brains of early vertebrates had 3 principal divisions (see Fig. 33.13, p. 323): 1. Forebrain (= prosencephalon) (smell) 2. Midbrain (= mesencephalon) (vision) 3. Hindbrain (+ rhombencephalon) (hearing and balance) Different vertebrate groups have evolved different kinds of brains over time; Comparis ...
Nerve Cell Physiology
... Note that the soma is located الفياض on a stalk off the main trunk of the axon رافع عاوي.د ...
... Note that the soma is located الفياض on a stalk off the main trunk of the axon رافع عاوي.د ...
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - somatic sensory and motor nerves of the skin and skeletal muscles - Group A fibers: large diameter and thick myelin 15-130 m/sec - visceral sensory and motor nerves of organs, small skin sensory fibers (pain and touch) - Group B fibers: intermediate diameter and lightly ...
... - somatic sensory and motor nerves of the skin and skeletal muscles - Group A fibers: large diameter and thick myelin 15-130 m/sec - visceral sensory and motor nerves of organs, small skin sensory fibers (pain and touch) - Group B fibers: intermediate diameter and lightly ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Sensory Neurons- pick up stimuli from the internal or external environment and convert into a nerve impulse. 2. Interneurons- are neurons that carry impulses from one neuron to another. 3. Motor Neurons- sends an impulse to a muscle or gland to react in response. ...
... 1. Sensory Neurons- pick up stimuli from the internal or external environment and convert into a nerve impulse. 2. Interneurons- are neurons that carry impulses from one neuron to another. 3. Motor Neurons- sends an impulse to a muscle or gland to react in response. ...
neurons
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
9 Chapter Nervous System Notes (p
... 8. What do dendrites look like and what do they do? 9. What do axons look like and what do they do? ...
... 8. What do dendrites look like and what do they do? 9. What do axons look like and what do they do? ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... 1. When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons on the ends of the terminal branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotran ...
... 1. When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons on the ends of the terminal branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotran ...