A Brief History of the Discovery of the Neuron Based on the History
... functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are discrete cells which are not continuous with other cells. The neuron is composed of 3 parts – the dendrites, axon and cell body. Information flows along the neuron in one direction (from the dendrites to the axon, via the cell body). ...
... functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are discrete cells which are not continuous with other cells. The neuron is composed of 3 parts – the dendrites, axon and cell body. Information flows along the neuron in one direction (from the dendrites to the axon, via the cell body). ...
Nervous Dia rams
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
Chapter 10
... – The RMP of a nerve cell is measured to be -70 mV or millivolts (inside / outside) – As long as the RMP in a nerve cell is undisturbed, it remains polarized. – In order for a nerve impulse to be started or propagated in a nerve cell, this resting potential must be disturbed ...
... – The RMP of a nerve cell is measured to be -70 mV or millivolts (inside / outside) – As long as the RMP in a nerve cell is undisturbed, it remains polarized. – In order for a nerve impulse to be started or propagated in a nerve cell, this resting potential must be disturbed ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
... Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insulates the axon to prevent losing impulses Synapse – space between two neurons whe ...
... Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insulates the axon to prevent losing impulses Synapse – space between two neurons whe ...
Non- directed synapses
... gastrointestinal tract and nasopharynx, and is often asymptomatic. The central nervous system, primarily the spinal cord, may be affected, leading to rapidly progressive paralysis, coarse FASCICULATION and hyporeflexia. Motor neurons are primarily affected. Encephalitis may also occur. The virus rep ...
... gastrointestinal tract and nasopharynx, and is often asymptomatic. The central nervous system, primarily the spinal cord, may be affected, leading to rapidly progressive paralysis, coarse FASCICULATION and hyporeflexia. Motor neurons are primarily affected. Encephalitis may also occur. The virus rep ...
Nervous System
... Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
... Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Has well-developed Nissl bodies (rough ER) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which axons arise ...
Neuron - Schoolwires.net
... travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
Respiratory and Nervous Systems
... The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft. The neurotransmitters bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back in ...
... The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft. The neurotransmitters bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back in ...
Chapter 43
... the outside (membrane potential) • Cell membrane is impermeable to negative ions (such as Cl-) • Sodium-potassium pump will transport positive ions • Ion channels for K+ are more numerous (allowing more K+ to transport out of cell) • Leads to resting potential of ~ -70mV ...
... the outside (membrane potential) • Cell membrane is impermeable to negative ions (such as Cl-) • Sodium-potassium pump will transport positive ions • Ion channels for K+ are more numerous (allowing more K+ to transport out of cell) • Leads to resting potential of ~ -70mV ...
Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... Concept 48.3: Action potentials (nerve impulses) are the signals conducted by axons • Neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli • You’ll want to review this pic after you understand the action potential ...
... Concept 48.3: Action potentials (nerve impulses) are the signals conducted by axons • Neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli • You’ll want to review this pic after you understand the action potential ...
The Nervous System
... • However, dendrites and somata typically lack voltagegated channels, which are found in abundance on the axon hillock and axolemma. – So what cannot occur on dendrites and somata? ...
... • However, dendrites and somata typically lack voltagegated channels, which are found in abundance on the axon hillock and axolemma. – So what cannot occur on dendrites and somata? ...
Slide ()
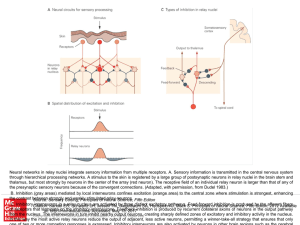
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
Neurons
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
... connected by the: – corpus callosum, a large band of neural fibers that transmits messages between hemispheres ...
AI_Connectionism_Excel
... Summary • The Brain is an Electrical System – Neurons fire in an all-or-none fashion – Neurons may either increase or decrease another neuron’s chances of firing ...
... Summary • The Brain is an Electrical System – Neurons fire in an all-or-none fashion – Neurons may either increase or decrease another neuron’s chances of firing ...
6 BIO Neurotransmitters - Appoquinimink High School
... the threshold has been met or exceeded, a chain reaction begins. With threshold being met, the cell becomes depolarized and allows positively charged ions into the axon at the nodes of ranvier. This mix of positive and negative ions causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 ...
... the threshold has been met or exceeded, a chain reaction begins. With threshold being met, the cell becomes depolarized and allows positively charged ions into the axon at the nodes of ranvier. This mix of positive and negative ions causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 ...
Nervous Regulation
... The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon of the original neuron syna ...
... The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. The axon of the original neuron syna ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... I. General Functions of the Nervous System A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical ...
... I. General Functions of the Nervous System A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical ...
Lesson 1 | The Nervous System
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
... 7. The central nervous system consists of the brain and (sensory system/spinal cord). 8. Thought processes are carried out in the (cerebrum/cerebellum). 9. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic and (central/autonomic) systems. 10. The most common cause of damage to the nervous system ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I: Basic Structure and Function
... golgi apparatus, and many microtubules. It also contains a large nucleus, chromatophilic substance, and cytoplasmic inclusions. C. Neurofibrils are fine threads that extend into axons. D. Chromatophilic substance is membranous sacs that contain rough endoplasmic reticulum. E. Mature neurons generall ...
... golgi apparatus, and many microtubules. It also contains a large nucleus, chromatophilic substance, and cytoplasmic inclusions. C. Neurofibrils are fine threads that extend into axons. D. Chromatophilic substance is membranous sacs that contain rough endoplasmic reticulum. E. Mature neurons generall ...
Milestone
... • Hypothesis is a prediction of a particular outcome. • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
... • Hypothesis is a prediction of a particular outcome. • Always hypothesize a difference. • Hypothesis must be testable. • You should include directionality in the hypothesis • Viewing more TV will increase anxiety. ...
Chapter 5a
... Action Potentials When a neuron fires, it releases neurotransmitters from terminals into synaptic cleft. Chemical in Neurotransmitter Stimulates or inhibits Postsynaptic Cell (Dendrite, Axon or Cell Body) If the postsynaptic cell receives enough stimulation, this neuron will fire. – Firing is ...
... Action Potentials When a neuron fires, it releases neurotransmitters from terminals into synaptic cleft. Chemical in Neurotransmitter Stimulates or inhibits Postsynaptic Cell (Dendrite, Axon or Cell Body) If the postsynaptic cell receives enough stimulation, this neuron will fire. – Firing is ...
Chapter 27 Lecture notes
... D. One cell receives input from numerous synaptic terminals from hundreds of neurons. The cell receives various magnitudes and numbers of both inhibitory and excitatory signals. The behavior of the receiving cell depends on the summation of all incoming signals (Figure 28.7). The more neurotransmit ...
... D. One cell receives input from numerous synaptic terminals from hundreds of neurons. The cell receives various magnitudes and numbers of both inhibitory and excitatory signals. The behavior of the receiving cell depends on the summation of all incoming signals (Figure 28.7). The more neurotransmit ...
Cell body
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Neurons Short Version
... blood- brain barrier. Since neurons are so vitally important and can’t carry out mitosis for replacement the body particularly tries to prevent dangerous substances from reaching them. Play a role in supplying the neurons with glucose. ...
... blood- brain barrier. Since neurons are so vitally important and can’t carry out mitosis for replacement the body particularly tries to prevent dangerous substances from reaching them. Play a role in supplying the neurons with glucose. ...