Autonomic Nervous System Peripheral NS and Spinal Cord A
... • Medulla primarily concerned with life support e.g. heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages throu ...
... • Medulla primarily concerned with life support e.g. heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, circulation. Cessation of activity in hind brain required for determination of brain death. It also relays sensory information from the various parts of the body to the brain and sends back motor messages throu ...
An implantable electrode design for both chronic in vivo
... Kutsch and Usherwood, 1970), for example, myogramm recordings have lead to important results on the coordinated use of various muscles. This technique also allows placement of the electrodes without restricting the animal’s movements, and thus more closely mirrors muscle activity in vivo. Using mode ...
... Kutsch and Usherwood, 1970), for example, myogramm recordings have lead to important results on the coordinated use of various muscles. This technique also allows placement of the electrodes without restricting the animal’s movements, and thus more closely mirrors muscle activity in vivo. Using mode ...
Document
... RF is implemented percutaneously by means of an insulated needle with a metal active tip that is placed in the appropriate nerve pathway. ...
... RF is implemented percutaneously by means of an insulated needle with a metal active tip that is placed in the appropriate nerve pathway. ...
Biology & Behavior
... a lover even…in other words, the relationship of running. “WHAT!?” many of you will be saying. “I thought that I was going to learn how to improve my 10k time.” GO read Runner’s World for that. You see, I don’t view running as what I DO or who I AM, but as this thing, this force, that changes ...
... a lover even…in other words, the relationship of running. “WHAT!?” many of you will be saying. “I thought that I was going to learn how to improve my 10k time.” GO read Runner’s World for that. You see, I don’t view running as what I DO or who I AM, but as this thing, this force, that changes ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fit ...
... locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fit ...
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of
... addition of currents that all follow the same basic rules. Let's now investigate just a few of these different neuronal ionic currents. First, imagine that we have just read Hodgkin and Huxley's series of articles in the Journal of Physiology and are quite impressed, but at the same time are wonderi ...
... addition of currents that all follow the same basic rules. Let's now investigate just a few of these different neuronal ionic currents. First, imagine that we have just read Hodgkin and Huxley's series of articles in the Journal of Physiology and are quite impressed, but at the same time are wonderi ...
chapt10_holes_lecture_animation
... • A cell membrane is usually electrically charged, or polarized, so that the inside of the membrane is negatively charged with respect to the outside of the membrane (which is then positively charged). • This is as a result of unequal distribution of ions on the inside and the outside of the membran ...
... • A cell membrane is usually electrically charged, or polarized, so that the inside of the membrane is negatively charged with respect to the outside of the membrane (which is then positively charged). • This is as a result of unequal distribution of ions on the inside and the outside of the membran ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... various brain disorders, is that during overstimulation, protective biochemical processes that are activated in neurons counteract this overstimulation by down regulating receptor proteins at synapses or by decreasing the amount of neurotransmitter they release. Imagine the drain in your sink is ...
... various brain disorders, is that during overstimulation, protective biochemical processes that are activated in neurons counteract this overstimulation by down regulating receptor proteins at synapses or by decreasing the amount of neurotransmitter they release. Imagine the drain in your sink is ...
Sensors - Castle High School
... Electrosensors are sensitive to changes in membrane potential. Chemoreceptors respond to the presence or absence of certain chemicals. Photoreceptors detect light. ...
... Electrosensors are sensitive to changes in membrane potential. Chemoreceptors respond to the presence or absence of certain chemicals. Photoreceptors detect light. ...
Neuronal Signaling
... between chemical (diffusion) and electrical forces • Ion pumps prevent long term run-down of membrane potential by ion leakage • The Nernst equation describes the equilibrium potential for a single ion species • The Goldman equation describes the equilibrium potential for many ion species ...
... between chemical (diffusion) and electrical forces • Ion pumps prevent long term run-down of membrane potential by ion leakage • The Nernst equation describes the equilibrium potential for a single ion species • The Goldman equation describes the equilibrium potential for many ion species ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as nerves. While bundle of afferent and efferent neurons within the CNS are referred to as tracts. 8) In the PNS the Schwann cells wrap around the axon and are referred to as the neurilemma. Between adjace ...
... 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as nerves. While bundle of afferent and efferent neurons within the CNS are referred to as tracts. 8) In the PNS the Schwann cells wrap around the axon and are referred to as the neurilemma. Between adjace ...
Anat 1: Ch 17 (SS99)
... C. Neuron #1 releases Ach, usually neuron #2 releases NE D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
... C. Neuron #1 releases Ach, usually neuron #2 releases NE D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
Nervous System
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
... The nervous system of many animals consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. This system allows animals to obtain quick feedback about their surroundings and to react immediately. The nervous system can be separated into two divisions, the central nervous system which includes the brain an ...
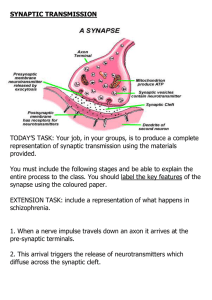
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...
... serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to be the result of excessive activity of the neurotransmitte ...
– Cell loss Brain, Neuron
... neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with normal function, notably learning, memory, and spatial recognition processes. Neuronal cell loss due ...
... neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with normal function, notably learning, memory, and spatial recognition processes. Neuronal cell loss due ...
The Nervous System
... Thalamus: serves as a relay station for almost all information that comes and goes to the cortex Limbic system (includes hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus) Amygdala: emotional reactions Hippocampus: memory ...
... Thalamus: serves as a relay station for almost all information that comes and goes to the cortex Limbic system (includes hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus) Amygdala: emotional reactions Hippocampus: memory ...
The Nervous System
... interpret the message from the sensory neurons, and relay the massage back to body parts. Motor output – motor or efferent neurons receive the message from interneuron and produce a response at the effector organ ( a muscle or a gland). ...
... interpret the message from the sensory neurons, and relay the massage back to body parts. Motor output – motor or efferent neurons receive the message from interneuron and produce a response at the effector organ ( a muscle or a gland). ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... Endocrine System: the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. - Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues - Adrenal Glands: a pair of endocrine ...
... Endocrine System: the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. - Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues - Adrenal Glands: a pair of endocrine ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
... Why is it important for all individuals to have regular eye checks, particularly as they age? Many eye defects can occur as one ages. In some cases where treatment is available, early detection means that treatment can begin sooner, and this may halt or slow the progress of the disease. ...
February 27
... processes. It is a complex series of events that occurs every second we are alive. In this lesson, students will explore communication inside the body by looking at the interaction between the cells of the nervous system, the neurons. The human body has literally billions of neurons, some of which f ...
... processes. It is a complex series of events that occurs every second we are alive. In this lesson, students will explore communication inside the body by looking at the interaction between the cells of the nervous system, the neurons. The human body has literally billions of neurons, some of which f ...
File
... bread. This is the CELL BODY. The cell body contains the NUCLEUS which controls what action will be taken. Shape the round piece of bread to look like a CELL BODY by pinching the bread in five places in order to place DENDRITES. The CELL BODY processes the impulse. Place an M&M in the bread in any l ...
... bread. This is the CELL BODY. The cell body contains the NUCLEUS which controls what action will be taken. Shape the round piece of bread to look like a CELL BODY by pinching the bread in five places in order to place DENDRITES. The CELL BODY processes the impulse. Place an M&M in the bread in any l ...
MEDIA REVIEW Neurons In Action: Computer Simulations with
... in the tutorials direct students to the relevant literature as well as provide students with informative and sometimes amusing quotes from such pioneers as Hodgkin, Huxley, and Cole. In addition, information is given on the difference between an ideal, typical, and “out of control” voltage clamp. Th ...
... in the tutorials direct students to the relevant literature as well as provide students with informative and sometimes amusing quotes from such pioneers as Hodgkin, Huxley, and Cole. In addition, information is given on the difference between an ideal, typical, and “out of control” voltage clamp. Th ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
... Cells are densely packed and intertwined Two main cell types: 1. Neurons Excitable – transmit electrical signals 2. Glial cells – support cells Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...