The Nervous System
... send) messages all around the body from neuron to neuron • Hormones-Chemicals that the body makes that control all of the functions of the body • Homeostasis-Balance that is maintained (ideally) between all of the systems of the body ...
... send) messages all around the body from neuron to neuron • Hormones-Chemicals that the body makes that control all of the functions of the body • Homeostasis-Balance that is maintained (ideally) between all of the systems of the body ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... Slow acting neurotransmitters do not affect ion movement across the post synaptic membranes directly but instead cause the release of secondary messengers inside post synaptic messengers which regulate fast synaptic transmission. ...
... Slow acting neurotransmitters do not affect ion movement across the post synaptic membranes directly but instead cause the release of secondary messengers inside post synaptic messengers which regulate fast synaptic transmission. ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
... Neurotransmitter release requires Ca2+ ions Normally, the concentration of Ca2+ in the pre-synaptic neuron l is kept very low (by the action of a Ca pump). The arrival of an action potential at the axon terminus opens voltage-gated Ca channels, and Ca2+ ions rush inside the pre-synaptic neuron The i ...
... Neurotransmitter release requires Ca2+ ions Normally, the concentration of Ca2+ in the pre-synaptic neuron l is kept very low (by the action of a Ca pump). The arrival of an action potential at the axon terminus opens voltage-gated Ca channels, and Ca2+ ions rush inside the pre-synaptic neuron The i ...
Learning Objectives
... 31. Explain how the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) function as a mammalian biological clock. 32. Distinguish between the functions of the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum. 33. Describe the specific functions of the brain regions associated with language, speech, emotions, memory, and learnin ...
... 31. Explain how the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) function as a mammalian biological clock. 32. Distinguish between the functions of the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum. 33. Describe the specific functions of the brain regions associated with language, speech, emotions, memory, and learnin ...
Biology and Behavior
... 2. Most sensory and motor pathways cross as they enter or leave the brain. As a result, the left hemisphere receives information from and controls movements of the right side of the body, and the right hemisphere does the same for the left side of the body. 3. Studies of split-brain patients highlig ...
... 2. Most sensory and motor pathways cross as they enter or leave the brain. As a result, the left hemisphere receives information from and controls movements of the right side of the body, and the right hemisphere does the same for the left side of the body. 3. Studies of split-brain patients highlig ...
Slide ()
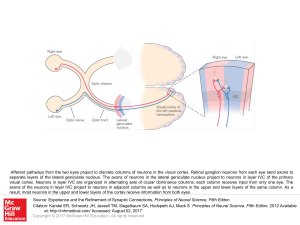
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Nervous Tissue - Northland Community & Technical College
... White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) ...
... White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) ...
Chater 2 - Study Guide
... 28. (Thinking Critically) Based on research, which of the following seems true about the specialized functions of the right and left hemispheres? A) They are more clear-cut in men than in women. B) They are more clear-cut in women than in men. C) Most complex tasks emerge from the activity of one o ...
... 28. (Thinking Critically) Based on research, which of the following seems true about the specialized functions of the right and left hemispheres? A) They are more clear-cut in men than in women. B) They are more clear-cut in women than in men. C) Most complex tasks emerge from the activity of one o ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
... controlling the eyes, have a small number of muscle fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 15 muscle fibers). Muscles with more general function, such as those controlling the calf muscle in the leg, have many fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 2,000 muscle fibers). ...
... controlling the eyes, have a small number of muscle fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 15 muscle fibers). Muscles with more general function, such as those controlling the calf muscle in the leg, have many fibers per motor neuron (about 1 neuron for every 2,000 muscle fibers). ...
Electrophysiology - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... The action potential appears to jump from node of Ranvier to node of Ranvier. Only the membrane at the node of Ranvier depolarizes, not the membrane under the myelin sheath. There are no ion channels under the myelin sheath. The jumping or saltatory conduction is much faster than depolarizing the en ...
... The action potential appears to jump from node of Ranvier to node of Ranvier. Only the membrane at the node of Ranvier depolarizes, not the membrane under the myelin sheath. There are no ion channels under the myelin sheath. The jumping or saltatory conduction is much faster than depolarizing the en ...
ppt - Castle High School
... charge across the membrane. These changes generate nerve impulses, or action potentials. An action potential is a rapid, large change in membrane potential that travels along an axon and causes release of chemical signals. ...
... charge across the membrane. These changes generate nerve impulses, or action potentials. An action potential is a rapid, large change in membrane potential that travels along an axon and causes release of chemical signals. ...
packet - mybiologyclass
... Sensory Input: the PNS receives information about environmental change (stimulus), then sensory neurons carry the information from the PNS to CNS. Integration: the CNS interprets the information sent from the PNS o Involves neurons located entirely within the CNS, called interneurons. Motor Ou ...
... Sensory Input: the PNS receives information about environmental change (stimulus), then sensory neurons carry the information from the PNS to CNS. Integration: the CNS interprets the information sent from the PNS o Involves neurons located entirely within the CNS, called interneurons. Motor Ou ...
Synapses and Synaptic Transmission
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...
... INTRODUCTION TO SYNAPSE: The CNS contains more than 100 billion neurons. Incoming signals enter the neuron through synapses located mostly on the neuronal dendrites, but also on the cell body. For different types of neurons, there may be only a few hundred or as many as 200,000 such synaptic connec ...
Day 4 - Scott County Schools
... Read this passage based on the text and answer the questions that follow. The structure of a neuron suits it for its function of transmitting nerve impulses. It has a special shape that lets it pass electrical signals to and from other cells. A neuron has three main parts: cell body, dendrites, and ...
... Read this passage based on the text and answer the questions that follow. The structure of a neuron suits it for its function of transmitting nerve impulses. It has a special shape that lets it pass electrical signals to and from other cells. A neuron has three main parts: cell body, dendrites, and ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... • Integrates and interprets sensory information and initiates voluntary movements • Has taken over many of the midbrain functions in lower vertebrates • Six layers • Isocortex (outer layer) is necessary for cognition and higher brain functions • More folded in more advanced mammals • Gyri – folds • ...
... • Integrates and interprets sensory information and initiates voluntary movements • Has taken over many of the midbrain functions in lower vertebrates • Six layers • Isocortex (outer layer) is necessary for cognition and higher brain functions • More folded in more advanced mammals • Gyri – folds • ...
Chp 7 (part 1)
... d. Unipolar Neurons: single process extending from cell body 1. the single process divides almost immediately into proximal and distal processes. 2. only small branches at the end of the distal process are dendrites 3. The remainder of the process acts as an axon. 4. The axon then sends impulses tow ...
... d. Unipolar Neurons: single process extending from cell body 1. the single process divides almost immediately into proximal and distal processes. 2. only small branches at the end of the distal process are dendrites 3. The remainder of the process acts as an axon. 4. The axon then sends impulses tow ...
The Nervous System
... most conscious and intelligent activities. Conscious thought occurs in the outer layer (cortex). Cerebrum is divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. ...
... most conscious and intelligent activities. Conscious thought occurs in the outer layer (cortex). Cerebrum is divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres. ...
1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study
... D) amygdala. 74. A brain tumor caused extensive damage to Mr. Thorndike's hypothalamus. It is most likely that he may suffer a loss of: A) visual perception. B) muscular coordination. C) sexual motivation. D) language comprehension. ...
... D) amygdala. 74. A brain tumor caused extensive damage to Mr. Thorndike's hypothalamus. It is most likely that he may suffer a loss of: A) visual perception. B) muscular coordination. C) sexual motivation. D) language comprehension. ...
Electrophysiology applications 1
... Another preparation that has been used to great advantage in understanding the cellular effects of opiates is the locus coeruleus (LC) slice. The extensive studies of opiates in LC slices by Aghajanian and colleagues and by North, Williams, and coworker are described in more detail in Foote and Asto ...
... Another preparation that has been used to great advantage in understanding the cellular effects of opiates is the locus coeruleus (LC) slice. The extensive studies of opiates in LC slices by Aghajanian and colleagues and by North, Williams, and coworker are described in more detail in Foote and Asto ...
Neuroscience Course Conference
... mineral oil (B), only a thin film of saline clung to the hydrophilic sheath of ...
... mineral oil (B), only a thin film of saline clung to the hydrophilic sheath of ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... Electrical Impulse—The movement of an ion current along the neuron membrane. It is generated in the cell body and moves along the axon to the terminal. Exocytosis—When an impulse arrives at the terminal, the vesicles fuse with the terminal membrane and release the neurotransmitters within them into ...
... Electrical Impulse—The movement of an ion current along the neuron membrane. It is generated in the cell body and moves along the axon to the terminal. Exocytosis—When an impulse arrives at the terminal, the vesicles fuse with the terminal membrane and release the neurotransmitters within them into ...
The human brain - "G. Galilei" – Pescara
... System: a branch of the autonomic nervous system responsible for mobilizing the body's energy and resources during times of stress and arousal. ...
... System: a branch of the autonomic nervous system responsible for mobilizing the body's energy and resources during times of stress and arousal. ...