Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... noise caused by the MRI gradient system are all factors altering the experimental effects. Study of spontaneous (paradigm-free) brain activity, such as natural variations in EEG background (alpha rhythm), wakefulness, or activity during resting state EEG–fMRI is one strategy that can ascribe the tim ...
... noise caused by the MRI gradient system are all factors altering the experimental effects. Study of spontaneous (paradigm-free) brain activity, such as natural variations in EEG background (alpha rhythm), wakefulness, or activity during resting state EEG–fMRI is one strategy that can ascribe the tim ...
Neurons Part 1
... Alternately the now negative area on the outside of the cell will flow towards the positive areas. However, this spread of depolarization is short lived because the lipid membrane is not a good conductor and is very leaky, so charges quickly balance out. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
... Alternately the now negative area on the outside of the cell will flow towards the positive areas. However, this spread of depolarization is short lived because the lipid membrane is not a good conductor and is very leaky, so charges quickly balance out. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
Central Nervous System
... • Involves enzymes that break down starches, proteins, fats, etc. in the small intestine. • Each type of molecule is broken down into its simplest part through the use of enzymes. ...
... • Involves enzymes that break down starches, proteins, fats, etc. in the small intestine. • Each type of molecule is broken down into its simplest part through the use of enzymes. ...
Slayt 1
... • According to him psychology was human behaviors• Heredity does not have adequate effects on human behaviors, • Human behaviors are regulated by the environment. • Hereditary characters and insincts were not so important • To him all behaviors must be fully measurable • Test groups must be evaluate ...
... • According to him psychology was human behaviors• Heredity does not have adequate effects on human behaviors, • Human behaviors are regulated by the environment. • Hereditary characters and insincts were not so important • To him all behaviors must be fully measurable • Test groups must be evaluate ...
Electroencephalography Student Protocol
... The cerebral cortex contains huge numbers of neurons. Activity of these neurons is to some extent synchronized in regular firing rhythms. These are referred to as brain waves. Electrodes placed in pairs on the scalp can pick up variations in electrical potential that derive from this underlying cort ...
... The cerebral cortex contains huge numbers of neurons. Activity of these neurons is to some extent synchronized in regular firing rhythms. These are referred to as brain waves. Electrodes placed in pairs on the scalp can pick up variations in electrical potential that derive from this underlying cort ...
The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
... Therefore, the linguistic system operates by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system do ...
... Therefore, the linguistic system operates by means of connections A person’s linguistic system is largely represented in his/her cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is a neural network A linguistic system is therefore represented as a neural network Therefore, any component of the system do ...
The Peripheral Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Question
... Inputs from these senses can modulate the somatic systems. Inputs from these senses can modulate the autonomic systems. Not all of the inputs pass through the brainstem. ...
... Inputs from these senses can modulate the somatic systems. Inputs from these senses can modulate the autonomic systems. Not all of the inputs pass through the brainstem. ...
Nervous System – Chapter 10
... d. ependyma – covers spaces in brain – made of cells shape from squamous to columnar cells . III. Cell Membrane Potential A. When nerve cells are at rest there is more sodium on the outside and potassium on the inside B. Potassium moves freely C. Sodium has to be transported IV. Nerve Impulse A. Fac ...
... d. ependyma – covers spaces in brain – made of cells shape from squamous to columnar cells . III. Cell Membrane Potential A. When nerve cells are at rest there is more sodium on the outside and potassium on the inside B. Potassium moves freely C. Sodium has to be transported IV. Nerve Impulse A. Fac ...
2nd class Nervous System
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
Anti-SPRR1a antibody ab125374 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 2 Images
... were incubated with primary antibody (1/300 in 1% BSA + 10% goat serum) for 16 hours at ...
... were incubated with primary antibody (1/300 in 1% BSA + 10% goat serum) for 16 hours at ...
Trauma and Brain Neurobiology
... co-occur in any given moment in time. This capacity allows us to survive but it also makes us vulnerable to false associations. These false associations impact children in a number of ways. They can cause a traumatized child to jump at a loud sound or lash out at a raised voice, either of which may ...
... co-occur in any given moment in time. This capacity allows us to survive but it also makes us vulnerable to false associations. These false associations impact children in a number of ways. They can cause a traumatized child to jump at a loud sound or lash out at a raised voice, either of which may ...
Chapter 10b
... of the middle ear, oval window create fluid which vibrate. waves within the cochlea. ...
... of the middle ear, oval window create fluid which vibrate. waves within the cochlea. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ ...
... 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ ...
Lab Activity Sheets
... appear on the models as numerous branches extending from the cell body. Be careful that you don’t confuse these with the synaptic knobs that are the ends of axons of other neurons arriving at this neuron. What's the generic name for the chemical substances stored in and released from synaptic knob ...
... appear on the models as numerous branches extending from the cell body. Be careful that you don’t confuse these with the synaptic knobs that are the ends of axons of other neurons arriving at this neuron. What's the generic name for the chemical substances stored in and released from synaptic knob ...
LTP
... • New neurons necessary for generating random context which minimizes interference, creates distinct codes (Becker, 2005) ...
... • New neurons necessary for generating random context which minimizes interference, creates distinct codes (Becker, 2005) ...
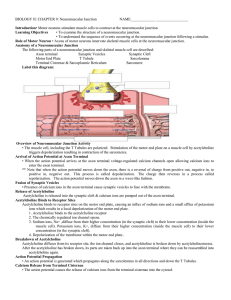
BIOLOGY II: CHAPTER 9: Neuromuscular Junction
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
... 3. Sodium ions, Na+ ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic cleft) to their lower concentration (inside the muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of ...
The Nervous System
... Tiny hairs, made of nerve fibers, dangle from all your olfactory receptors. They are covered with a layer of mucus. • If a smell, formed by chemicals in the air, dissolves in this mucus, the hairs absorb it and excite your olfactory receptors. ...
... Tiny hairs, made of nerve fibers, dangle from all your olfactory receptors. They are covered with a layer of mucus. • If a smell, formed by chemicals in the air, dissolves in this mucus, the hairs absorb it and excite your olfactory receptors. ...
Oct2011_Computers_Brains_Extra_Mural
... completely unless one understands how that region fits into the brain's overall functional information processing architecture. The Hypothalamus is the core of the brain having spontaneously active neurons that “animate” everything else. Other brain regions just layer on various constraints to these ...
... completely unless one understands how that region fits into the brain's overall functional information processing architecture. The Hypothalamus is the core of the brain having spontaneously active neurons that “animate” everything else. Other brain regions just layer on various constraints to these ...
BIOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL SHAPING OF MIND AND BEHAVIOUR
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
nervous system
... Because proteins are negatively charged, the inside layer of the cell membrane has a negative charge. Outside of the cell, there are many electrolytes, especially sodium (Na+), which have a positive charge. They stay outside of the cell because they cannot get in unless sodium channels in the cell m ...
... Because proteins are negatively charged, the inside layer of the cell membrane has a negative charge. Outside of the cell, there are many electrolytes, especially sodium (Na+), which have a positive charge. They stay outside of the cell because they cannot get in unless sodium channels in the cell m ...
Does spike-time dependant plasticity occurs in dorsal horn neurons
... In the case of wind-up, presynaptic spikes from Aβ fibers cause a fast depolarization in the dorsal horn neurons. This depolarization cannot lead to any postsynaptic action potential in the dorsal horn, but up-regulates the NMDA receptors, which are located on the dorsal horn. Then, spikes from C fi ...
... In the case of wind-up, presynaptic spikes from Aβ fibers cause a fast depolarization in the dorsal horn neurons. This depolarization cannot lead to any postsynaptic action potential in the dorsal horn, but up-regulates the NMDA receptors, which are located on the dorsal horn. Then, spikes from C fi ...
Synaptic Integration in Rat Frontal Cortex Shaped by Network Activity
... neocortical neurons, under conditions of strong spontaneous modulations of network activity. Specifically, we made use of the fact that pyramidal neurons in the rat neocortex express membrane potential fluctuations where hyperpolarized, quiescent periods alternate with depolarized periods with large ...
... neocortical neurons, under conditions of strong spontaneous modulations of network activity. Specifically, we made use of the fact that pyramidal neurons in the rat neocortex express membrane potential fluctuations where hyperpolarized, quiescent periods alternate with depolarized periods with large ...
Teacher Guide
... because the axon hillock actually increases the potential of the signal before transmitting down the axon. 5. Determine the resistance of each segment of the axon, and label it on the diagram on the previous page under the current arrows. What is the relationship of the resistance of each segment to ...
... because the axon hillock actually increases the potential of the signal before transmitting down the axon. 5. Determine the resistance of each segment of the axon, and label it on the diagram on the previous page under the current arrows. What is the relationship of the resistance of each segment to ...
Document
... action and emotion reflects its activity. Its signaling device, or means of communicating with body cells, is electrical impulses, which are rapid and specific and cause almost immediate responses. ...
... action and emotion reflects its activity. Its signaling device, or means of communicating with body cells, is electrical impulses, which are rapid and specific and cause almost immediate responses. ...