RUSTWOL: A Tool for Automatic Russian Word Form Recognition
... tool for automatic Russian word form recognition. The theoretical foundation of the RUSTWOL program is the two-level model, a language-independent model of morphological analysis and synthesis by Kimmo Koskenniemi (1983). My description is based on a document written by me, when I was working as a l ...
... tool for automatic Russian word form recognition. The theoretical foundation of the RUSTWOL program is the two-level model, a language-independent model of morphological analysis and synthesis by Kimmo Koskenniemi (1983). My description is based on a document written by me, when I was working as a l ...
Parts of Speech
... how something is done. It may also tell you when or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere ...
... how something is done. It may also tell you when or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere ...
Vocabulary: Compound Words
... up here is a verb with a preposition and forms a single unit of meaning. Back up means to make a copy just in case there is a problem with the original. You cannot say back your files. It is always back up your files/back your files up.) My backup files got destroyed by a virus. (Backup here functio ...
... up here is a verb with a preposition and forms a single unit of meaning. Back up means to make a copy just in case there is a problem with the original. You cannot say back your files. It is always back up your files/back your files up.) My backup files got destroyed by a virus. (Backup here functio ...
English Morphology – Lecture 1
... • Concepts can be expressed by noun groups or larger units; for ex. the man who lives next door or that beautiful summer morning of 1985 when we drove to the beach on an old CV2 • Function words may not have an easily identifiable meaning (for ex. can you specify the meaning of the?) ...
... • Concepts can be expressed by noun groups or larger units; for ex. the man who lives next door or that beautiful summer morning of 1985 when we drove to the beach on an old CV2 • Function words may not have an easily identifiable meaning (for ex. can you specify the meaning of the?) ...
Year 6 Grammar coverage
... informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing (such as the use of question tags, e.g. He’s your friend, isn’t he?, or the use of the subjunctive in some very formal writing and speech) ...
... informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing (such as the use of question tags, e.g. He’s your friend, isn’t he?, or the use of the subjunctive in some very formal writing and speech) ...
PARTNERSHIP FOR REVISING FLORIDA`S CONSTITUTION
... Use words that are in common use by the general public. A simple test is to write to the same audience as a quality newspaper or a person with a high school education. 2. ELIMINATE UNNECESSARY ...
... Use words that are in common use by the general public. A simple test is to write to the same audience as a quality newspaper or a person with a high school education. 2. ELIMINATE UNNECESSARY ...
I Once picked my nose `til it bleeded. Child Language
... often go ahead and apply the rule anyway, resulting in utterances such as Ralph Wiggum’s “I once picked my nose ‘til it bleeded” (The Dad who Knew Too Little). The nativist answer is that children are born with a default-rule (“add the thing that – in your language – is the regular marker”) that ste ...
... often go ahead and apply the rule anyway, resulting in utterances such as Ralph Wiggum’s “I once picked my nose ‘til it bleeded” (The Dad who Knew Too Little). The nativist answer is that children are born with a default-rule (“add the thing that – in your language – is the regular marker”) that ste ...
English for Academic Skills Independence [EASI]
... From Session 2 on formal vs informal language. We should avoid using informal language in academic writing. Share with a partner some examples for each of these types of informal language: ...
... From Session 2 on formal vs informal language. We should avoid using informal language in academic writing. Share with a partner some examples for each of these types of informal language: ...
Introduction to Linguistics and its role in Natural Language Processing
... Semantics: the study of the meaning of language. Can be decomposed into: Lexical semantics: the study of meaning of individual words Global semantics: how the meaning of individual words are combined into meaning of sentences (or more). One approach to lexical semantics is to study how word meanings ...
... Semantics: the study of the meaning of language. Can be decomposed into: Lexical semantics: the study of meaning of individual words Global semantics: how the meaning of individual words are combined into meaning of sentences (or more). One approach to lexical semantics is to study how word meanings ...
words - I blog di Unica - Università di Cagliari
... events, or about the ability of performing an action. They only function as auxiliary verbs ...
... events, or about the ability of performing an action. They only function as auxiliary verbs ...
Literacy glossary - Professional skills tests
... Luckily, all the children were happy with the arrangements - modifies a whole sentence. Adverbs are often (but not always) formed by adding the letters 'ly' to the end of an adjective. Adverbs of manner are used to describe the way in which something is done (slowly, noisily); adverbs of place descr ...
... Luckily, all the children were happy with the arrangements - modifies a whole sentence. Adverbs are often (but not always) formed by adding the letters 'ly' to the end of an adjective. Adverbs of manner are used to describe the way in which something is done (slowly, noisily); adverbs of place descr ...
Theme 6 Study Guide
... o Stories have a beginning, middle, and end. In An Important Debate, the beginning is when Speaker Stevens’ dialogue sets up the problem/conflict. Congressman Rock’s dialogue and Congresswoman Green’s dialogue make up the middle of the play and provide the climax. Speaker Stevens’ final dialogue rep ...
... o Stories have a beginning, middle, and end. In An Important Debate, the beginning is when Speaker Stevens’ dialogue sets up the problem/conflict. Congressman Rock’s dialogue and Congresswoman Green’s dialogue make up the middle of the play and provide the climax. Speaker Stevens’ final dialogue rep ...
SPAG terms Meaning / examples Noun A noun is an object, place
... Subordinating conjunctions – WUBA conjunctions, (which, while, when, unless, until, before, because, as, although, after) since, despite,if etc. Subordinating conjunctions will mark the beginning of a subordinate clause. Prepositions indicate where or when something happens. In, under, by, near, bef ...
... Subordinating conjunctions – WUBA conjunctions, (which, while, when, unless, until, before, because, as, although, after) since, despite,if etc. Subordinating conjunctions will mark the beginning of a subordinate clause. Prepositions indicate where or when something happens. In, under, by, near, bef ...
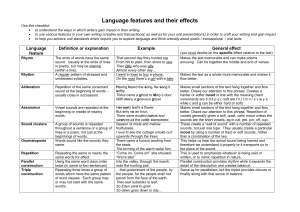
Language features and their effects
... better. Draws our attention to this phrase. Creates a harder or softer mood in line with the meaning (hard consonants are b d k p q t, soft are f h j l m n r s v w y z, while c and g can be either hard or soft) Makes small sections of the text hang together and flow better. Draws our attention to th ...
... better. Draws our attention to this phrase. Creates a harder or softer mood in line with the meaning (hard consonants are b d k p q t, soft are f h j l m n r s v w y z, while c and g can be either hard or soft) Makes small sections of the text hang together and flow better. Draws our attention to th ...
Literacy Mat
... Complex sentences: A complex sentence contains a conjunction such as because, since, after, although or when . • Because Robert felt tired, he only studied for an ...
... Complex sentences: A complex sentence contains a conjunction such as because, since, after, although or when . • Because Robert felt tired, he only studied for an ...
The California Language Arts Content Standards
... catharsis – therapeutic release of emotion upon identifying with and being moved by a piece of literature catastrophe – final event of a dramatic work, usually ruin or death characterization – the process of developing a character in a narrative or drama, often through the conflict of the plot circu ...
... catharsis – therapeutic release of emotion upon identifying with and being moved by a piece of literature catastrophe – final event of a dramatic work, usually ruin or death characterization – the process of developing a character in a narrative or drama, often through the conflict of the plot circu ...
Modification - (`Dick`) Hudson
... verb is the head of the whole sentence and has various other words as dependents, which in turn have other dependents and so on. Each dependent modifies the meaning of its head, and through it the meaning of the head verb which carries the meaning of the whole sentence. Almost every kind of word can ...
... verb is the head of the whole sentence and has various other words as dependents, which in turn have other dependents and so on. Each dependent modifies the meaning of its head, and through it the meaning of the head verb which carries the meaning of the whole sentence. Almost every kind of word can ...
Lecture 06
... Language use involves a rather complex system of subconscious grammatical knowledge. This is revealed most obviously in the study of how words are combined to form sentences. In this lecture, we will consider the system of rules and categories underlying sentence formation in human language. This co ...
... Language use involves a rather complex system of subconscious grammatical knowledge. This is revealed most obviously in the study of how words are combined to form sentences. In this lecture, we will consider the system of rules and categories underlying sentence formation in human language. This co ...
Reminders for Writing Essays on the AP Exam (AP
... “particular” (except where “certain” means confident, or “particular” means exacting). If you are unsure of the meaning of a word, go the conservative route and just leave it out…your task is not to bewilder the reader with awkward ...
... “particular” (except where “certain” means confident, or “particular” means exacting). If you are unsure of the meaning of a word, go the conservative route and just leave it out…your task is not to bewilder the reader with awkward ...
LOS OBJETOS DE LA CLASE Mandatos Commands
... There are three simple rules for making a noun plural in Spanish. 1. If the noun ends with a vowel (a, e, i, o, u), add “s”. 2. If the noun ends with a consonant, add “es”. 3. If the noun ends with the letter “z”, change “z” to “c” then add “es”. The definite articles and indefinite articles must al ...
... There are three simple rules for making a noun plural in Spanish. 1. If the noun ends with a vowel (a, e, i, o, u), add “s”. 2. If the noun ends with a consonant, add “es”. 3. If the noun ends with the letter “z”, change “z” to “c” then add “es”. The definite articles and indefinite articles must al ...
Diapositiva 1
... Wait a minute the first sentence is much shorter than the second sentence! You are only partially right! This simple exercise makes a very important point about how we speak and use English. Namely, English is considered a stressed language (it is also called a stresstimed language) while many othe ...
... Wait a minute the first sentence is much shorter than the second sentence! You are only partially right! This simple exercise makes a very important point about how we speak and use English. Namely, English is considered a stressed language (it is also called a stresstimed language) while many othe ...
Chapter four - UNT Department of English
... At the beginning of the previous chapter, we noted that Steven Pinker and his colleagues have been conducting model-organism research, but not on phonology. The area of linguistics in which he has been doing this work is known as morphology, which deals with the smallest meaningful units and how the ...
... At the beginning of the previous chapter, we noted that Steven Pinker and his colleagues have been conducting model-organism research, but not on phonology. The area of linguistics in which he has been doing this work is known as morphology, which deals with the smallest meaningful units and how the ...
Grammar Glossary - St Stephen`s Catholic Primary School
... Direct speech and indirect speech There are two ways of showing what somebody says: Direct speech: This is where the actual words that the person says are shown in speech marks (in some forms they would be in speech bubbles) John said, ‘I want to go home now.’ ‘Would you like to come with me?’ said ...
... Direct speech and indirect speech There are two ways of showing what somebody says: Direct speech: This is where the actual words that the person says are shown in speech marks (in some forms they would be in speech bubbles) John said, ‘I want to go home now.’ ‘Would you like to come with me?’ said ...
Knowledge Map Document
... 34. Resolution is the ending of the story where the conflict is resolved. (3.2) 35. Foreshadowing is the use of clues that hint at events that will occur later in the plot. (3.2) 36. Irony is the difference between what is expected and what actually happens. (3.2) 37. Suspense is a feeling of growin ...
... 34. Resolution is the ending of the story where the conflict is resolved. (3.2) 35. Foreshadowing is the use of clues that hint at events that will occur later in the plot. (3.2) 36. Irony is the difference between what is expected and what actually happens. (3.2) 37. Suspense is a feeling of growin ...






![English for Academic Skills Independence [EASI]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004613594_1-e68d304a37713d0fc8f26766c736a28a-300x300.png)