Writing Strategy
... She is a nice person. He is sad about his old bike. The box is heavy. The fat cat is hungry. I am very late to the teacher meeting. The balloon is thin and long. ...
... She is a nice person. He is sad about his old bike. The box is heavy. The fat cat is hungry. I am very late to the teacher meeting. The balloon is thin and long. ...
2298 Parts of Speech PC GUD
... display posters. Each poster corresponds to a set of 15 cards. (The poster and corresponding cards have the same color border.) There are 5 cards for each part of speech. Place the 3 parts of speech title cards in the window of the storage pockets as shown. For convenient storage, organize all the n ...
... display posters. Each poster corresponds to a set of 15 cards. (The poster and corresponding cards have the same color border.) There are 5 cards for each part of speech. Place the 3 parts of speech title cards in the window of the storage pockets as shown. For convenient storage, organize all the n ...
D.L.P. – Week Three Grade eight Day One – Skills Elimination of
... Unless a group of words asks a question, it is punctuated with a period or exclamation mark. Telling about what someone would ask is not a question; therefore, it would end in a period. Ex. I asked if he would need a pencil. The person is not actually asking the question. They are telling what they ...
... Unless a group of words asks a question, it is punctuated with a period or exclamation mark. Telling about what someone would ask is not a question; therefore, it would end in a period. Ex. I asked if he would need a pencil. The person is not actually asking the question. They are telling what they ...
MORPHOLOGY - introduction
... 1. 2. By contrast, contemporary linguists adopt a descriptive approach to language, and are concerned to describe what people actually say (rather than prescribe what they ought to say). They try to give all the possibilities of the expressions which are grammatically correct, esp. differences betwe ...
... 1. 2. By contrast, contemporary linguists adopt a descriptive approach to language, and are concerned to describe what people actually say (rather than prescribe what they ought to say). They try to give all the possibilities of the expressions which are grammatically correct, esp. differences betwe ...
Speeches of English Grammar
... Which points to a specific thing This, That, These, Those They also indicate whether the thing is close or far "That" (singular) and "Those" (plural) refer to an object or person far AWAY. Who owns that house? (distant - physical) Is this John's house? (near - physical) ...
... Which points to a specific thing This, That, These, Those They also indicate whether the thing is close or far "That" (singular) and "Those" (plural) refer to an object or person far AWAY. Who owns that house? (distant - physical) Is this John's house? (near - physical) ...
Glossary of Grammatical Terms and Errors active voice: The
... active voice: The common name for syntactical structures in which subjects do things, rather than have things done to them, the active voice arises when a clause‟s object receives the action or effect of a verb, which is enacted by the subject. For example, “John ate cookies” is a sentence using the ...
... active voice: The common name for syntactical structures in which subjects do things, rather than have things done to them, the active voice arises when a clause‟s object receives the action or effect of a verb, which is enacted by the subject. For example, “John ate cookies” is a sentence using the ...
Glossary of Writing Terms
... about, above, across, after, against, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, since, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, until, up, upon, with, without, ...
... about, above, across, after, against, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, since, through, throughout, till, to, toward, under, until, up, upon, with, without, ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Adjective Suffixes
... These endings are called adjective suffixes Some of these adjective suffixes are -able, ful, -ish, -less, -y, and -ous. ...
... These endings are called adjective suffixes Some of these adjective suffixes are -able, ful, -ish, -less, -y, and -ous. ...
Used to describe a person doing something that involves himself or
... Often use reflexive verbs to refer to emotions, feelings, and reactions ...
... Often use reflexive verbs to refer to emotions, feelings, and reactions ...
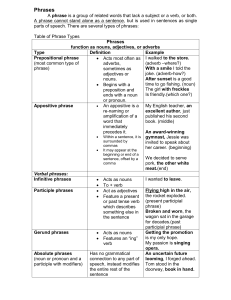
Phrases - KoplikEnglish10
... Although white dogs are pretty, they are not popular. Such words are either subordinating conjunctions (such as: although, since, because, like, while, as, if, while, when, since) or relative pronouns (such as: which, that, who, whom, what, whatever, whoever). Dependent clauses are used as single pa ...
... Although white dogs are pretty, they are not popular. Such words are either subordinating conjunctions (such as: although, since, because, like, while, as, if, while, when, since) or relative pronouns (such as: which, that, who, whom, what, whatever, whoever). Dependent clauses are used as single pa ...
PDF
... How many nouns are in this sentence: 'The fluffy dog ate some stinky cheese, crisps and an old newspaper.' A ...
... How many nouns are in this sentence: 'The fluffy dog ate some stinky cheese, crisps and an old newspaper.' A ...
Subject
... Collective nouns: Nouns that name groups of people, things, or ideas as single entities. Group, army, jury, society, department. Pronouns: Names a person or thing doing or being something. Subject Pronoun: A pronoun that identifies and names the specific person or thing doing or being something. ...
... Collective nouns: Nouns that name groups of people, things, or ideas as single entities. Group, army, jury, society, department. Pronouns: Names a person or thing doing or being something. Subject Pronoun: A pronoun that identifies and names the specific person or thing doing or being something. ...
Guide to Parsing
... For example, πάντες [1/3ADJ-MNP], “all,” is the masculine nominative plural form of the adjective πᾶς, πᾶσα, πᾶν, which takes endings of the first and third declensions. And ἀξιώτατε [s1/2ADJ-MVS], “O most worthy (one)!” is the masculine vocative singular form of the adjective ἄξιος, ἀξία, ἄξιον, wh ...
... For example, πάντες [1/3ADJ-MNP], “all,” is the masculine nominative plural form of the adjective πᾶς, πᾶσα, πᾶν, which takes endings of the first and third declensions. And ἀξιώτατε [s1/2ADJ-MVS], “O most worthy (one)!” is the masculine vocative singular form of the adjective ἄξιος, ἀξία, ἄξιον, wh ...
writing cheat sheet
... He drove nearby. [where] He drove yesterday. [when] He drove carefully. [how] Gerund Always ending with the suffix –ing, a gerund is a verbal noun. Example: Swimming is my favorite sport. (Swimming, although a verb in most instances, acts as the sentence’s subject.) ...
... He drove nearby. [where] He drove yesterday. [when] He drove carefully. [how] Gerund Always ending with the suffix –ing, a gerund is a verbal noun. Example: Swimming is my favorite sport. (Swimming, although a verb in most instances, acts as the sentence’s subject.) ...
appendix Xii uK vs. us english
... In the English of the United Kingdom, collective nouns can take either the singular or plural verb forms, depending on whether the emphasis is on the collective as a whole or on the individual members respectively. Some collective nouns, such as the Government or staff, nearly always take the plural ...
... In the English of the United Kingdom, collective nouns can take either the singular or plural verb forms, depending on whether the emphasis is on the collective as a whole or on the individual members respectively. Some collective nouns, such as the Government or staff, nearly always take the plural ...
Editor`s Nitpicking # 2 - American Journal of Neuroradiology
... “Today” is a commonly used adverb signifying on this day or at the present time (as in “Today, the preferred method of treating aneurysms is embolization”). When used as a noun, its meaning is the same. If used as an adjective, it means something that is characteristic of the current times. The word ...
... “Today” is a commonly used adverb signifying on this day or at the present time (as in “Today, the preferred method of treating aneurysms is embolization”). When used as a noun, its meaning is the same. If used as an adjective, it means something that is characteristic of the current times. The word ...
Slide 1 - TeacherTube
... used to describe a noun in the sentence. There are often more than one adjectives in a sentence. ...
... used to describe a noun in the sentence. There are often more than one adjectives in a sentence. ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... Verbs • Verbs are action words; they show what the subject is doing, or make a statement about the subject • Just like subjects, there are two types of verbs ...
... Verbs • Verbs are action words; they show what the subject is doing, or make a statement about the subject • Just like subjects, there are two types of verbs ...
Pronoun Summary General definition: A pronoun is a word used in
... verb acts on himself or herself (e.g. I taught myself chess; that’s why I stink at it.) —reflexives and intensives look alike (-self, -selves), but intensives only reinforce (intensify) a noun or pronoun just mentioned in the sentence. (e.g. I myself will fix the problem.) —pronouns that specify alm ...
... verb acts on himself or herself (e.g. I taught myself chess; that’s why I stink at it.) —reflexives and intensives look alike (-self, -selves), but intensives only reinforce (intensify) a noun or pronoun just mentioned in the sentence. (e.g. I myself will fix the problem.) —pronouns that specify alm ...
Rhetorical Devices
... Some useful expletives include the following: in fact, of course, indeed, I think, without doubt, to be sure, naturally, it seems, after all, for all that, in brief, on the whole, in short, to tell the truth, in any event, clearly, I suppose, I hope, at least, assuredly, certainly, remarkably, impor ...
... Some useful expletives include the following: in fact, of course, indeed, I think, without doubt, to be sure, naturally, it seems, after all, for all that, in brief, on the whole, in short, to tell the truth, in any event, clearly, I suppose, I hope, at least, assuredly, certainly, remarkably, impor ...
A typology of reduplication in Cushitic
... Reduplication occurs lexically and as grammatical process. The former is presumably often the result of the latter. Grammatical reduplication includes plural formation in nouns, frequentative on verbs and habitual on verbs. The epenthetic vowel a is the most commonly used epenthetic vowel in redupli ...
... Reduplication occurs lexically and as grammatical process. The former is presumably often the result of the latter. Grammatical reduplication includes plural formation in nouns, frequentative on verbs and habitual on verbs. The epenthetic vowel a is the most commonly used epenthetic vowel in redupli ...
Universidad Virtual English
... • There are three articles in English: a, an and the. • They always go before a noun. • A/an refers to countable singular nouns. They refer to any person, place or thing. • I want a porter to help me carry my luggage. • (It can be any of the porters working at the station) • They wanted to have a ni ...
... • There are three articles in English: a, an and the. • They always go before a noun. • A/an refers to countable singular nouns. They refer to any person, place or thing. • I want a porter to help me carry my luggage. • (It can be any of the porters working at the station) • They wanted to have a ni ...
chapter1-theory-of-parts-of
... occurs in a dictionary, where work, works, working, worked will all be counted as different grammatical forms of the word work. This distinction however is not always necessary, for it is only important with certain parts of speech that have inflections; that is endings or modifications that change ...
... occurs in a dictionary, where work, works, working, worked will all be counted as different grammatical forms of the word work. This distinction however is not always necessary, for it is only important with certain parts of speech that have inflections; that is endings or modifications that change ...
grammar - rdonnell
... Verbs have a subject (a doer of the action). Sometimes the verb also has an object (something that has the action done to it) e.g. You play. Play = verb, you = subject or ‘doer’ of the action. Play is therefore an intransitive verb – (no object). You play the guitar. The guitar is the object that is ...
... Verbs have a subject (a doer of the action). Sometimes the verb also has an object (something that has the action done to it) e.g. You play. Play = verb, you = subject or ‘doer’ of the action. Play is therefore an intransitive verb – (no object). You play the guitar. The guitar is the object that is ...
grammar - rdonnell
... Verbs have a subject (a doer of the action). Sometimes the verb also has an object (something that has the action done to it) e.g. You play. Play = verb, you = subject or ‘doer’ of the action. Play is therefore an intransitive verb – (no object). You play the guitar. The guitar is the object that is ...
... Verbs have a subject (a doer of the action). Sometimes the verb also has an object (something that has the action done to it) e.g. You play. Play = verb, you = subject or ‘doer’ of the action. Play is therefore an intransitive verb – (no object). You play the guitar. The guitar is the object that is ...