Word Classes
... They are sweet __________ salty. I will, __________ you won’t. They are sweet and salty. They are sweet yet salty. ...
... They are sweet __________ salty. I will, __________ you won’t. They are sweet and salty. They are sweet yet salty. ...
Parts of speech in natural language
... pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, they prepositions: on, under, over, near, by, at, from, to, with determiners: a, an, the conjunctions: and, but, or, as, if, when numerals: one, two, three, first, second, third particles: up, down, on, off, in, out, at, by “Particle” is the technical term for “we don’ ...
... pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, they prepositions: on, under, over, near, by, at, from, to, with determiners: a, an, the conjunctions: and, but, or, as, if, when numerals: one, two, three, first, second, third particles: up, down, on, off, in, out, at, by “Particle” is the technical term for “we don’ ...
Proper nouns
... A subordinate clause depends on the main clause to make sense. e.g. It was raining (main clause) so I took my umbrella (subordinate clause) ...
... A subordinate clause depends on the main clause to make sense. e.g. It was raining (main clause) so I took my umbrella (subordinate clause) ...
Holt Handbook Chapter 3
... actions (or tells something about the subject) without the action passing to a receiver, or object. ...
... actions (or tells something about the subject) without the action passing to a receiver, or object. ...
A guide to grammar - Accounting and Information Systems
... Sometimes it is difficult to decide whether the subject is singular or plural, especially when the subject is a pronoun. The following are singular: another, each, every, neither, one, and compound pronouns made with any, every, some and no. The following are plural: many, few, both, others, several ...
... Sometimes it is difficult to decide whether the subject is singular or plural, especially when the subject is a pronoun. The following are singular: another, each, every, neither, one, and compound pronouns made with any, every, some and no. The following are plural: many, few, both, others, several ...
english revision book sats 2016
... particular people, place names, days and months. Common nouns: are not names of any particular person, place or thing: child, village, dog. Noun phrases: groups of words doing the job of a noun: The old man walked slowly up the hill. Pronouns: used in place of nouns e.g. she, he. Mine and yours are ...
... particular people, place names, days and months. Common nouns: are not names of any particular person, place or thing: child, village, dog. Noun phrases: groups of words doing the job of a noun: The old man walked slowly up the hill. Pronouns: used in place of nouns e.g. she, he. Mine and yours are ...
GRAMMAR Review day 2
... To find the DIRECT OBJECT, find the action verb, and ask who or what receives the action. In some sentences the DIRECT OBJECT is compound Try These: Jane studied the stars. At the age of twelve, she observed an eclipse and a meteor shower. She watched the sky at night through a telescope. She re ...
... To find the DIRECT OBJECT, find the action verb, and ask who or what receives the action. In some sentences the DIRECT OBJECT is compound Try These: Jane studied the stars. At the age of twelve, she observed an eclipse and a meteor shower. She watched the sky at night through a telescope. She re ...
Relationships between ideas -1
... Parallel structure: the use of a conjunction to connect words/phrases that have the same grammatical function in a sentence – and, but, or, nor Noun + and + noun: Steve and his friend are coming to dinner. Verb + and + verb: Susan raised her hands and snapped her fingers. ...
... Parallel structure: the use of a conjunction to connect words/phrases that have the same grammatical function in a sentence – and, but, or, nor Noun + and + noun: Steve and his friend are coming to dinner. Verb + and + verb: Susan raised her hands and snapped her fingers. ...
Updated AR Conjugation Notes - Holy Angels Regional School
... Notice that the Spanish word hablar is changed by removing the “ar” ending and replacing it with either “o”, “as”, or “a” along with the pronoun. The pronoun as well as the ending of the verb tells the reader or listener who the person is that is doing the action. Students are encouraged to memoriz ...
... Notice that the Spanish word hablar is changed by removing the “ar” ending and replacing it with either “o”, “as”, or “a” along with the pronoun. The pronoun as well as the ending of the verb tells the reader or listener who the person is that is doing the action. Students are encouraged to memoriz ...
example - Greater Atlanta Christian Schools
... • 1st person pronouns– I, me, us, we, our, ours • 2nd person pronouns- you, your, yours • 3rd person pronouns- he, him, his, hers, it, its, they, them, theirs ...
... • 1st person pronouns– I, me, us, we, our, ours • 2nd person pronouns- you, your, yours • 3rd person pronouns- he, him, his, hers, it, its, they, them, theirs ...
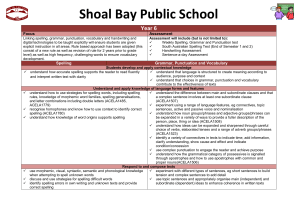
File - Shoal Bay Public School Curriculum
... understand the difference between main and subordinate clauses and that rules, knowledge of morphemic word families, spelling generalisations, a complex sentence involves at least one subordinate clause and letter combinations including double letters (ACELA1485, (ACELA1507) ACELA1779) experimen ...
... understand the difference between main and subordinate clauses and that rules, knowledge of morphemic word families, spelling generalisations, a complex sentence involves at least one subordinate clause and letter combinations including double letters (ACELA1485, (ACELA1507) ACELA1779) experimen ...
Unit 7:<Contracting long sentences>
... The position of the words in a sentence is the principal means of showing their relationship. Confusion and ambiguity result when words are badly placed. The place of the modifier or whether to have a comma or not, can make the sentence mean differently. Sometimes, the modifier seems so normal that ...
... The position of the words in a sentence is the principal means of showing their relationship. Confusion and ambiguity result when words are badly placed. The place of the modifier or whether to have a comma or not, can make the sentence mean differently. Sometimes, the modifier seems so normal that ...
Phonology
... Word order; inherent knowledge Semantics: The study of linguistic meaning; the meaning of words, phrases and sentences Pragmatics: The study of how language is used to ...
... Word order; inherent knowledge Semantics: The study of linguistic meaning; the meaning of words, phrases and sentences Pragmatics: The study of how language is used to ...
Inspiring Women Magazine Stylebook
... 2. Capitalize all nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and pronouns, regardless of the length of the word. 3. Capitalize prepositions of four or more letters (like over, from, and with). 4. Capitalize conjunctions of four or more letters (like unless and than), as well as if and how and why. Do not ca ...
... 2. Capitalize all nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and pronouns, regardless of the length of the word. 3. Capitalize prepositions of four or more letters (like over, from, and with). 4. Capitalize conjunctions of four or more letters (like unless and than), as well as if and how and why. Do not ca ...
Name: Date: 6B- _____ Grammar: Nouns 1 Steps to Identify Case
... 1. Find the verb. A verb shows action. Sentences may have more than one verb. 2. Possessive: Locate apostrophes. Nouns with apostrophes are probably possessive. Once you locate a noun with an apostrophe, check that it owns, possesses, or “has” something else. This means it’s possessive. There may be ...
... 1. Find the verb. A verb shows action. Sentences may have more than one verb. 2. Possessive: Locate apostrophes. Nouns with apostrophes are probably possessive. Once you locate a noun with an apostrophe, check that it owns, possesses, or “has” something else. This means it’s possessive. There may be ...
Complements - HausauerIntroLit
... the DO will appear near the beginning of the sentence, before the verb. To find the DO, rephrase the question. Ex: Which book did you read? You did read which book? A verb may have more than ...
... the DO will appear near the beginning of the sentence, before the verb. To find the DO, rephrase the question. Ex: Which book did you read? You did read which book? A verb may have more than ...
1. Words and morphemes
... STEM: main portion of a word onto which prefixes/suffixes are stuck. For the root electrwe have stems like electrify and electron, we can add further endings electrifies, electrons In some languages stems must have a suffix to make a complete word. A root is normally a single morpheme; a stem might ...
... STEM: main portion of a word onto which prefixes/suffixes are stuck. For the root electrwe have stems like electrify and electron, we can add further endings electrifies, electrons In some languages stems must have a suffix to make a complete word. A root is normally a single morpheme; a stem might ...
D.L.P. – Week Three Grade eight Day One – Skills Punctuation
... Indefinite pronouns are words that can take the place of nouns, but they are not specific. They are also complicated to use since they affected by whether they are singular or plural. They must agree with the verb and other pronouns in the sentence. Another, anybody, anyone, anything, everybody, eve ...
... Indefinite pronouns are words that can take the place of nouns, but they are not specific. They are also complicated to use since they affected by whether they are singular or plural. They must agree with the verb and other pronouns in the sentence. Another, anybody, anyone, anything, everybody, eve ...
Pet Peeves - Asher
... Identify the subject of the sentence; don’t rely solely on how the sentence sounds. Don’t be misled by prepositional phrases (unless the subject is a fraction or percentage). Remember that “there” and “here” at the beginning of a sentence are false subjects; the true subject is elsewhere in the sent ...
... Identify the subject of the sentence; don’t rely solely on how the sentence sounds. Don’t be misled by prepositional phrases (unless the subject is a fraction or percentage). Remember that “there” and “here” at the beginning of a sentence are false subjects; the true subject is elsewhere in the sent ...
Grammar Check!
... • A Semi- Colon is different from a Colon. The Semi- colon has a different meaning a Semi- Colon will separate two different pieces of a sentence. Example I like Pizza; but I was told it is greasy. ...
... • A Semi- Colon is different from a Colon. The Semi- colon has a different meaning a Semi- Colon will separate two different pieces of a sentence. Example I like Pizza; but I was told it is greasy. ...