Parts of Speech
... Verb: expresses action, occurrence, or state of being (Hint: If you’re unsure if a word in a sentence is a verb, try replacing it for a different tense of the word. If the sentence still makes sense, the word is a verb.) ...
... Verb: expresses action, occurrence, or state of being (Hint: If you’re unsure if a word in a sentence is a verb, try replacing it for a different tense of the word. If the sentence still makes sense, the word is a verb.) ...
Linking Verbs Linking verbs link the subject with another word in the
... Have students memorize the following linking verbs: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been Teach students that a few other verbs can be linking verbs also: seems, appears, looks, feels, becomes, tastes Teach that linking verbs link two parts of a sentence Teach that a predicate noun is a noun that ...
... Have students memorize the following linking verbs: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been Teach students that a few other verbs can be linking verbs also: seems, appears, looks, feels, becomes, tastes Teach that linking verbs link two parts of a sentence Teach that a predicate noun is a noun that ...
Part I: Give the nominative singular and genitive singular form of the
... 1. A participle has characteristics of what two parts of speech? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. TRUE or FALSE: A participle formed from a transitive verb can have a direct object. 3. The present active participle of "walk" may be translated as any o ...
... 1. A participle has characteristics of what two parts of speech? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. TRUE or FALSE: A participle formed from a transitive verb can have a direct object. 3. The present active participle of "walk" may be translated as any o ...
Welcome to... A Game of X`s and O`s
... This kind of word or phrase provides additional information or identifies a noun or pronoun. ...
... This kind of word or phrase provides additional information or identifies a noun or pronoun. ...
The verbs “lay” and “lie” are both known as irregular verbs. An
... The confusion forms because the word “lay” is the past tense form of lie. However, the two words are completely different. So how can you tell the difference between the two? “Lay” is a transitive verb while “Lie” is an intransitive verb. What are transitive verbs and intransitive verbs? A transitiv ...
... The confusion forms because the word “lay” is the past tense form of lie. However, the two words are completely different. So how can you tell the difference between the two? “Lay” is a transitive verb while “Lie” is an intransitive verb. What are transitive verbs and intransitive verbs? A transitiv ...
Study Guide Big test 4
... be able to pick adjectives out of a sentence. Adjectives describe/modify nouns, and remember the three questions to ask. An adjective will either answer: Which one? What kind? How many? Example: The enormous elephant loved peanuts. Elephant is your noun, and enormous is the adjective describing that ...
... be able to pick adjectives out of a sentence. Adjectives describe/modify nouns, and remember the three questions to ask. An adjective will either answer: Which one? What kind? How many? Example: The enormous elephant loved peanuts. Elephant is your noun, and enormous is the adjective describing that ...
Past Participles as Adjectives
... Past participles are frequently used with the verb “estar” to describe the result of an action. To form most past participles of verbs in Spanish, you drop the ending of the infinitive (ar/er/ir) and add –ado to the stem for –ar verbs or –ido to the stem for er/ir verbs. As with all adjectives i ...
... Past participles are frequently used with the verb “estar” to describe the result of an action. To form most past participles of verbs in Spanish, you drop the ending of the infinitive (ar/er/ir) and add –ado to the stem for –ar verbs or –ido to the stem for er/ir verbs. As with all adjectives i ...
The past participle and the present perfect tense
... • To say that someone has or has not done something we use the present perfect. In English it looks something like this: I have finished. • Note that there are two parts to its formation which makes it a compound tense. ...
... • To say that someone has or has not done something we use the present perfect. In English it looks something like this: I have finished. • Note that there are two parts to its formation which makes it a compound tense. ...
Outline of Grammar Focus of Draft Spanish Scheme of Work for Key
... saying a day and ‘on’ a particular day prepositions ‘en’ and ‘de’ with compass points followed by place ...
... saying a day and ‘on’ a particular day prepositions ‘en’ and ‘de’ with compass points followed by place ...
Lady Bankes Infant and Nursery School
... conjunctions: It was raining but it wasn’t cold. We won’t go out if the weather’s bad. There are two kinds of conjunction: Co-ordinating conjunctions (and, but, or and so). These join (and are placed between) two clauses of equal weight. Do you want to go now or shall we wait a bit longer? And, but ...
... conjunctions: It was raining but it wasn’t cold. We won’t go out if the weather’s bad. There are two kinds of conjunction: Co-ordinating conjunctions (and, but, or and so). These join (and are placed between) two clauses of equal weight. Do you want to go now or shall we wait a bit longer? And, but ...
LATIN I MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE
... If you complete your exam with time to spare, it is expected that you will work quietly on your own and use your time productively to prepare for another exam without distracting any classmate who may require more time for the exam. ...
... If you complete your exam with time to spare, it is expected that you will work quietly on your own and use your time productively to prepare for another exam without distracting any classmate who may require more time for the exam. ...
Introduction to Grammar
... Ws/E2.2 (E2.2a) Use adjectives (a) Understand that adjectives extend the information in sentences, by providing some detail about a noun Rs/E3.1 Recognise and understand the organisational features and typical language of instructional texts (c) Know and use the term verb and understand its importan ...
... Ws/E2.2 (E2.2a) Use adjectives (a) Understand that adjectives extend the information in sentences, by providing some detail about a noun Rs/E3.1 Recognise and understand the organisational features and typical language of instructional texts (c) Know and use the term verb and understand its importan ...
File
... immediately before the auxiliary haber; Indirect Object pronouns + direct object pronouns + haber + past participle Never separate the auxiliary and the past participle; when you conjugate verbs in this tense they must always stay together! The no and object pronouns go in front! ...
... immediately before the auxiliary haber; Indirect Object pronouns + direct object pronouns + haber + past participle Never separate the auxiliary and the past participle; when you conjugate verbs in this tense they must always stay together! The no and object pronouns go in front! ...
The Structure of Sentences
... Cross-Linguistic Variation in POS Each language has its own set of distributional criteria. Not all languages have the same sets of parts of speech as English. Some may have less (eg. They may not distinguish verbs from adjectives) or they may have more! ...
... Cross-Linguistic Variation in POS Each language has its own set of distributional criteria. Not all languages have the same sets of parts of speech as English. Some may have less (eg. They may not distinguish verbs from adjectives) or they may have more! ...
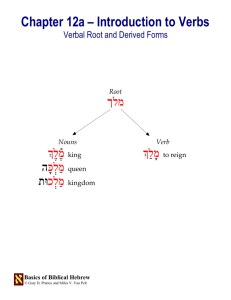
Chapter 12a – Introduction to Verbs
... Masculine referring to masculine subjects Feminine referring to feminine subjects Common referring to masculine or feminine subjects ...
... Masculine referring to masculine subjects Feminine referring to feminine subjects Common referring to masculine or feminine subjects ...
(2006) Ossetic
... marks the compared object with comparatives or the language in which something is written, said, etc. (Iron-au ‘in Iron’), the comitative the partner involved in an action. Plurals are formed by adding -t- to the stem plus the same case markers as in the singular. Sometimes, infixes are added after ...
... marks the compared object with comparatives or the language in which something is written, said, etc. (Iron-au ‘in Iron’), the comitative the partner involved in an action. Plurals are formed by adding -t- to the stem plus the same case markers as in the singular. Sometimes, infixes are added after ...
Week 7 Style Exercises
... 19. Carlos is the only one of those students who has/have lived up to the potential described in the yearbook. 20. The International Club, as well as the Choral Society and the Rowing Club, need/needs to submit a new constitution. 21. One of my best friends is/are an extra on Seinfeld this week. 22. ...
... 19. Carlos is the only one of those students who has/have lived up to the potential described in the yearbook. 20. The International Club, as well as the Choral Society and the Rowing Club, need/needs to submit a new constitution. 21. One of my best friends is/are an extra on Seinfeld this week. 22. ...
Document
... •Some indefinite pronouns are always singular. Here are some examples: anybody, anyone, everyone, someone, no one, nobody, each, neither, either. •Others can be either singular or plural (all, some) • Everybody loves grammar! • Some people love grammar. ...
... •Some indefinite pronouns are always singular. Here are some examples: anybody, anyone, everyone, someone, no one, nobody, each, neither, either. •Others can be either singular or plural (all, some) • Everybody loves grammar! • Some people love grammar. ...