Greekfor the Rest of Us
... Number. Greek indicates singular or plural with different case endings. Agreement. When a word like an adjective or article modifies another word, it will agree with that word in case, number and gender. Uninflected. Some words in Greek do not inflect, such as personal names and word borrowed from o ...
... Number. Greek indicates singular or plural with different case endings. Agreement. When a word like an adjective or article modifies another word, it will agree with that word in case, number and gender. Uninflected. Some words in Greek do not inflect, such as personal names and word borrowed from o ...
Structure Class Words
... A particular problem for many students is the fact that some determiners have the same forms as some pronouns (see below). Consider the following sentences: 1. Have you seen these new shoe styles? Have you seen these? 2. This house will be yours someday. This will all be yours someday. 3. Some peopl ...
... A particular problem for many students is the fact that some determiners have the same forms as some pronouns (see below). Consider the following sentences: 1. Have you seen these new shoe styles? Have you seen these? 2. This house will be yours someday. This will all be yours someday. 3. Some peopl ...
GRAMMATICAL TERMS
... A noun that refers to an idea or quality that cannot be identified by one of the senses. Examples: shame; delight; tolerance. See also concrete noun. See verb A word that modifies (limits or describes) a noun or pronoun. “The concert was long, but it was exciting.” (The adjective long modifies the n ...
... A noun that refers to an idea or quality that cannot be identified by one of the senses. Examples: shame; delight; tolerance. See also concrete noun. See verb A word that modifies (limits or describes) a noun or pronoun. “The concert was long, but it was exciting.” (The adjective long modifies the n ...
Name: Period: ______ Grammar Unit 3: Verbs Study Guide A verb is
... The word that a linking verb connects its subject to is called a subject complement. The subject complement identifies or describes the subject. Some common linking verbs are is, feel, seem, and look. A subject complement can be a predicate noun or a predicate adjective. A predicate noun is a noun t ...
... The word that a linking verb connects its subject to is called a subject complement. The subject complement identifies or describes the subject. Some common linking verbs are is, feel, seem, and look. A subject complement can be a predicate noun or a predicate adjective. A predicate noun is a noun t ...
Module 7 grammaire-Indirect object pronouns, y and en Y and en
... Ex: Sandrine lance le ballon. What does she throw? The ball. 2. An indirect object pronoun indicates to whom or for whom the action is done. Ex: Sandrine lance le ballon à Paul. Who does she throw it to? Paul. 3. If the person or thing is preceded by the preposition à or pour, that person/thing is a ...
... Ex: Sandrine lance le ballon. What does she throw? The ball. 2. An indirect object pronoun indicates to whom or for whom the action is done. Ex: Sandrine lance le ballon à Paul. Who does she throw it to? Paul. 3. If the person or thing is preceded by the preposition à or pour, that person/thing is a ...
Present Perfect Subjunctive
... • Present perfect subjunctive is formed by using the present subjunctive of haber + the past participle. ...
... • Present perfect subjunctive is formed by using the present subjunctive of haber + the past participle. ...
Noun plurals
... name, we use names in an editorial fashion only, and to the benefit of the trademark owner, with no intention of infringement of the trademark. Where such designations appear in this book, they have been printed with initial caps. McGraw-Hill eBooks are available at special quantity discounts to use ...
... name, we use names in an editorial fashion only, and to the benefit of the trademark owner, with no intention of infringement of the trademark. Where such designations appear in this book, they have been printed with initial caps. McGraw-Hill eBooks are available at special quantity discounts to use ...
PRONOUNS
... (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). There are three cases: nominative, objective, and possessive. The way a pronoun is used in a sentence determines its case. Subject and predicate pronouns use the nominative case. Object pronouns use the objective case. Possessive pronouns use ...
... (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). There are three cases: nominative, objective, and possessive. The way a pronoun is used in a sentence determines its case. Subject and predicate pronouns use the nominative case. Object pronouns use the objective case. Possessive pronouns use ...
MULTI-WORD VERBS
... verbs forming phrasal verbs are put, take, look, get, bring, go, come, wake, give … The most common adverbs are down, up, in on, out, off, back, forth, over, etc… (This is only an opinion based on frequency of appearance; there is no obvious limit to these verbs or particles, no rules at all). Also, ...
... verbs forming phrasal verbs are put, take, look, get, bring, go, come, wake, give … The most common adverbs are down, up, in on, out, off, back, forth, over, etc… (This is only an opinion based on frequency of appearance; there is no obvious limit to these verbs or particles, no rules at all). Also, ...
Parts of a sentence check 1. Find the subject 2. Find the verb Ask
... Identify the italicized words. Beasley destroyed the book on the counter. 1. The subject? Beasley 2. The verb? Destroyed – transitive or linking? Transitive 3. Destroyed what? The book The sequence stops there, so book is the direct object. Beasley brought me the bone. 1. The subject? Beasley 2. The ...
... Identify the italicized words. Beasley destroyed the book on the counter. 1. The subject? Beasley 2. The verb? Destroyed – transitive or linking? Transitive 3. Destroyed what? The book The sequence stops there, so book is the direct object. Beasley brought me the bone. 1. The subject? Beasley 2. The ...
ecbatic 50 ecbatic. adj. Denoting result. The term is used in
... *dative, *locative, *instrumental, *accusative and *vocative). The determination of the number of cases is based on their function; thus some of the cases are identical in form: ablative and genitive; likewise the dative, locative and instrumental. See also five-case system. Einleitung. Germ. “intro ...
... *dative, *locative, *instrumental, *accusative and *vocative). The determination of the number of cases is based on their function; thus some of the cases are identical in form: ablative and genitive; likewise the dative, locative and instrumental. See also five-case system. Einleitung. Germ. “intro ...
The Verb Train: Teaching Ancient Greek Verbs at Secondary
... The sounds used in the program are limited so that the learner is not distracted, especially in the computer lab. Yet the complete absence of music and sounds would be dissatisfying and would impede the comprehension of the message. There are analogue sounds that are a direct reference to the real w ...
... The sounds used in the program are limited so that the learner is not distracted, especially in the computer lab. Yet the complete absence of music and sounds would be dissatisfying and would impede the comprehension of the message. There are analogue sounds that are a direct reference to the real w ...
1 Verbs: the bare infinitive (=without to), the to
... I have often heard that dog bark (series of completed acts) I heard it barking all night (activity in progress) 2) Activity in progress or a new act? I like dancing (activity in progress) Would you like to dance? (begin a new act) This distinction between a new act (infinitive) and an activity havin ...
... I have often heard that dog bark (series of completed acts) I heard it barking all night (activity in progress) 2) Activity in progress or a new act? I like dancing (activity in progress) Would you like to dance? (begin a new act) This distinction between a new act (infinitive) and an activity havin ...
Predicate Nouns and Adjectives
... So far… • So far we have talked about Objects that come after action verbs. • We are now learning what comes after linking verbs. ...
... So far… • So far we have talked about Objects that come after action verbs. • We are now learning what comes after linking verbs. ...
Patrick - Cloudfront.net
... So far… • So far we have talked about Objects that come after action verbs. • We are now learning what comes after linking verbs. ...
... So far… • So far we have talked about Objects that come after action verbs. • We are now learning what comes after linking verbs. ...
Verb Tenses: The Future Perfect Continuous
... Verb Tenses: The Future Perfect Continuous Created by Kathryn Reilly ...
... Verb Tenses: The Future Perfect Continuous Created by Kathryn Reilly ...
Presentation Exercise: Chapter 30
... Fill in the Blank. The formula for indirect questions in Latin is a verb of the _______________, plus a/n __________________ word, plus a verb in the ___________________________ mood. Fill in the Blank. Any ________________________________ word can serve as the conjunction ...
... Fill in the Blank. The formula for indirect questions in Latin is a verb of the _______________, plus a/n __________________ word, plus a verb in the ___________________________ mood. Fill in the Blank. Any ________________________________ word can serve as the conjunction ...
Sentence Structure - RISD Writing Center
... A compound-complex sentence is made up of two or more main clauses and one or more subordinate clauses. Accurate cues to meaning become even more important in such complicated sentences, so be careful to follow the word order and conventions of both compound and complex sentences at once. My paintin ...
... A compound-complex sentence is made up of two or more main clauses and one or more subordinate clauses. Accurate cues to meaning become even more important in such complicated sentences, so be careful to follow the word order and conventions of both compound and complex sentences at once. My paintin ...
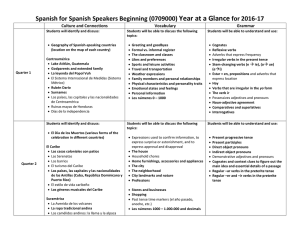
Spanish for Spanish Speakers Beginning (0709000) Year at a
... Reflexive verbs Adverbs that express frequency Irregular verbs in the present tense Stem-changing verbs (e ie), (o ue) (ei) Estar + en, prepositions and adverbs that express location Hay Verbs that are irregular in the yo form The verb ir Possessives adjectives and pronouns Noun-adjective agreem ...
... Reflexive verbs Adverbs that express frequency Irregular verbs in the present tense Stem-changing verbs (e ie), (o ue) (ei) Estar + en, prepositions and adverbs that express location Hay Verbs that are irregular in the yo form The verb ir Possessives adjectives and pronouns Noun-adjective agreem ...
Participles
... been praised) (participle stem + us,a,um) laudaturus (about to praise, laudandus, a, um (to be Going to praise) praised, fit to be praised) (participle stem + urus,a,um) Pres. stem + ndus,nda,ndum ...
... been praised) (participle stem + us,a,um) laudaturus (about to praise, laudandus, a, um (to be Going to praise) praised, fit to be praised) (participle stem + urus,a,um) Pres. stem + ndus,nda,ndum ...
1. Constituency and Constructions Construction
... Construction that typically has a noun or a pronoun as its head – (the central constituent that the phrase is built around) – any other constituents are modifiers – (they tell us something about it – modify) Certain nouns can occur by themselves (e.g. without any determiners) – proper nouns, plural ...
... Construction that typically has a noun or a pronoun as its head – (the central constituent that the phrase is built around) – any other constituents are modifiers – (they tell us something about it – modify) Certain nouns can occur by themselves (e.g. without any determiners) – proper nouns, plural ...
Review: Parts of the Sentence
... Sometimes, however, the noun will be the object, as in the following example: I consider the driver tired. In this case, the noun "driver" is the direct object of the verb "consider," but the adjective "tired" is still acting as its complement. In general, verbs which have to do with perceiving, jud ...
... Sometimes, however, the noun will be the object, as in the following example: I consider the driver tired. In this case, the noun "driver" is the direct object of the verb "consider," but the adjective "tired" is still acting as its complement. In general, verbs which have to do with perceiving, jud ...
Adjectives, Articles and Adverbs
... and these are called predicate adjectives: The roses in my garden are beautiful. The roses in my garden smell beautiful. ...
... and these are called predicate adjectives: The roses in my garden are beautiful. The roses in my garden smell beautiful. ...
Magic Writing Page
... 8. Pronoun/antecedent agreement: A singular pronoun must replace a singular noun; a plural pronoun must replace a plural noun. A phrase or clause between the subject and verb does not change the number of the antecedent. Example: The can of pinto beans sits on its shelf. 9. These pronouns are singul ...
... 8. Pronoun/antecedent agreement: A singular pronoun must replace a singular noun; a plural pronoun must replace a plural noun. A phrase or clause between the subject and verb does not change the number of the antecedent. Example: The can of pinto beans sits on its shelf. 9. These pronouns are singul ...
Towards a Consistent Morphological Tagset for Slavic Languages
... Another norm existed during the rule of the Bulgarian Agrarian Popular Union (1921–23), when the choice of the full or short form of the article was based on euphonic rather than syntactic grounds (it depended on whether the following word began with a vowel or a consonant). In Serbo-Croat and Slove ...
... Another norm existed during the rule of the Bulgarian Agrarian Popular Union (1921–23), when the choice of the full or short form of the article was based on euphonic rather than syntactic grounds (it depended on whether the following word began with a vowel or a consonant). In Serbo-Croat and Slove ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.