CASE - PBworks
... Nominative—used for the subject or words describing the subject Genitive-used for possession and with some adjectives, verbs and prepositions Dative-used for the indirect object (to or for someone or something) and with some verbs Accusative-used mainly for the direct object and with some prepositio ...
... Nominative—used for the subject or words describing the subject Genitive-used for possession and with some adjectives, verbs and prepositions Dative-used for the indirect object (to or for someone or something) and with some verbs Accusative-used mainly for the direct object and with some prepositio ...
File
... Answer this… The subject did something to whom? (direct object) To whom or for whom was the action done if anyone? (indirect object) Prosecutors charge people with crimes. The knife’s sharp edge cut the chef. Law enforcement had previously convicted the man. (identify the action and the di ...
... Answer this… The subject did something to whom? (direct object) To whom or for whom was the action done if anyone? (indirect object) Prosecutors charge people with crimes. The knife’s sharp edge cut the chef. Law enforcement had previously convicted the man. (identify the action and the di ...
LESSON IV - Igbo Catholic Community
... If you are visiting our Language Centre for the first time, you are probably not conversant with the terms I-dot and I-dotless verbs. If that is the case, we urge you to go back and read lessons II and III before this one. Our common-sense approach to the teaching and interpretation of Igbo is so un ...
... If you are visiting our Language Centre for the first time, you are probably not conversant with the terms I-dot and I-dotless verbs. If that is the case, we urge you to go back and read lessons II and III before this one. Our common-sense approach to the teaching and interpretation of Igbo is so un ...
passive i - English6th2009
... Ron decorates the street every year. = Active. (I know that Ron decorates the street every ...
... Ron decorates the street every year. = Active. (I know that Ron decorates the street every ...
WEAK NOUN PHRASES: SEMANTICS AND SYNTAX
... the Spanish bare plurals as properties with Zimmermann’s analysis of the objects of opaque verbs as properties. In the bare plural analysis, it is the NPs that are specified as being of property type; they combine with ordinary verbs that take ordinary e-type arguments, and the verbs shift to accomm ...
... the Spanish bare plurals as properties with Zimmermann’s analysis of the objects of opaque verbs as properties. In the bare plural analysis, it is the NPs that are specified as being of property type; they combine with ordinary verbs that take ordinary e-type arguments, and the verbs shift to accomm ...
Steven Pinker`s lecture
... string–strung, swing–swung, sting–stung, and fling–flung. This is not what we would expect if the irregular verbs were memorized individually by rote, in which case they could just as easily all be idiosyncratic. Moreover, these aren’t just redundancies in memory; they are occasionally generalized. ...
... string–strung, swing–swung, sting–stung, and fling–flung. This is not what we would expect if the irregular verbs were memorized individually by rote, in which case they could just as easily all be idiosyncratic. Moreover, these aren’t just redundancies in memory; they are occasionally generalized. ...
present perfect
... refer to a situation which started in the past at an unknown or unstated time - and which has some connection with the present: The social networking website Facebook _______________ enormously popular throughout the world. ...
... refer to a situation which started in the past at an unknown or unstated time - and which has some connection with the present: The social networking website Facebook _______________ enormously popular throughout the world. ...
Active voice cheat sheet, 4 Syllables
... To de-emphasise an unknown or unimportant agent ‘Over 100 contaminants have been dumped into the river.’ Passive voice is appropriate because we don’t know who has done this. When the agent is obvious or your readers really don’t need to know who it is ‘The press release was sent at 6pm yesterday.’ ...
... To de-emphasise an unknown or unimportant agent ‘Over 100 contaminants have been dumped into the river.’ Passive voice is appropriate because we don’t know who has done this. When the agent is obvious or your readers really don’t need to know who it is ‘The press release was sent at 6pm yesterday.’ ...
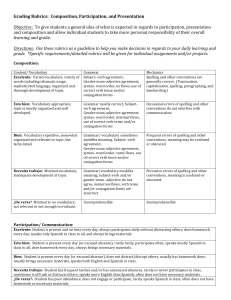
General Grading Rubrics
... Necesita trabajo: Student has frequent tardies and/or has unexcused absences, rarely or never participates in class, sometimes is off task or distracts others, speaks more English than Spanish, often does ...
... Necesita trabajo: Student has frequent tardies and/or has unexcused absences, rarely or never participates in class, sometimes is off task or distracts others, speaks more English than Spanish, often does ...
Ingmar Söhrman* The Position of Clitics in Phrases with an Infinite
... Portuguese does at a first glance resemble Romansh since the regular word-order is SVC (8a and 8b). The difference is that in Portuguese the pronouns are clitics and they are clearly enclitically linked to the finite verb (8a and 8b), even prosodically and not just orthographically with a hyphen. Th ...
... Portuguese does at a first glance resemble Romansh since the regular word-order is SVC (8a and 8b). The difference is that in Portuguese the pronouns are clitics and they are clearly enclitically linked to the finite verb (8a and 8b), even prosodically and not just orthographically with a hyphen. Th ...
THE COMPOUND VERB IN MARATHI: DEFINITIONAL ISSUES AND
... sentences at par with those containing of V1 alone. As a matter of fact CV semantically differ from serial or conjunct verbs on the one hand and from corresponding simple verbs on the other. This distinction is legitimate and should be made (Cf. Section 3 for more details). From the foregoing overvi ...
... sentences at par with those containing of V1 alone. As a matter of fact CV semantically differ from serial or conjunct verbs on the one hand and from corresponding simple verbs on the other. This distinction is legitimate and should be made (Cf. Section 3 for more details). From the foregoing overvi ...
Reflexive and Reciprocal Actions The reflexive verb construction
... When you conjugate a reflexive you assign the verb to each person (1st, 2nd , 3rd, singular or plural) by making a change to the ending and/or stem. Then, you assign the appropriate reflexive pronoun in front of the verb. The finished conjugation results in two words. ...
... When you conjugate a reflexive you assign the verb to each person (1st, 2nd , 3rd, singular or plural) by making a change to the ending and/or stem. Then, you assign the appropriate reflexive pronoun in front of the verb. The finished conjugation results in two words. ...
EL INFINITIVO Y LA FORMA EN –ING: SUS USOS 1.
... identical in form with the present indicative, the present subjunctive and the imperative. When the infinitive function as a noun, it may be subject, object or predicative. For example: Subject: To err is human, to forgive divine. Object. Men fear death as children fear to go in the dark. Predicativ ...
... identical in form with the present indicative, the present subjunctive and the imperative. When the infinitive function as a noun, it may be subject, object or predicative. For example: Subject: To err is human, to forgive divine. Object. Men fear death as children fear to go in the dark. Predicativ ...
Kinande Anaphora Sketch
... There are some patterns of particular theoretical interest that distinguish the Kinande anaphora system from patterns found in other Bantu languages, but these only emerge in careful study of the details of particular morphemes and the constructions they enter into, since Kinande shares many feature ...
... There are some patterns of particular theoretical interest that distinguish the Kinande anaphora system from patterns found in other Bantu languages, but these only emerge in careful study of the details of particular morphemes and the constructions they enter into, since Kinande shares many feature ...
Present Continuous Tense
... happening these days, but not necessarily right now She is studying at MiraCosta College. ...
... happening these days, but not necessarily right now She is studying at MiraCosta College. ...
Present Continuous Tense
... happening these days, but not necessarily right now She is studying at MiraCosta College. ...
... happening these days, but not necessarily right now She is studying at MiraCosta College. ...
Subject pronoun
... Adjective has three degree: ................................................................................ 32 What is syllable: .......................................................................... 32 Tense ...................................................................................... ...
... Adjective has three degree: ................................................................................ 32 What is syllable: .......................................................................... 32 Tense ...................................................................................... ...
An International Journal of English Studies 24/2
... NB: the lowering of AF/non-CF en-, em- > an-, am- in pretonic position is attested in numerous loanwords in (Early) Middle English manuscripts, e.g. MS Cleopatra of the Ancrene Riwle (c1225-30) – see E. J. Dobson, ed., 1972, XC – XCIII & footnotes. Under main stress Anglo-French/non-Central French d ...
... NB: the lowering of AF/non-CF en-, em- > an-, am- in pretonic position is attested in numerous loanwords in (Early) Middle English manuscripts, e.g. MS Cleopatra of the Ancrene Riwle (c1225-30) – see E. J. Dobson, ed., 1972, XC – XCIII & footnotes. Under main stress Anglo-French/non-Central French d ...
Chapter 1
... saber to say that you know a fact or piece of information. Use saber followed by an infinitive to say you know how to do something. No sé hablar francés. I don’t know how to speak French. ¿Sabes la dirección? Do you know the address? 2. Use conocer to say whether you know or are familiar with people ...
... saber to say that you know a fact or piece of information. Use saber followed by an infinitive to say you know how to do something. No sé hablar francés. I don’t know how to speak French. ¿Sabes la dirección? Do you know the address? 2. Use conocer to say whether you know or are familiar with people ...
Action Verb
... A verb is a word used to express an action, a condition, or a state of being. The two main kinds of verbs are action verbs and linking verbs. Both kinds can be appear with helping verbs An action verb tells what the subject does. The action may be physical or mental. She rides motorcycles. (physical ...
... A verb is a word used to express an action, a condition, or a state of being. The two main kinds of verbs are action verbs and linking verbs. Both kinds can be appear with helping verbs An action verb tells what the subject does. The action may be physical or mental. She rides motorcycles. (physical ...
complete subject
... Paul was disappointed with his strikeout. The crowd grew restless because of the long delay. Before the concert, the singer appeared very nervous. Audrey sounded quite cheerful on the phone. ...
... Paul was disappointed with his strikeout. The crowd grew restless because of the long delay. Before the concert, the singer appeared very nervous. Audrey sounded quite cheerful on the phone. ...
Somali Verb Conjugation Paradigms: Present, Past, and Future
... person feminine subject is changed to <-s> in the past tense of.
Another important change worthy of attention is the one that takes place between the root
and the past tense suffix when C1VC2C3V verbs are involved. In both and qabso>, C3
corresponds to /s/. The addition of the past ...
... person feminine subject is changed to <-s> in the past tense of
About Imperfectivity Phenomena
... arrival. The hypothesis that imperfective appears because progressive requires a past tense which agrees with its aspectual nature is plausible. But the compatibility of progressive with the Simple Past tense, though restricted as (4 c) shows, suggests there is more. In (4 d) the progressive Past Te ...
... arrival. The hypothesis that imperfective appears because progressive requires a past tense which agrees with its aspectual nature is plausible. But the compatibility of progressive with the Simple Past tense, though restricted as (4 c) shows, suggests there is more. In (4 d) the progressive Past Te ...