Document
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
... • A neuron which carries signals from tissue to brain is a sensory neuron or afferent neuron. • A neuron which carries signals from the brain to tissue is a motor neuron or efferent neuron. ...
The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... impulse caused by a change in the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron fires, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
... impulse caused by a change in the electrical charge across the cell membrane of the axon. When the neuron fires, this charge travels down the axon and causes neurotransmitters to be released by the terminal buttons. Sets off a chain reaction like a set of falling dominos. ...
Document
... __A__6. Neurons with myelin sheath conduct nerve impulses a. faster than neurons without myelin sheaths. b. slower than neurons without myelin sheaths. c. at the same speed as neurons without myelin sheaths. d. in greater numbers than neurons without myelin sheaths. __D__7. Gray matter is best descr ...
... __A__6. Neurons with myelin sheath conduct nerve impulses a. faster than neurons without myelin sheaths. b. slower than neurons without myelin sheaths. c. at the same speed as neurons without myelin sheaths. d. in greater numbers than neurons without myelin sheaths. __D__7. Gray matter is best descr ...
biopsychology-2-synaptic-transmission
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
... • Occurs because myelin insulates the current and does not allow it to leak out ...
Name
... 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve cell which conducts an impulse 8. nerve type which conducts an impulse to the CNS 9. ...
... 3. whitish, fatty covering which protects and insulates nerve fibers 4. short, branched afferent process of a neuron 5. bundles of neuron processes in the CNS 6. long, slender, efferent process of a neuron 7. nerve cell which conducts an impulse 8. nerve type which conducts an impulse to the CNS 9. ...
Answers to Questions — neurons
... cramps, confusion, coma. It is known to happen to marathon runners when they have not be replenishing sodium levels inside their bodies. This is why drinks with salts such as Gatorade are popular and beneficial for athletes. 4. Dendrite comes from the Greek word dendron, which means "tree." Explain ...
... cramps, confusion, coma. It is known to happen to marathon runners when they have not be replenishing sodium levels inside their bodies. This is why drinks with salts such as Gatorade are popular and beneficial for athletes. 4. Dendrite comes from the Greek word dendron, which means "tree." Explain ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and K return to their original state and the resting membrane potentil is restored Absolute refractory period: when the Na gates are open and the neuron is totally insensitive to additional stimuli Relative refractory period: if a very strong stimuli is able t ...
... Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and K return to their original state and the resting membrane potentil is restored Absolute refractory period: when the Na gates are open and the neuron is totally insensitive to additional stimuli Relative refractory period: if a very strong stimuli is able t ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... (stimuli) from the external and internal environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... (stimuli) from the external and internal environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
File
... Think back to the PET scans viewed in activity 2 of lesson 1. Different areas showed up as red or yellow in response to a stimulus. What composes those regions of the brain? (Why did those areas show up as red or yellow?) ...
... Think back to the PET scans viewed in activity 2 of lesson 1. Different areas showed up as red or yellow in response to a stimulus. What composes those regions of the brain? (Why did those areas show up as red or yellow?) ...
File
... Refractory Period & Pumps Refractory Period: After a neuron fires an action potential it pauses for a short period to recharge itself to fire again. ...
... Refractory Period & Pumps Refractory Period: After a neuron fires an action potential it pauses for a short period to recharge itself to fire again. ...
Mind Is Matter
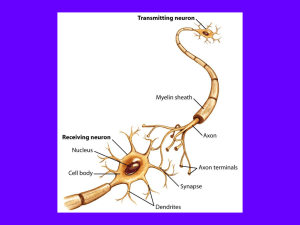
... 2. Draw a diagram of a neuron and label each structure below. Describe the function of each structure. Cell body Dendrites Axon Myelin sheath Terminal endings Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with ...
... 2. Draw a diagram of a neuron and label each structure below. Describe the function of each structure. Cell body Dendrites Axon Myelin sheath Terminal endings Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with ...
Neural Pathways
... • routes traveled by nerve impulses are called neural pathways • one type of neural pathway is a reflex arc • the simplest and quickest • consists only of 2 neurons • bypasses the brain ...
... • routes traveled by nerve impulses are called neural pathways • one type of neural pathway is a reflex arc • the simplest and quickest • consists only of 2 neurons • bypasses the brain ...
Topology - UCSB Physics
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
... The topology of the central nervous system has been, and remains today a topic of considerable study. It is known that for humans, the central nervous system starts in the embryo as a plate, eventually deforming into a tube, one end of which thickens to become the brain (the remainder being the spin ...
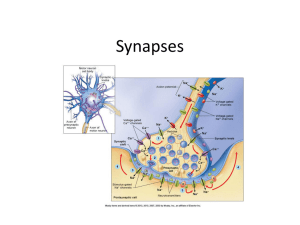
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... won’t start AP in next neuron—may need several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... won’t start AP in next neuron—may need several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
... Ferries are boats that carry cars and people across a river. If the river represents the synapse… 1. What could the ferry represent? 2. What could the cars / people represent? 3. What could the road leading the ferry represent? ...
Brain Development
... Brain Development • Neurogenesis: Proliferation of neurons through cell division ...
... Brain Development • Neurogenesis: Proliferation of neurons through cell division ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Processes the information and sends signals to various parts of the body ...
... Processes the information and sends signals to various parts of the body ...
Neuron Summary - MsHughesPsychology
... incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to other neurons 3. Axon – a single tube like extension that transmits messages (neural impulses) from the soma to ot ...
... incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to other neurons 3. Axon – a single tube like extension that transmits messages (neural impulses) from the soma to ot ...
Brain and Behaviour
... Myelin Sheath – insulates to help speed Axon – passes information to other neurons Dendrites – receive information from other neurons For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing ...
... Myelin Sheath – insulates to help speed Axon – passes information to other neurons Dendrites – receive information from other neurons For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing ...