10-21-09
... multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC. This experiment will be compared to monkeys damaged in the lOFC from previous experiments. The experiments involved selecting from three stimuli on a screen, e ...
... multiple options. mOFC damage influences how much the third option influences the choice in options. Four monkeys were lesioned in the mOFC. This experiment will be compared to monkeys damaged in the lOFC from previous experiments. The experiments involved selecting from three stimuli on a screen, e ...
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems - Biology at Mott
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an emot ...
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an emot ...
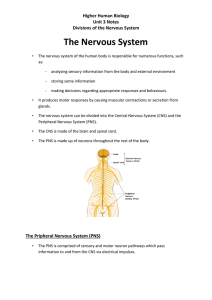
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... The ANS is made up of two parts, the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems. ...
... The ANS is made up of two parts, the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems. ...
File
... Like all vertebrate brains, the human brain develops from three sections known as the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Each of these contains fluid-filled cavities called ventricles. The forebrain develops into the cerebrum and underlying structures; the midbrain becomes part of the brainstem; an ...
... Like all vertebrate brains, the human brain develops from three sections known as the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Each of these contains fluid-filled cavities called ventricles. The forebrain develops into the cerebrum and underlying structures; the midbrain becomes part of the brainstem; an ...
Synaptic inhibition is caused by:
... a. synaptic cleft (gap) b. post-synaptic receptors c. synaptic vesicles d. endoplasmic reticulum of the neuron's soma e. dendritic endings ...
... a. synaptic cleft (gap) b. post-synaptic receptors c. synaptic vesicles d. endoplasmic reticulum of the neuron's soma e. dendritic endings ...
Document
... and PNS work together to allow you to raise your hand? Your CNS passes a signal to a motor neuron in your PNS causing you to raise your hand. ...
... and PNS work together to allow you to raise your hand? Your CNS passes a signal to a motor neuron in your PNS causing you to raise your hand. ...
Chapter 7 part two
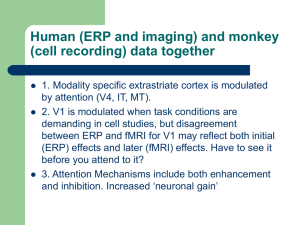
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
R24Summary Statement - University of Illinois Archives
... requisite expertise. Although the phase I proposal itself does not present particularly novel ideas, there are compelling scientific reasons to encourage a "dendrite biology consortium" at this time. Dendrites are the major sites of input to individual neurons. The background material presented lays ...
... requisite expertise. Although the phase I proposal itself does not present particularly novel ideas, there are compelling scientific reasons to encourage a "dendrite biology consortium" at this time. Dendrites are the major sites of input to individual neurons. The background material presented lays ...
Nervous System - Mrs. Riggs Online
... action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by fast-acting, voltagesensing ion gates that quickly open and close, allowing Na and K ions to briefly flow into and out of cell; after action potential p ...
... action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by fast-acting, voltagesensing ion gates that quickly open and close, allowing Na and K ions to briefly flow into and out of cell; after action potential p ...
Central nervous system
... the progressive increase in the excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) in postsynaptic neuron when: * many presynaptic excitatory terminals are stimulated simultaneously * or when single presynaptic terminal is stimulated repeatedly. 5-electricale property: The electrical properties of the synaps ...
... the progressive increase in the excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) in postsynaptic neuron when: * many presynaptic excitatory terminals are stimulated simultaneously * or when single presynaptic terminal is stimulated repeatedly. 5-electricale property: The electrical properties of the synaps ...
Neural Networks – State of Art, Brief History, Basic Models and
... In 1980s several events caused a renewed interest. Kohonen has made many contributions to the field of artificial neural networks. He introduced the artificial neural network sometimes called a Kohonen map or network [10]. Hopfield of Caltech in 1982 presented a paper Neural Networks and Physical System ...
... In 1980s several events caused a renewed interest. Kohonen has made many contributions to the field of artificial neural networks. He introduced the artificial neural network sometimes called a Kohonen map or network [10]. Hopfield of Caltech in 1982 presented a paper Neural Networks and Physical System ...
Sensory play research project
... To gain an overall perspective of the challenges of the EYFS and the NC To reflect and form your own values and perspectives ...
... To gain an overall perspective of the challenges of the EYFS and the NC To reflect and form your own values and perspectives ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous
... 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potential and possibly an AP if threshold is reached Postsynaptic potentials – can be Excitatory or Inhibitory: a. Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) = Membrane potential moves ___________ ...
... 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potential and possibly an AP if threshold is reached Postsynaptic potentials – can be Excitatory or Inhibitory: a. Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) = Membrane potential moves ___________ ...
Developmental biology 2008 Fates of the ectoderm: The neural tube
... Primary and secondary neurulation Primary neurulation, the folding and closure of the neural tube as described above, creates the brain and most of the spinal cord. In mammals, neurulation caudal to the future upper sacral level occurs by secondary neurulation. In the tail bud, a stem-cell populati ...
... Primary and secondary neurulation Primary neurulation, the folding and closure of the neural tube as described above, creates the brain and most of the spinal cord. In mammals, neurulation caudal to the future upper sacral level occurs by secondary neurulation. In the tail bud, a stem-cell populati ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... The cerebellum provides the precise timing for coordinating skeletal muscle activity and controls balance and equilibrium. It also stores memories of previous movements. c. brain stem: about the size of a thumb in diameter and approximately three inches long. It is the most inferior brain structure. ...
... The cerebellum provides the precise timing for coordinating skeletal muscle activity and controls balance and equilibrium. It also stores memories of previous movements. c. brain stem: about the size of a thumb in diameter and approximately three inches long. It is the most inferior brain structure. ...
Physiology - Soran University
... There are different types of neurons. They all carry electro-chemical nerve signals, but differ in structure (the number of processes, or axons, emanating from the cell body) and are found in different parts of the body. Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense recepto ...
... There are different types of neurons. They all carry electro-chemical nerve signals, but differ in structure (the number of processes, or axons, emanating from the cell body) and are found in different parts of the body. Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense recepto ...
Developmental_Part2 - Pemberton Counseling has changed
... deferred imitation—perception of something someone else does (modeling), then performing action at a later time ...
... deferred imitation—perception of something someone else does (modeling), then performing action at a later time ...
CHAPTER 4: Physical, Motor, and Sensory Development
... Gray matter consists of nerve cell bodies, which are grayish in color. Kinesthetic perception is the sensation of position, movement, and tension in parts of the body perceived through the nerves in the muscles, tendons, and joints. Limbic system consists of the structures of the brain involved in e ...
... Gray matter consists of nerve cell bodies, which are grayish in color. Kinesthetic perception is the sensation of position, movement, and tension in parts of the body perceived through the nerves in the muscles, tendons, and joints. Limbic system consists of the structures of the brain involved in e ...
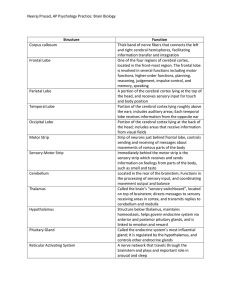
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top o ...
... One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top o ...
Artificial Neural Network Architectures and Training
... Opposite to offline learning, in online learning, the adjustments on the weights and thresholds of the network are performed after presenting each training sample. Thus, after executing the adjustment step, the respective sample can be discarded. Online learning with this configuration is usually use ...
... Opposite to offline learning, in online learning, the adjustments on the weights and thresholds of the network are performed after presenting each training sample. Thus, after executing the adjustment step, the respective sample can be discarded. Online learning with this configuration is usually use ...
L23-Neurotransmitter
... hypothalamus also found in gastric mucosa and in mast cells. • Formed by decarboxylation of amino acid histidine with the help of enzyme histaminase. • Three known types of histamine receptors in found e.g. H1, H2, H3. • H3 receptors are presynaptic. Its function in brain is not very certain. Its ma ...
... hypothalamus also found in gastric mucosa and in mast cells. • Formed by decarboxylation of amino acid histidine with the help of enzyme histaminase. • Three known types of histamine receptors in found e.g. H1, H2, H3. • H3 receptors are presynaptic. Its function in brain is not very certain. Its ma ...
Motor System & Behavior
... • All observable behavior is directly related to activity in the motor system. • Without the motor system, we could experience sensation, think, reason, problem solve, read, write, and do mental math, but we would not be able to communicate our thoughts and abilities to anyone. ...
... • All observable behavior is directly related to activity in the motor system. • Without the motor system, we could experience sensation, think, reason, problem solve, read, write, and do mental math, but we would not be able to communicate our thoughts and abilities to anyone. ...
File
... Consists of a tract and a nucleus. Tracts are groups or bundles of axons that travel together in the CNS and connects two masses of gray matter. Each tract may work with multiple nuclei groups in the CNS. A nucleus is a collection of neuron cell bodies located within the CNS. ...
... Consists of a tract and a nucleus. Tracts are groups or bundles of axons that travel together in the CNS and connects two masses of gray matter. Each tract may work with multiple nuclei groups in the CNS. A nucleus is a collection of neuron cell bodies located within the CNS. ...
Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... Components of electrochemical (passive) driving force for membrane movement Factors that determine the ion distribution and resting membrane potential of neurons and the relative contribution of each EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS Components of neurons and their function(s) Definitions of nerves, ...
... Components of electrochemical (passive) driving force for membrane movement Factors that determine the ion distribution and resting membrane potential of neurons and the relative contribution of each EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS Components of neurons and their function(s) Definitions of nerves, ...