Anatomy Review - Interactive Physiology
... 1. (1) Because of their unique anatomical design. (2) Because they are excitable. 2. Other neurons, muscles, and glands. 3. (1) a cell body (2) a receptive portion (3) a transmitting portion 4. many dendrites and one axon 5. A. Dendrites B. Cell body C. Axon 6. a. cell body and dendrite b. cell body ...
... 1. (1) Because of their unique anatomical design. (2) Because they are excitable. 2. Other neurons, muscles, and glands. 3. (1) a cell body (2) a receptive portion (3) a transmitting portion 4. many dendrites and one axon 5. A. Dendrites B. Cell body C. Axon 6. a. cell body and dendrite b. cell body ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... • Most can't produce action potentials (too few or no Na+ channels) • Transmit current by passive spread down dendrites to the soma • Therefore the membrane potential decreases as move along dendrite due to current loss thanks to our friends ri, rm and cm • Dendrites have no voltage gated Na+ channe ...
... • Most can't produce action potentials (too few or no Na+ channels) • Transmit current by passive spread down dendrites to the soma • Therefore the membrane potential decreases as move along dendrite due to current loss thanks to our friends ri, rm and cm • Dendrites have no voltage gated Na+ channe ...
Biological Foundations of Behavior
... Neurons: The Units of the Nervous System Neuron – individual nerve cell Parts of neurons Cell body: central part of nerve cell; contains ...
... Neurons: The Units of the Nervous System Neuron – individual nerve cell Parts of neurons Cell body: central part of nerve cell; contains ...
The Neuron - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... • A chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from a terminal button (axon) of a sending neuron, crosses a synapse, and binds to appropriate receptor sites on the dendrites or cell body of a receiving neuron, influencing the cell either to fire or not to fire; • Has an excitatory or inhibito ...
... • A chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from a terminal button (axon) of a sending neuron, crosses a synapse, and binds to appropriate receptor sites on the dendrites or cell body of a receiving neuron, influencing the cell either to fire or not to fire; • Has an excitatory or inhibito ...
Lecture 27 Powerpoint File
... fire when monkey sees a graspable object or a stimulus that could be interacted with ...
... fire when monkey sees a graspable object or a stimulus that could be interacted with ...
Nervous System
... extend through the body in the peripheral nervous system. These nerves are categorized into the following functional groups: sensory nerves, which carry sensory input to the brain or spinal cord from the environment. • motor nerves, which carry motor impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles ...
... extend through the body in the peripheral nervous system. These nerves are categorized into the following functional groups: sensory nerves, which carry sensory input to the brain or spinal cord from the environment. • motor nerves, which carry motor impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles ...
NAS 150 The Skeletal System Brilakis Fall, 2003
... muscles with environmental information. Maintains balance, posture, and all coordinated movements. (What happens when you drink alcohol…can u touch your nose?) 4. cerebrum with cerebral cortex Exhibits two hemispheres connected by an axon rich Corpus Callosum that connects the two halves. Many folds ...
... muscles with environmental information. Maintains balance, posture, and all coordinated movements. (What happens when you drink alcohol…can u touch your nose?) 4. cerebrum with cerebral cortex Exhibits two hemispheres connected by an axon rich Corpus Callosum that connects the two halves. Many folds ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
Olfactory processing: maps, time and codes Gilles Laurent
... The possible importance of time Most of our sensory experiences are dynamic. We listen to speech and music, observe insects (some of us), cars and children, and, therefore, are constantly assessing the state of our changing sensory environment. Our ability to deal with such complex situations — such ...
... The possible importance of time Most of our sensory experiences are dynamic. We listen to speech and music, observe insects (some of us), cars and children, and, therefore, are constantly assessing the state of our changing sensory environment. Our ability to deal with such complex situations — such ...
Seminar High Performance Computers
... In context of event-driven computation the previously mentioned connection machine follows a different programming paradigm model in contrast to the linear sequential programming model of von Neumann [1]. Driven by that statement the question which may emerge is: How is a program actually stored in ...
... In context of event-driven computation the previously mentioned connection machine follows a different programming paradigm model in contrast to the linear sequential programming model of von Neumann [1]. Driven by that statement the question which may emerge is: How is a program actually stored in ...
Slide ()
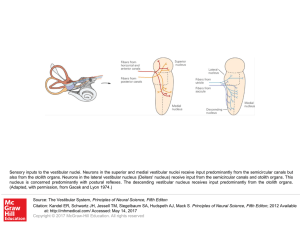
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
Neuron Function
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
The Nervous System
... anatomical structure, the axon hillock is also the part of the neuron that has the greatest density of voltage-dependent sodium channels. This makes it the most easily-excited part of the neuron and the spike initiation zone for the axon: in neurological terms it has the greatest hyperpolarized acti ...
... anatomical structure, the axon hillock is also the part of the neuron that has the greatest density of voltage-dependent sodium channels. This makes it the most easily-excited part of the neuron and the spike initiation zone for the axon: in neurological terms it has the greatest hyperpolarized acti ...
Membrane potential synchrony of simultaneously recorded striatal
... b, Cross-correlation of the waveforms within individual simultaneously recorded `up' states from a single pair of neurons. c, As a, but the `up' state in cell 1 is the `up' state subsequent to that from cell 0. d, Shuf¯ed cross-correlation of the waveforms within individual `up' states. The `up' sta ...
... b, Cross-correlation of the waveforms within individual simultaneously recorded `up' states from a single pair of neurons. c, As a, but the `up' state in cell 1 is the `up' state subsequent to that from cell 0. d, Shuf¯ed cross-correlation of the waveforms within individual `up' states. The `up' sta ...
Skeletal, Muscular, & Nervous System
... You have 206 bones in your body Axial Skeleton – the 80 bones of the skull, spine, ribs, vertebrae, and sternum or breastbone Appendicular skeleton – the remaining 126 bones of the upper and lower limbs, shoulders, and hips ...
... You have 206 bones in your body Axial Skeleton – the 80 bones of the skull, spine, ribs, vertebrae, and sternum or breastbone Appendicular skeleton – the remaining 126 bones of the upper and lower limbs, shoulders, and hips ...
Positive sparse coding of natural images: a theory for simple cell
... tuned to the orientation and polarity of edges in visual stimuli [1]. While orientation tuning has been the subject of intense investigation, the polarity tuning of cells is poorly understood; a simple cell responds either to a bright edge with dark flanks, or to the opposite polarity, a dark edge w ...
... tuned to the orientation and polarity of edges in visual stimuli [1]. While orientation tuning has been the subject of intense investigation, the polarity tuning of cells is poorly understood; a simple cell responds either to a bright edge with dark flanks, or to the opposite polarity, a dark edge w ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
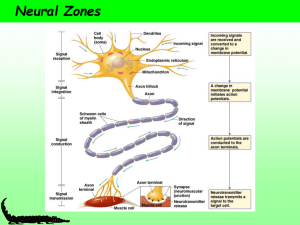
... • A typical nerve cell has a cell body, which is attached to one major fiber or axon with a number of fibrous branches called dendrites. • Dendrites receive messages coming into the neurons, which, in turn, combine and integrate the signals. • The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. • ...
... • A typical nerve cell has a cell body, which is attached to one major fiber or axon with a number of fibrous branches called dendrites. • Dendrites receive messages coming into the neurons, which, in turn, combine and integrate the signals. • The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. • ...
action potential
... is a good model for studying neuron function Nervous systems process information in three stages: sensory input, integration, and motor output ...
... is a good model for studying neuron function Nervous systems process information in three stages: sensory input, integration, and motor output ...
01.22.10 Lecture 5: Membrane transport
... Helps to maintain a negative electric potential inside the cell ...
... Helps to maintain a negative electric potential inside the cell ...
Unit 2, the Brain
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
... A typical nerve cell has a cell body, which is attached to one major fiber or axon with a number of fibrous branches called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages coming into the neurons, which, in turn, combine and integrate the signals. The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. ...
... A typical nerve cell has a cell body, which is attached to one major fiber or axon with a number of fibrous branches called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages coming into the neurons, which, in turn, combine and integrate the signals. The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. ...
lecture 4
... • F can usually be fit with 2 Gaussians or a bifurcated Gaussian • A cut on F corresponds to an (n-1)-diemensional plane cut through the ndimensional variable space ...
... • F can usually be fit with 2 Gaussians or a bifurcated Gaussian • A cut on F corresponds to an (n-1)-diemensional plane cut through the ndimensional variable space ...
Neural Oscillations
... Oscillations allow to synchronize neurons across multiple brain regions: – Modulatory systems that set oscillatory patterns project to many brain areas simultaneously Oscillation-based models allow to consider individual spikes rather than firing rates: – Randomness is reduced or eliminated by synch ...
... Oscillations allow to synchronize neurons across multiple brain regions: – Modulatory systems that set oscillatory patterns project to many brain areas simultaneously Oscillation-based models allow to consider individual spikes rather than firing rates: – Randomness is reduced or eliminated by synch ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF RESPIRATION LEARNING
... system allow pain and emotions to affect respiration .e.g. in gasping, laughing and crying. ...
... system allow pain and emotions to affect respiration .e.g. in gasping, laughing and crying. ...