Regulation of breathing
... oxygen is used by the tissues. The alveolar PO2 and PCO2 both remain constant. ...
... oxygen is used by the tissues. The alveolar PO2 and PCO2 both remain constant. ...
Document
... make connections with postsynaptic cells participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering o ...
... make connections with postsynaptic cells participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering o ...
Computation with Spikes in a Winner-Take-All Network
... the excitatory connections from excitatory neurons to interneurons and the inhibitory connections from interneurons to excitatory neurons. In our model, we assume the forward connections between the excitatory and the inhibitory neurons to be strong, so that each spike of an excitatory neuron trigge ...
... the excitatory connections from excitatory neurons to interneurons and the inhibitory connections from interneurons to excitatory neurons. In our model, we assume the forward connections between the excitatory and the inhibitory neurons to be strong, so that each spike of an excitatory neuron trigge ...
7. MODELING THE SOMATOTOPIC MAP 7.1 The Somatotopic Map
... In this chapter we demonstrate the formation of a “somatotopic map” by means of a computer simulation of Kohonen’s algorithm (Ritter and Schulten 1986). The somatotopic map is the projection of the body surface onto a brain area that is responsible for our sense of touch and that is called the somat ...
... In this chapter we demonstrate the formation of a “somatotopic map” by means of a computer simulation of Kohonen’s algorithm (Ritter and Schulten 1986). The somatotopic map is the projection of the body surface onto a brain area that is responsible for our sense of touch and that is called the somat ...
Group Redundancy Measures Reveals Redundancy Reduction in the Auditory Pathway
... systems are composed of a series of processing stations, representing more and more complex aspects of sensory inputs. Among the computational principles proposed to govern the mapping between these stations are the transformation to sparse and distributed representations, information maximization a ...
... systems are composed of a series of processing stations, representing more and more complex aspects of sensory inputs. Among the computational principles proposed to govern the mapping between these stations are the transformation to sparse and distributed representations, information maximization a ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal dev ...
... bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal dev ...
Invited Paper Neural networks in engineering D.T. Pham Intelligent
... In eqn (3(a)), net, is the total weighted sum of input signals to neuron j and y.(t) is the target output for neuron j. As there are no target outputs for hidden neurons, in eqn (3(b)), the difference between the target and actual output of a hidden neuron j is replaced by the weighted sum of the 6^ ...
... In eqn (3(a)), net, is the total weighted sum of input signals to neuron j and y.(t) is the target output for neuron j. As there are no target outputs for hidden neurons, in eqn (3(b)), the difference between the target and actual output of a hidden neuron j is replaced by the weighted sum of the 6^ ...
embj201488977-sup-0010-Suppl
... secretagogin was performed in the presence of 10 µM Ca2+. Criteria for positive protein identification are shown at the top. Proteins were classified by color coding to correspond to the cumulative data shown in Fig. 5C1. Non-targeted IgG in the presence of 10 µM Ca2+ was used as negative control. P ...
... secretagogin was performed in the presence of 10 µM Ca2+. Criteria for positive protein identification are shown at the top. Proteins were classified by color coding to correspond to the cumulative data shown in Fig. 5C1. Non-targeted IgG in the presence of 10 µM Ca2+ was used as negative control. P ...
The Brain - Gordon State College
... – Limbic system: influences fear, aggression, and new memories – Cerebral cortex: located on top of these structures; the most complex part of the brain ...
... – Limbic system: influences fear, aggression, and new memories – Cerebral cortex: located on top of these structures; the most complex part of the brain ...
The Third Generation of Neural Networks
... advice. However, just because a single layer network can, in theory, learn anything, the universal approximation theorem does not say anything about how easy it will be to learn. Additional hidden layers make problems easier to learn because they provide the hierarchical abstraction that is an inher ...
... advice. However, just because a single layer network can, in theory, learn anything, the universal approximation theorem does not say anything about how easy it will be to learn. Additional hidden layers make problems easier to learn because they provide the hierarchical abstraction that is an inher ...
Physiology
... distribution of ions (atoms with a positive or negative charge) on the two sides of the nerve cell membrane. This POTENTIAL generally measures about 70 millivolts (with the INSIDE of the membrane negative with respect to the outside). So, the RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL is expressed as -70 mV, and th ...
... distribution of ions (atoms with a positive or negative charge) on the two sides of the nerve cell membrane. This POTENTIAL generally measures about 70 millivolts (with the INSIDE of the membrane negative with respect to the outside). So, the RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL is expressed as -70 mV, and th ...
Editorial: Cell Assemblies - CommuniGate Pro uni
... “cell assembly”. A cell assembly is comprised by a group of neurones with strong mutual excitatory connections. Thus, the definition relies on the interrelation of structural and physiological properties of nerve cells. Since a cell assembly, once a subset of its cells are stimulated, tends to be ac ...
... “cell assembly”. A cell assembly is comprised by a group of neurones with strong mutual excitatory connections. Thus, the definition relies on the interrelation of structural and physiological properties of nerve cells. Since a cell assembly, once a subset of its cells are stimulated, tends to be ac ...
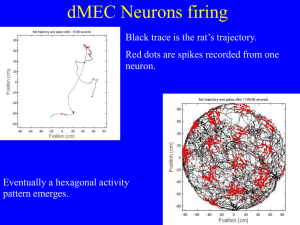
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... The number of cells per site is set by the need to have a statistically significant difference in the number of counts when comparing -A rat running over an activity blob -A rat running a past a blob (at the resolution limit) We model the firing rate as constant background plus gaussian blobs: After ...
... The number of cells per site is set by the need to have a statistically significant difference in the number of counts when comparing -A rat running over an activity blob -A rat running a past a blob (at the resolution limit) We model the firing rate as constant background plus gaussian blobs: After ...
Spike-Timing-Dependent Hebbian Plasticity as
... model predicts that cortical neurons may employ different temporal windows of plasticity at different dendritic locations to allow them to capture correlations between pre- and postsynaptic activity at different timescales (see section 6). A preliminary report of this work appeared as Rao and Sejnow ...
... model predicts that cortical neurons may employ different temporal windows of plasticity at different dendritic locations to allow them to capture correlations between pre- and postsynaptic activity at different timescales (see section 6). A preliminary report of this work appeared as Rao and Sejnow ...
Brain
... • Clusters of capillaries that form tissue fluid filters, which hang from the roof of each ventricle • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
... • Clusters of capillaries that form tissue fluid filters, which hang from the roof of each ventricle • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
Building the realities of working memory and neural functioning into
... What are important take-home messages of a learning brain for teachers? This session considers this question, initially, by briefly focusing on the current theory constructs of working memory, long-term memory, neural connections and why evolution may have presented us with the type of brain we use ...
... What are important take-home messages of a learning brain for teachers? This session considers this question, initially, by briefly focusing on the current theory constructs of working memory, long-term memory, neural connections and why evolution may have presented us with the type of brain we use ...
Cellular and network mechanisms of electrographic
... crucial role in seizure dynamics. The complexity of the interaction dynamics between neuronal networks and ion concentrations during epileptiform activity requires a combined approach of experimental work and computational models. Here, we discuss recent modeling results regarding mechanisms of epil ...
... crucial role in seizure dynamics. The complexity of the interaction dynamics between neuronal networks and ion concentrations during epileptiform activity requires a combined approach of experimental work and computational models. Here, we discuss recent modeling results regarding mechanisms of epil ...
neural-networks
... • Neurons: the cells that perform information processing in the brain. It is the fundamental functional unit of all nervous system tissue, including brain • Soma: The neuron’s cell body • Dendrites: collection of fibers branching out of the soma body cell • Axon: A single long fiber in the collectio ...
... • Neurons: the cells that perform information processing in the brain. It is the fundamental functional unit of all nervous system tissue, including brain • Soma: The neuron’s cell body • Dendrites: collection of fibers branching out of the soma body cell • Axon: A single long fiber in the collectio ...
C. elegans Neurology Supplement - Bio-Rad
... which are highly branched and receive signals from other neurons or sensory structures; axons, which transmit signals to other neurons or effector cells; and an axon hillock, the point at which the cell body and axon meet that serves as the point for generation of action potentials. One major differ ...
... which are highly branched and receive signals from other neurons or sensory structures; axons, which transmit signals to other neurons or effector cells; and an axon hillock, the point at which the cell body and axon meet that serves as the point for generation of action potentials. One major differ ...
Practical 6: Ben-Yishai network of visual cortex
... d) Take λ0 = 5, λ1 = 0, ϵ = 0.1. This means that there is uniform recurrent inhibition. Vary the contrast c (range 0.1 to 10) and observe the steady state. You will see three regimes: no output, a rectified cosine, and a cosine plus offset. e) Next, take a small value for ϵ, take λ0 = 2, and vary λ1 ...
... d) Take λ0 = 5, λ1 = 0, ϵ = 0.1. This means that there is uniform recurrent inhibition. Vary the contrast c (range 0.1 to 10) and observe the steady state. You will see three regimes: no output, a rectified cosine, and a cosine plus offset. e) Next, take a small value for ϵ, take λ0 = 2, and vary λ1 ...