Composition of the Nervous System
... -The structure of a typical neuronal cell is comprised of a body, many branching dendrites and a single branching axon. The proximal part of the axon is called the axon hillock. -Schematic neurons: Particularly when drawing circuits neurons can represented in a schematic way by a circle (cell body a ...
... -The structure of a typical neuronal cell is comprised of a body, many branching dendrites and a single branching axon. The proximal part of the axon is called the axon hillock. -Schematic neurons: Particularly when drawing circuits neurons can represented in a schematic way by a circle (cell body a ...
The Cellular Level of Organization
... – Cell bodies of unipolar neurons are found in ganglia located just outside the spinal ...
... – Cell bodies of unipolar neurons are found in ganglia located just outside the spinal ...
Invited Re vie W The distribution of cholinergic neurons in the
... ChAT, an in situ hybridization technique has been induced to detect ChAT mRNA in neurons for identifying authentic cholinergic neurons. The present article reviews immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies on the distribution of neurons expressing ChAT in the human central nervous system ...
... ChAT, an in situ hybridization technique has been induced to detect ChAT mRNA in neurons for identifying authentic cholinergic neurons. The present article reviews immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies on the distribution of neurons expressing ChAT in the human central nervous system ...
Chapter 7
... • Order of events: – Sensory nerve sends impulse to spinal column – Interneurons activate motor neurons – Motor neurons control movement of muscles ...
... • Order of events: – Sensory nerve sends impulse to spinal column – Interneurons activate motor neurons – Motor neurons control movement of muscles ...
BIO 132
... Each neuron from the core can influence more than 100,000 postsynaptic neurons spread all over the brain The synapses are not terminal but rather run along axons (called boutons en passant) Each system only modulates the actions of other neurons and does not turn them on or off. ...
... Each neuron from the core can influence more than 100,000 postsynaptic neurons spread all over the brain The synapses are not terminal but rather run along axons (called boutons en passant) Each system only modulates the actions of other neurons and does not turn them on or off. ...
6-Autonomic nervous system
... College of Medicine King Saud University E-mail: [email protected] ...
... College of Medicine King Saud University E-mail: [email protected] ...
5-Autonomic nervous system
... College of Medicine King Saud University E-mail: [email protected] ...
... College of Medicine King Saud University E-mail: [email protected] ...
1 Name: Period: _____ Laboratory Exercise and Activity: Nervous
... Neurons are the longest cells in the body they can be over 3 feet long. All neurons have three basic parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. The dendrites and the single axon are extensions of the cell body called processes. Dendrites receive information from receptors or other neurons and send ...
... Neurons are the longest cells in the body they can be over 3 feet long. All neurons have three basic parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. The dendrites and the single axon are extensions of the cell body called processes. Dendrites receive information from receptors or other neurons and send ...
Chapter 12
... 14. Describe the difference between gray and white matter, and give examples of each. ELECTRICAL SIGNALS IN NEURONS 15. Distinguish between action potential and graded potentials. Ion Channels 16. Identify the basic types of ion channels and the stimuli that operate gated ion channels. Resting Membr ...
... 14. Describe the difference between gray and white matter, and give examples of each. ELECTRICAL SIGNALS IN NEURONS 15. Distinguish between action potential and graded potentials. Ion Channels 16. Identify the basic types of ion channels and the stimuli that operate gated ion channels. Resting Membr ...
Turning neurons into a nervous system
... nasal axons (green, N) project to the posterior (P) tectum; and axons from intermediate positions in the retina (yellow) terminate in the center of the tectum. (B) Dorsal view of a lakritz (atoh7) mutant zebrafish in which a single ganglion cell has developed from a transplanted clone of wild-type c ...
... nasal axons (green, N) project to the posterior (P) tectum; and axons from intermediate positions in the retina (yellow) terminate in the center of the tectum. (B) Dorsal view of a lakritz (atoh7) mutant zebrafish in which a single ganglion cell has developed from a transplanted clone of wild-type c ...
Nervous System
... • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract and remove the paw ...
... • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract and remove the paw ...
Visual-Vestibular Interaction Hypothesis for the Control
... •The proposed visual-vestibular interaction controlling the activity of OPNs was shown to accurately reproduce alternations between fast and slow phases of combined eye-head gaze movements, which are not controlled uniquely by a gaze motor error signal. •Inputs to the OPNs are based on a weighted pr ...
... •The proposed visual-vestibular interaction controlling the activity of OPNs was shown to accurately reproduce alternations between fast and slow phases of combined eye-head gaze movements, which are not controlled uniquely by a gaze motor error signal. •Inputs to the OPNs are based on a weighted pr ...
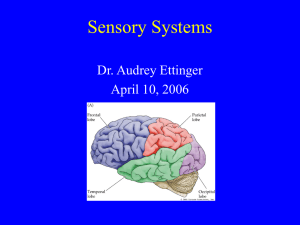
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
The Nervous System
... axon terminal of the presynaptic cell and causes V-gated Ca2+ channels to open. • Ca2+ rushes in, binds to regulatory proteins & initiates NT exocytosis. • NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsyna ...
... axon terminal of the presynaptic cell and causes V-gated Ca2+ channels to open. • Ca2+ rushes in, binds to regulatory proteins & initiates NT exocytosis. • NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsyna ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
... The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
What is an adult stem cell?
... 3. candidate adult SC can be isolated, grown in vitro and manipulated, by adding growth factors or introducing genes that help determine what differentiated cells types they will yield. ...
... 3. candidate adult SC can be isolated, grown in vitro and manipulated, by adding growth factors or introducing genes that help determine what differentiated cells types they will yield. ...
BIOL241NSintro12aJUL2012
... • Form epithelium called ependyma • Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain: – secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – have cilia or microvilli that circulate CSF – monitor CSF – contain stem cells for repair ...
... • Form epithelium called ependyma • Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain: – secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – have cilia or microvilli that circulate CSF – monitor CSF – contain stem cells for repair ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.